有没有现成的方法可以使json.dumps()输出以漂亮的格式显示为JSON在ipython笔记本中?
IPython Notebook中漂亮的JSON格式化
1
json.dumps有一个indent参数,直接打印输出结果就足够了:
print(json.dumps(obj, indent=2))
3
json.dumps默认为ensure_ascii=True,这会转义中文(或者说:任何非ASCII)字符。使用print(json.dumps(obj, indent=2, ensure_ascii=False)),你就可以得到未转义的字符了。 - filmor这可能略微不同于OP所要求的,但您可以使用IPython.display.JSON来交互式查看JSON/dict对象。
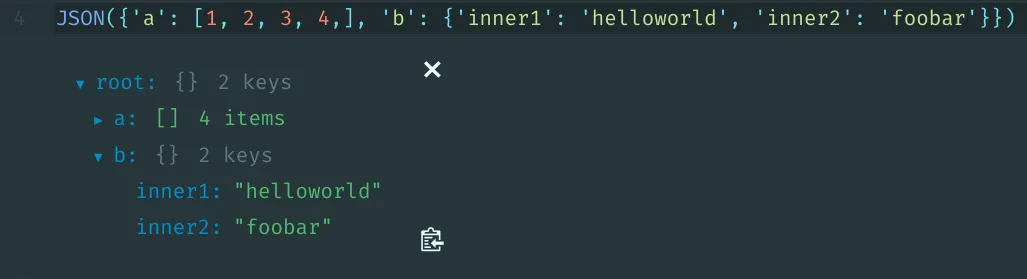
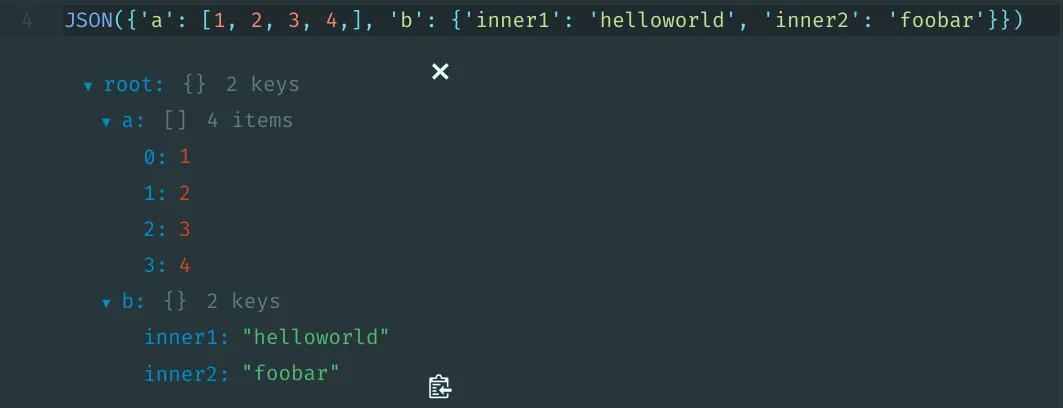
from IPython.display import JSON
JSON({'a': [1, 2, 3, 4,], 'b': {'inner1': 'helloworld', 'inner2': 'foobar'}})
编辑:此代码适用于 Hydrogen 和 JupyterLab,但不适用于 Jupyter Notebook 或 IPython 终端。
在 Hydrogen 中:
2
import uuid
from IPython.display import display_javascript, display_html, display
import json
class RenderJSON(object):
def __init__(self, json_data):
if isinstance(json_data, dict):
self.json_str = json.dumps(json_data)
else:
self.json_str = json_data
self.uuid = str(uuid.uuid4())
def _ipython_display_(self):
display_html('<div id="{}" style="height: 600px; width:100%;"></div>'.format(self.uuid), raw=True)
display_javascript("""
require(["https://rawgit.com/caldwell/renderjson/master/renderjson.js"], function() {
document.getElementById('%s').appendChild(renderjson(%s))
});
""" % (self.uuid, self.json_str), raw=True)
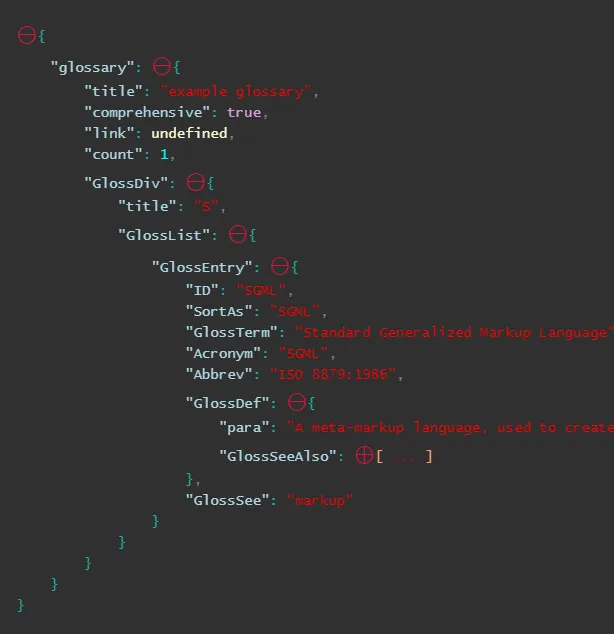
要将你的数据以可折叠的格式输出:
RenderJSON(your_json)
从这里复制粘贴: https://www.reddit.com/r/IPython/comments/34t4m7/lpt_print_json_in_collapsible_format_in_ipython/
Github链接: https://github.com/caldwell/renderjson
7
self.json_str = json_data。这解决了@user474491报告的问题。 - Hassan__init __()中添加了一个显式调用_ipython_display_(),以确保我们可以安全地交错调用python的本机print()和RenderJSON(),并仍然使其工作。
https://gist.github.com/t27/48b3ac73a1479914f9fe9383e5d45325 - Tarang Shah我只是在 @Kyle Barron 的回答中添加了扩展变量:
from IPython.display import JSON
JSON(json_object, expanded=True)
6
TypeError: __init __()收到了一个意外的关键字参数“expanded”。 - mrvol<IPython.core.display.JSON object>,没有交互式漂亮打印。 - ShnitzelKillerprint(JSON(...))来打印它。 - undefined<IPython.core.display.JSON object>。 - undefined\n的方法。我们正在使用Jupyter进行编码面试,我想要一种以漂亮的方式显示函数结果的方法。我的Jupyter版本(4.1.0)并没有将它们渲染为实际的换行符。我提出的解决方案是(我有点希望这不是最好的方法,但是...)import json
output = json.dumps(obj, indent=2)
line_list = output.split("\n") # Sort of line replacing "\n" with a new line
# Now that our obj is a list of strings leverage print's automatic newline
for line in line_list:
print line
希望这能帮助到某些人!
这只是对@filmor答案(https://dev59.com/yWMk5IYBdhLWcg3w5R2k#18873131)的一个扩展。
它编码了一些可能与json.dumps不兼容的元素,并提供了一个方便的函数,可以像使用print一样使用它。
import json
class NpEncoder(json.JSONEncoder):
def default(self, obj):
if isinstance(obj, np.integer):
return int(obj)
if isinstance(obj, np.floating):
return float(obj)
if isinstance(obj, np.ndarray):
return obj.tolist()
if isinstance(obj, np.bool_):
return bool(obj)
return super(NpEncoder, self).default(obj)
def print_json(json_dict):
print(json.dumps(json_dict, indent=2, cls=NpEncoder))
使用方法:
json_dict = {"Name":{"First Name": "Lorem", "Last Name": "Ipsum"}, "Age":26}
print_json(json_dict)
>>>
{
"Name": {
"First Name": "Lorem",
"Last Name": "Ipsum"
},
"Age": 26
}
对于某些用途,缩进应该这样做:
print(json.dumps(parsed, indent=2))
一个Json结构基本上就是树形结构。 在尝试寻找更加花哨的东西时,我发现了这篇很好的论文,其中描述了其他形式的漂亮树形结构,可能会很有趣:https://blog.ouseful.info/2021/07/13/exploring-the-hierarchical-structure-of-dataframes-and-csv-data/。
它包含一些交互式树形结构,甚至还附带了一些代码,包括链接到这个问题和来自Shankar ARUL的可折叠树形结构。
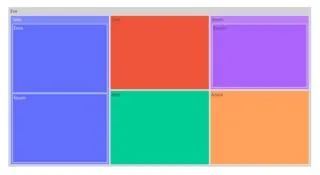
其他示例包括使用plotly。以下是来自plotly的代码示例:
import plotly.express as px
fig = px.treemap(
names = ["Eve","Cain", "Seth", "Enos", "Noam", "Abel", "Awan", "Enoch", "Azura"],
parents = ["", "Eve", "Eve", "Seth", "Seth", "Eve", "Eve", "Awan", "Eve"]
)
fig.update_traces(root_color="lightgrey")
fig.update_layout(margin = dict(t=50, l=25, r=25, b=25))
fig.show()
并使用treelib。另外,这个github也提供了很好的可视化效果。以下是一个使用treelib的示例:
#%pip install treelib
from treelib import Tree
country_tree = Tree()
# Create a root node
country_tree.create_node("Country", "countries")
# Group by country
for country, regions in wards_df.head(5).groupby(["CTRY17NM", "CTRY17CD"]):
# Generate a node for each country
country_tree.create_node(country[0], country[1], parent="countries")
# Group by region
for region, las in regions.groupby(["GOR10NM", "GOR10CD"]):
# Generate a node for each region
country_tree.create_node(region[0], region[1], parent=country[1])
# Group by local authority
for la, wards in las.groupby(['LAD17NM', 'LAD17CD']):
# Create a node for each local authority
country_tree.create_node(la[0], la[1], parent=region[1])
for ward, _ in wards.groupby(['WD17NM', 'WD17CD']):
# Create a leaf node for each ward
country_tree.create_node(ward[0], ward[1], parent=la[1])
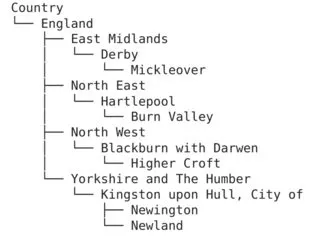
# Output the hierarchical data
country_tree.show()
基于此,我创建了一个将JSON转换为树形结构的函数:
from treelib import Node, Tree, node
def json_2_tree(o , parent_id=None, tree=None, counter_byref=[0], verbose=False, listsNodeSymbol='+'):
if tree is None:
tree = Tree()
root_id = counter_byref[0]
if verbose:
print(f"tree.create_node({'+'}, {root_id})")
tree.create_node('+', root_id)
counter_byref[0] += 1
parent_id = root_id
if type(o) == dict:
for k,v in o.items():
this_id = counter_byref[0]
if verbose:
print(f"tree.create_node({str(k)}, {this_id}, parent={parent_id})")
tree.create_node(str(k), this_id, parent=parent_id)
counter_byref[0] += 1
json_2_tree(v , parent_id=this_id, tree=tree, counter_byref=counter_byref, verbose=verbose, listsNodeSymbol=listsNodeSymbol)
elif type(o) == list:
if listsNodeSymbol is not None:
if verbose:
print(f"tree.create_node({listsNodeSymbol}, {counter_byref[0]}, parent={parent_id})")
tree.create_node(listsNodeSymbol, counter_byref[0], parent=parent_id)
parent_id=counter_byref[0]
counter_byref[0] += 1
for i in o:
json_2_tree(i , parent_id=parent_id, tree=tree, counter_byref=counter_byref, verbose=verbose,listsNodeSymbol=listsNodeSymbol)
else: #node
if verbose:
print(f"tree.create_node({str(o)}, {counter_byref[0]}, parent={parent_id})")
tree.create_node(str(o), counter_byref[0], parent=parent_id)
counter_byref[0] += 1
return tree
例如:
import json
json_2_tree(json.loads('{"2": 3, "4": [5, 6]}'),verbose=False,listsNodeSymbol='+').show()
提供:
+
├── 2
│ └── 3
└── 4
└── +
├── 5
└── 6
当
json_2_tree(json.loads('{"2": 3, "4": [5, 6]}'),listsNodeSymbol=None).show()
提供
+
├── 2
│ └── 3
└── 4
├── 5
└── 6
正如您所看到的,根据一个人想要多么明确或紧凑,他可以制作不同的树形结构。 我最喜欢的之一,也是最紧凑的之一,可能是使用yaml:
import yaml
j = json.loads('{"2": "3", "4": ["5", "6"], "7": {"8": "9"}}')
print(yaml.dump(j, sort_keys=False))
提供简洁明了的内容:
'2': '3'
'4':
- '5'
- '6'
'7':
'8': '9'
from IPython.display import Markdown
def jsonviewer(d):
f=open('file.json','w')
json.dump(d,f)
f.close()
print('open in firefox new tab:')
return Markdown('[file.json](./file.json)')
jsonviewer('[{"A":1}]')
'open in firefox new tab:
原文链接
- 相关问题
- 18 在IPython/Jupyter Notebook中格式化SQL查询
- 5 在IPython Notebook中,Sympy出现格式化错误
- 14 启动ipython notebook
- 61 如何在 IPython Notebook 中使用 SymPy 进行漂亮的打印输出?
- 10 IPython Notebook中的vi快捷键
- 749 如何将JSON输出进行“漂亮”格式化
- 9 IPython: Notebook似乎不是JSON
- 3 iPython Notebook中默认的笔记本目录 - iPython 3.0.0
- 6 IPython Notebook中的Pyzmq错误
- 7 在Flask中如何实现漂亮的JSON格式化

pprint()来打印JSON (from pprint import pprint)。 - PeJota