我已经为此编写了一个库,它可以使您免除管理android账户所需的繁琐工作,如定义绑定服务、认证器xml等。使用这个库只需要5个简单的步骤:
步骤1
将以下内容添加到应用程序的build.gradle文件中的依赖项中:
compile 'com.digigene.android:account-authenticator:1.3.0'
步骤2
将您的认证账户类型定义为字符串在strings.xml中:
<string name="auth_account_type">DigiGene</string>
请将“DigiGene”替换为您自己的帐户类型。在
此截图中,这是在Android帐户中显示的内容。
第3步:
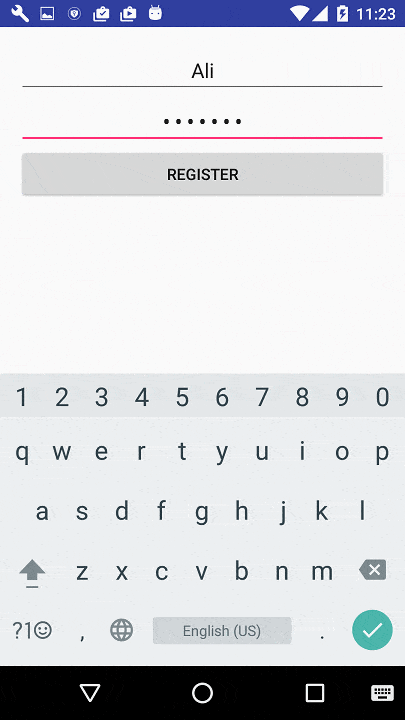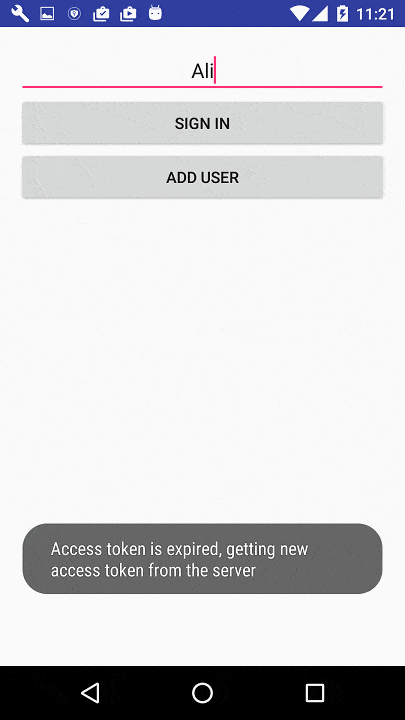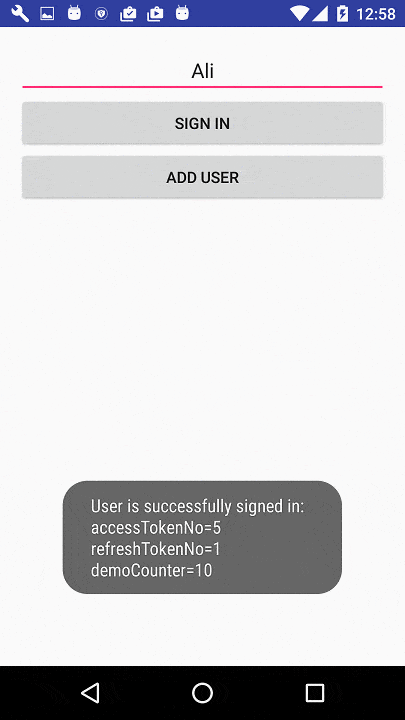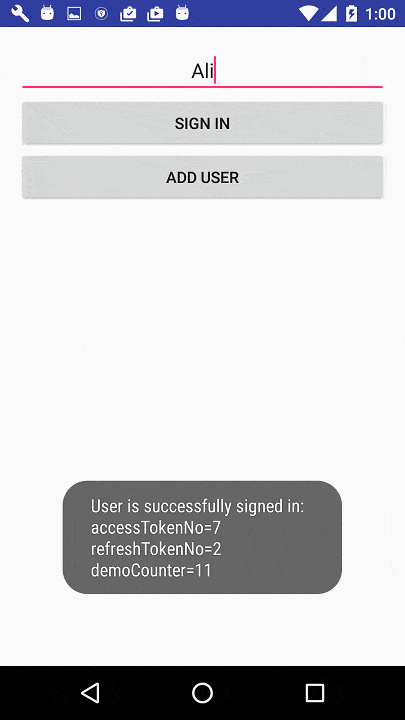
设计您的注册布局以注册用户(例如
此图像):
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="com.digigene.authenticatortest.MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/account_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:hint="User Name"
/>
<EditText
android:id="@+id/password"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/account_name"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:hint="Password"
android:inputType="textPassword"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/register"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/password"
android:text="register"
android:onClick="startAuthentication"/>
</RelativeLayout>
新建一个类,比如说MyRegistrationActivity.java,并使用以下代码:
import com.digigene.accountauthenticator.activity.RegistrationActivity;
public class MyRegistrationActivity extends RegistrationActivity {
private EditText accountNameEditText, passwordEditText;
@Override
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.registration_layout);
accountNameEditText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.account_name);
passwordEditText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.password);
}
public void startAuthentication(View view) {
register(accountNameEditText.getText().toString(), passwordEditText.getText().toString(),
null, null);
}
}
第四步
按照这里的示例创建一个条目布局:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
xmlns:tools="http://schemas.android.com/tools"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:paddingBottom="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
android:paddingLeft="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingRight="@dimen/activity_horizontal_margin"
android:paddingTop="@dimen/activity_vertical_margin"
tools:context="com.digigene.authenticatortest.MainActivity">
<EditText
android:id="@+id/account_name"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:gravity="center_horizontal"
android:hint="User Name"
/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/register"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/account_name"
android:text="Sign in"
android:onClick="signIn"/>
<Button
android:id="@+id/add"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_below="@+id/register"
android:text="Add user"
android:onClick="addUser"/>
</RelativeLayout>
这种布局与以下类相伴:
import com.digigene.accountauthenticator.AuthenticatorManager;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
EditText accountNameEditText;
protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.activity_main);
accountNameEditText = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.account_name);
}
public void signIn(View view) {
AuthenticatorManager authenticatorManager = new AuthenticatorManager(MainActivity.this,
getString(R.string.auth_account_type), this, MyRegistrationActivity.class,
MyInterfaceImplementation.class);
String authTokenType = "REGULAR_USER";
AuthenticatorManager.authenticatorManager = authenticatorManager;
authenticatorManager.getAccessToken(accountNameEditText.getText().toString(),
authTokenType, null);
}
public void addUser(View view) {
AuthenticatorManager authenticatorManager = new AuthenticatorManager(MainActivity.this,
getString(R.string.auth_account_type), this, MyRegistrationActivity.class,
MyInterfaceImplementation.class);
String authTokenType = "REGULAR_USER";
AuthenticatorManager.authenticatorManager = authenticatorManager;
authenticatorManager.addAccount(authTokenType, null, null);
}
}
第五步
这是最后一步,需要实现连接服务器以进行注册和登录,并在此之后。与实际情况相反,在下面的示例中,服务器连接被模拟,以展示库的功能。您可以将以下实现替换为自己的实际实现。
import com.digigene.accountauthenticator.AbstractInterfaceImplementation;
import com.digigene.accountauthenticator.AuthenticatorManager;
import com.digigene.accountauthenticator.result.RegisterResult;
import com.digigene.accountauthenticator.result.SignInResult;
import com.digigene.accountauthenticator.result.SignUpResult;
public class MyInterfaceImplementation extends AbstractInterfaceImplementation {
public static int accessTokenCounter = 0;
public static int refreshTokenCounter = 0;
public static int demoCounter = 0;
public static int accessTokenNo = 0;
public static int refreshTokenNo = 0;
public final int ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRATION_COUNTER = 2;
public final int REFRESH_TOKEN_EXPIRATION_COUNTER = 5;
public final int DEMO_COUNTER = 15;
@Override
public String[] userAccessTypes() {
return new String[]{"REGULAR_USER", "SUPER_USER"};
}
@Override
public void doAfterSignUpIsUnsuccessful(Context context, Account account, String
authTokenType, SignUpResult signUpResult, Bundle options) {
Toast.makeText(context, "Sign-up was not possible due to the following:\n" + signUpResult
.errMessage, Toast.LENGTH_LONG).show();
AuthenticatorManager.authenticatorManager.addAccount(authTokenType, null, options);
}
@Override
public void doAfterSignInIsSuccessful(Context context, Account account, String authTokenType,
String authToken, SignInResult signInResult, Bundle
options) {
demoCounter = demoCounter + 1;
Toast.makeText(context, "User is successfully signed in: \naccessTokenNo=" +
accessTokenNo + "\nrefreshTokenNo=" + refreshTokenNo +
"\ndemoCounter=" + demoCounter, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show();
}
@Override
public SignInResult signInToServer(Context context, Account account, String authTokenType,
String accessToken, Bundle options) {
accessTokenCounter = accessTokenCounter + 1;
SignInResult signInResult = new SignInResult();
signInResult.isSuccessful = true;
synchronized (this) {
try {
this.wait(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if ((accessTokenCounter > ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRATION_COUNTER || demoCounter > DEMO_COUNTER)) {
signInResult.isSuccessful = false;
signInResult.isAccessTokenExpired = true;
if (demoCounter < DEMO_COUNTER) {
signInResult.errMessage = "Access token is expired";
return signInResult;
}
}
return signInResult;
}
@Override
public SignUpResult signUpToServer(Context context, Account account, String authTokenType,
String refreshToken, Bundle options) {
SignUpResult signUpResult = new SignUpResult();
synchronized (this) {
try {
this.wait(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
refreshTokenCounter = refreshTokenCounter + 1;
signUpResult.isSuccessful = true;
signUpResult.accessToken = "ACCESS_TOKEN_NO_" + accessTokenNo;
signUpResult.refreshToken = "REFRESH_TOKEN_NO_" + refreshTokenNo;
if (demoCounter > DEMO_COUNTER) {
signUpResult.isSuccessful = false;
signUpResult.errMessage = "You have reached your limit of using the demo version. " +
"Please buy it for further usage";
return signUpResult;
}
if (refreshTokenCounter > REFRESH_TOKEN_EXPIRATION_COUNTER) {
refreshTokenCounter = 0;
signUpResult.isSuccessful = false;
signUpResult.errMessage = "User credentials have expired, please login again";
return signUpResult;
}
if (accessTokenCounter > ACCESS_TOKEN_EXPIRATION_COUNTER) {
accessTokenCounter = 0;
accessTokenNo = accessTokenNo + 1;
signUpResult.accessToken = "ACCESS_TOKEN_NO_" + accessTokenNo;
}
return signUpResult;
}
@Override
public RegisterResult registerInServer(Context context, Account account, String password,
String authTokenType, String[] requiredFeatures,
Bundle options) {
RegisterResult registerResult = new RegisterResult();
registerResult.isSuccessful = false;
synchronized (this) {
try {
this.wait(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (true) {
refreshTokenNo = refreshTokenNo + 1;
accessTokenNo = accessTokenNo + 1;
registerResult.isSuccessful = true;
registerResult.refreshToken = "REFRESH_TOKEN_NO_" + refreshTokenNo;
}
return registerResult;
}
@Override
public boolean setDoesCallbackRunInBackgroundThread() {
return false;
}
}
结果
以下是该库的示例。您可以在我的网站上找到完整的教程(此处),以及关于Android中AccountManager如何工作的三篇文章:第一部分,第二部分,第三部分。