假设我正在对一个对象的运动从X1坐标到X2坐标进行缓出(Ease-Out)和缓入(Ease-In)动画,需要在S步骤中以相等的时间间隔完成。有人能提供计算该运动X坐标的公式吗?
6个回答
99
个人而言,我更愿意使用一个接受[0; 1]范围内的时间值,并输出[0; 1]范围内的值的函数,这样我们就可以将结果应用于任何类型(2D向量、3D向量等)。
解决方案1(二次函数)
对于二次缓动的进入/退出效果,曲线根据
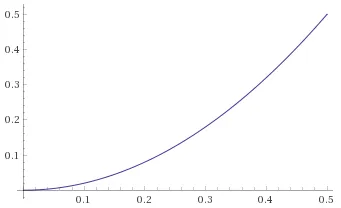
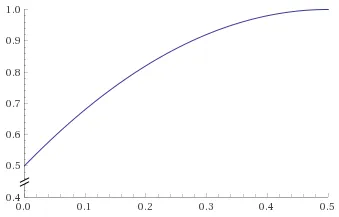
当 t <= 0.5 时,f(x) = 2 * x * x,其中 x 属于 [0;0.5](图表链接1)。 当 t > 0.5 时,f(x) = 2 * x * (1 - x) + 0.5,其中 x 属于 [0;0.5](图表链接2)。
以下是图表: 由于第二个函数也在[0;0.5]范围内,但是当我们开始使用它时,
以下是C语言中的结果:
解决方案1(二次函数)
对于二次缓动的进入/退出效果,曲线根据
t的值分为两个不同的函数:当 t <= 0.5 时,f(x) = 2 * x * x,其中 x 属于 [0;0.5](图表链接1)。 当 t > 0.5 时,f(x) = 2 * x * (1 - x) + 0.5,其中 x 属于 [0;0.5](图表链接2)。
以下是图表: 由于第二个函数也在[0;0.5]范围内,但是当我们开始使用它时,
t的值大于0.5,因此我们需要将t减去0.5。以下是C语言中的结果:
float InOutQuadBlend(float t)
{
if(t <= 0.5f)
return 2.0f * t * t;
t -= 0.5f;
return 2.0f * t * (1.0f - t) + 0.5f;
}
解决方案2(贝塞尔曲线)
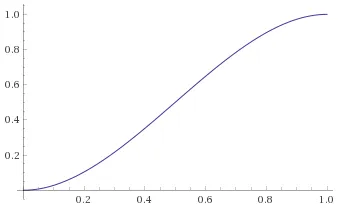
另一个有趣的混合曲线是由贝塞尔曲线提供的,它具有相当优化的优势(无需条件判断)。以下是来自Wolfram的曲线:
这是C代码:float BezierBlend(float t)
{
return t * t * (3.0f - 2.0f * t);
}
解决方案3(参数函数)
另一种方法是由@DannyYaroslavski提出的简单公式,可以在这里找到链接。
它是参数化的,并且具有良好的加速和减速效果。
当alpha = 2时,您将得到以下函数:
float ParametricBlend(float t)
{
float sqt = t * t;
return sqt / (2.0f * (sqt - t) + 1.0f);
}
- Creak
9
10我说的是:sqr 不等于 sqrt ;) - Creak
1你是对的 @DannyYaroslavski,我改变了公式来修复它。 - Creak
在最后一个函数中,我认为X实际上是函数的T参数,对吗? - Coldsteel48
你说得对 @ygoe,我已经修正了公式和解释。谢谢! - Creak
1在2021年的野外试验并经过验证。看起来很棒。 - SaganRitual
显示剩余4条评论
48
二次缓出动画方程:
t = 当前时间
b = 起始值
c = 变化量
d = 持续时间
function (float time, float startValue, float change, float duration) {
time /= duration / 2;
if (time < 1) {
return change / 2 * time * time + startValue;
}
time--;
return -change / 2 * (time * (time - 2) - 1) + startValue;
};
source: http://gizma.com/easing/
- Toad
9
Toad,当你说“t = time”时,你是指从动画开始的时间还是上一帧的时间? - Sir
t 的取值范围为 0 到 1,其中 0 表示动画的开始,1 表示结束。对于每个关键帧,您应该更改值并让 t 再次从 0 到 1 变化。 - Toad
2价值的变化是多少?我不明白它来自哪里。 - starbeamrainbowlabs
1首先,你需要使用公式从关键帧1到关键帧2(即b为关键帧1的值,而c为关键帧2的值)。然后,你让t从0.0到1.0。当你到达1.0时,重复这些步骤,只是现在你使用keyframe2和keyframe3。 - Toad
1假设起始值为3,你想要平滑过渡到值5。那么值的变化量为2。因此,值的变化量等于结束值减去起始值。 - Toad
显示剩余4条评论
3
以上所有解决方案都缺乏使用示例。
在此处找到了一个很好的解决方案(链接):
function animate({timing, draw, duration}) {
let start = performance.now();
requestAnimationFrame(function animate(time) {
// timeFraction goes from 0 to 1
let timeFraction = (time - start) / duration;
if (timeFraction > 1) timeFraction = 1;
// calculate the current animation state
let progress = timing(timeFraction)
draw(progress); // draw it
if (timeFraction < 1) {
requestAnimationFrame(animate);
}
});
}
使用示例:
animate({
duration: 1000,
timing(timeFraction) { // here you can put other functions
return timeFraction;
},
draw(progress) {
elem.style.width = progress * 100 + '%';
}
});
其他功能:
function quad(timeFraction) {
return Math.pow(timeFraction, 2)
}
更多内容在此
- Alexander Poshtaruk
2
我遇到了同样的问题:想要给我的图表添加动画效果(Ease in-out)。
我进行了头脑风暴,找到了两种方法:
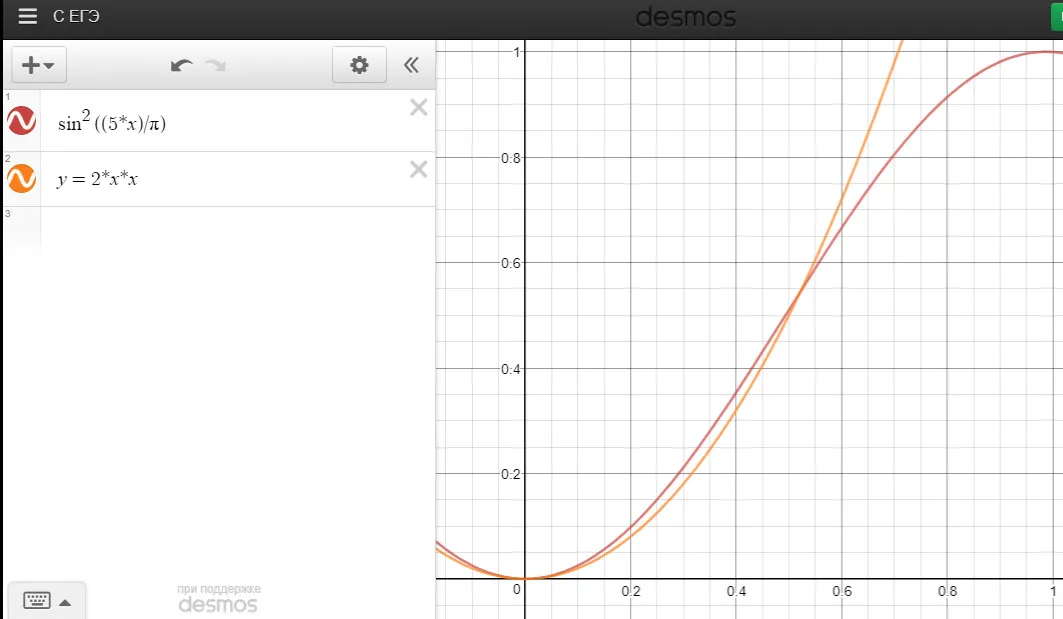
1)三角函数公式。首先,我写下了 y=(sin(x/π*10-π/2)+1)/2,它的类比公式是 sin^2((5*x)/π)
float TrygoEase (float x) {
float y=(float)Math.pow(Math.sin(5*x/Math.PI),2);
return y;
}
2) 两个抛物线。这并不难。我只是在[0;0.5]上使用了y=2*x*x,在[0.5;1]上使用了y=-2(x-1)^2+1
float ParabolEase(float x) {
float y=2*x*x;
if(x>0.5f){
x-=1;
y=-2*x*x+1;
}
return y;
}
使用以下方法对x=[0;1]进行操作,同时返回y=[0;1]。
现在您可以比较这些图表:
- Egor
0
此版本允许您使用任何缓入和缓出函数(EaseIn 和 EaseOut)。 两个函数都必须接受一个介于 0 和 1 之间的时间值参数,并返回介于 0 和 1 之间的缓动时间值。
float EaseInOut(float t)
{
if (t <= 0.5f)
{
return EaseIn(t * 2) * 0.5f;
}
else
{
t -= 0.5f;
return (EaseOut(t * 2) * 0.5f) + 0.5f;
}
}
- ImmortalMazeWalker
0
这里有一个版本,其中曲率量作为参数,遵循Creak链接的这个通用解决方案。
/*
* applyCurve: apply an S-curve to an input value.
* The highest positive curvature will result in a step from 0 to 1,
* the most negative curvature will result in a constant of 0.5.
*
* progress: the input value between 0 and 1,
* curvature: the amount of curvature between -1 and 1.
* Negative values curve the other way, 0 applies no curvature.
*/
double applyCurve(double progress, double curvature) {
assert(progress >= 0.0 && progress <= 1.0);
assert(curvature >= -1.0 && curvature <= 1.0);
if (curvature >= 0.0) {
if (curvature > 0.99999) return progress > 0.5 ? 1.0 : 0.0;
float exp = 1.0 / (1.0 - curvature); // find s-curve exponent
return pow(progress, exp) / (pow(progress, exp) + pow(1.0 - progress, exp)); // apply s-curve
} else {
if (curvature < -0.99999) return 0.5;
float exp = 1.0 + curvature; // find s-curve exponent
return pow(progress, exp) / (pow(progress, exp) + pow(1.0 - progress, exp)); // apply s-curve
}
}
- Mattijs
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接