我所有的React项目文件大小都非常大(bundle.js为4.87 MB,vendor.bundle.js为2.87 MB)。我不知道为什么会这么大。我已经启用了uglifyJS,但它似乎并没有帮助很多(5.09> 4.87 MB和2.9> 2.87 MB)。
var webpack = require('webpack');
var ExtractTextPlugin = require("extract-text-webpack-plugin");
require('es6-promise').polyfill();
var config = {
entry: {
app: [
'./src/entry.jsx'
],
vendor: [
'react',
'lodash',
'superagent'
]
},
output: {
path: './build',
filename: "bundle.js"
},
eslint: {
configFile: './.eslintrc'
},
devtool: 'eval-source-map',
module: {
loaders: [
{ test: /\.(js|jsx)$/, loaders: ['react-hot', 'babel?experimental'], exclude: /node_modules/},
{ test: /\.(js|jsx)$/, loader: "eslint-loader", exclude: /node_modules/},
{ test: /\.json$/, loader: 'json' },
{ test: /\.yml$/, loader: 'json!yaml' },
{ test: /\.scss$/, loader: 'style!css!sass' },
{ test: /\.(png|woff|woff2|eot|ttf|svg)$/, loader: 'url-loader?limit=100000' }
]
},
plugins: [
new webpack.DefinePlugin({'process.env': {'NODE_ENV': JSON.stringify('production')}}),
new webpack.optimize.CommonsChunkPlugin("vendor", "vendor.bundle.js"),
new webpack.optimize.UglifyJsPlugin({minimize: true}),
new webpack.NoErrorsPlugin()
]
};
module.exports = config;
我的package.json
{
"license": "MIT",
"engines": {
"iojs": ">= 1.6.2"
},
"scripts": {
"create:index": "mustang -t index.tmpl -i config.json -o build/index.html",
"predev": "mkdir -p build/ && npm run create:index",
"dev": "webpack-dev-server --host 0.0.0.0 --hot --progress --colors --content-base build",
"backend": "NODE_ENV=production node server/server.js",
"backend:dev": "DEBUG=tinderlicht node server/server.js",
"predeploy": "mkdir -p build/ && npm run create:index",
"deploy": "NODE_ENV=production webpack -p",
"test": "node webpack-mocha.config.js"
},
"devDependencies": {
"autoprefixer-loader": "^3.2.0",
"axios": "^0.7.0",
"babel": "^5.8.23",
"babel-core": "^5.8.25",
"babel-eslint": "^4.1.3",
"babel-loader": "^5.3.2",
"bluebird": "^2.10.2",
"css-loader": "^0.19.0",
"es6-collections": "^0.5.1",
"es6-promise": "^3.0.2",
"eslint": "^1.6.0",
"eslint-loader": "^1.1.0",
"eslint-plugin-react": "^3.5.1",
"extract-text-webpack-plugin": "^0.8.2",
"file-loader": "^0.8.1",
"firebase": "^2.3.1",
"fireproof": "^3.0.3",
"jquery": "^2.2.0",
"json-loader": "^0.5.1",
"jsonld": "^0.4.2",
"jsx-loader": "^0.13.2",
"lodash": "^3.3.0",
"mustang": "^0.1.3",
"node-sass": "^3.3.3",
"react": "^0.14.0",
"react-dom": "^0.14.0",
"react-hot-loader": "^1.1.5",
"sass-loader": "3.0.0",
"style-loader": "^0.12.4",
"superagent": "^1.4.0",
"url-loader": "^0.5.5",
"webpack": "^1.5.3",
"webpack-dev-server": "^1.7.0"
},
"dependencies": {
"body-parser": "^1.15.0",
"cors": "^2.7.1",
"debug": "^2.2.0",
"express": "^4.13.4",
"mustache": "^2.2.1",
"nodemailer": "^2.1.0",
"nodemailer-sendmail-transport": "^1.0.0",
"react-radio-group": "^2.2.0",
"uglifyjs": "^2.4.10"
}
}
有没有人知道如何解决这个问题?
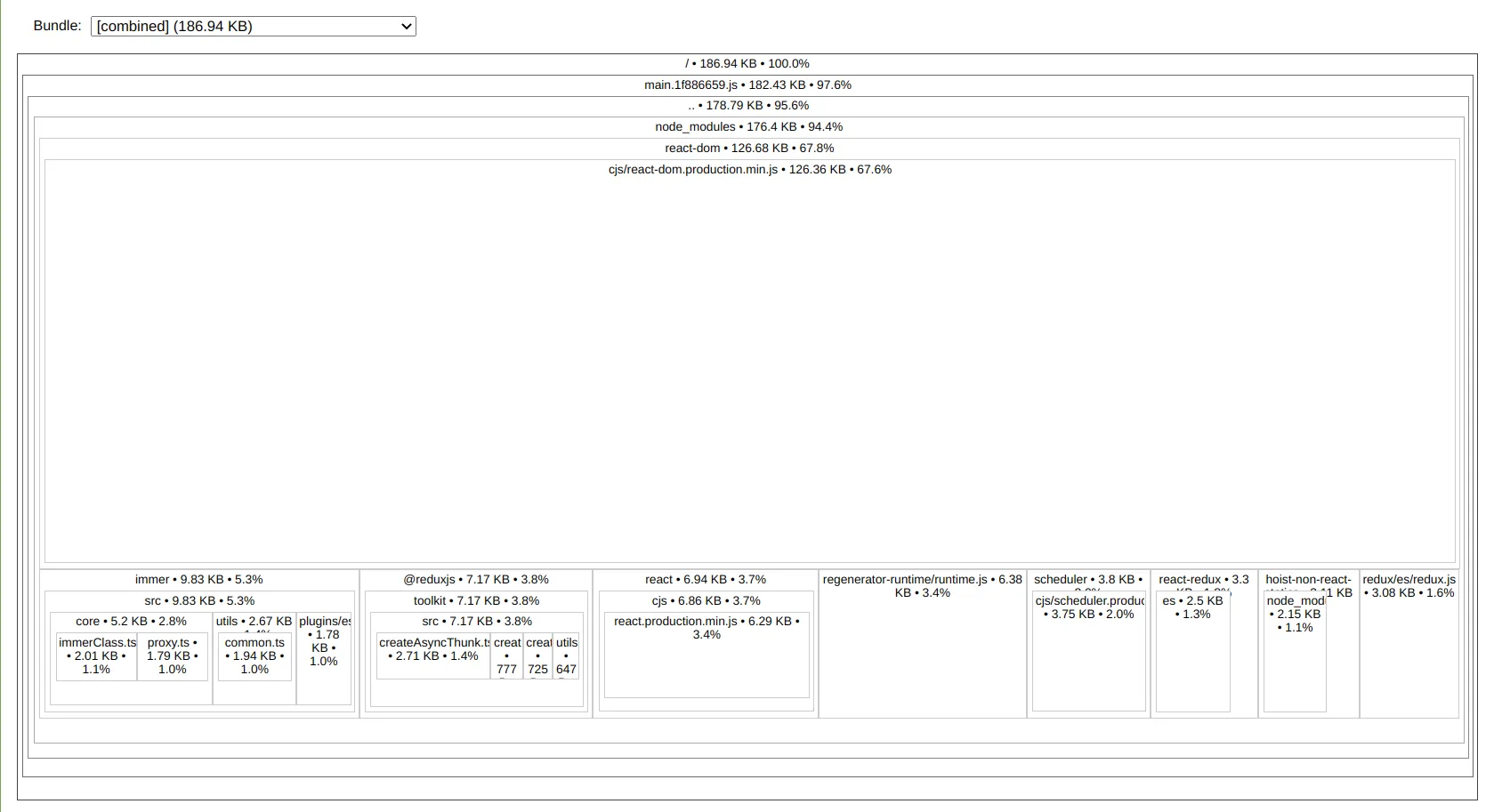
devtool:"eval-source-map",该选项提供良好的开发人员体验,但它会将整个源代码作为数据URL包含在内。您不应在生产环境中使用此选项。 - Johannes Ewald