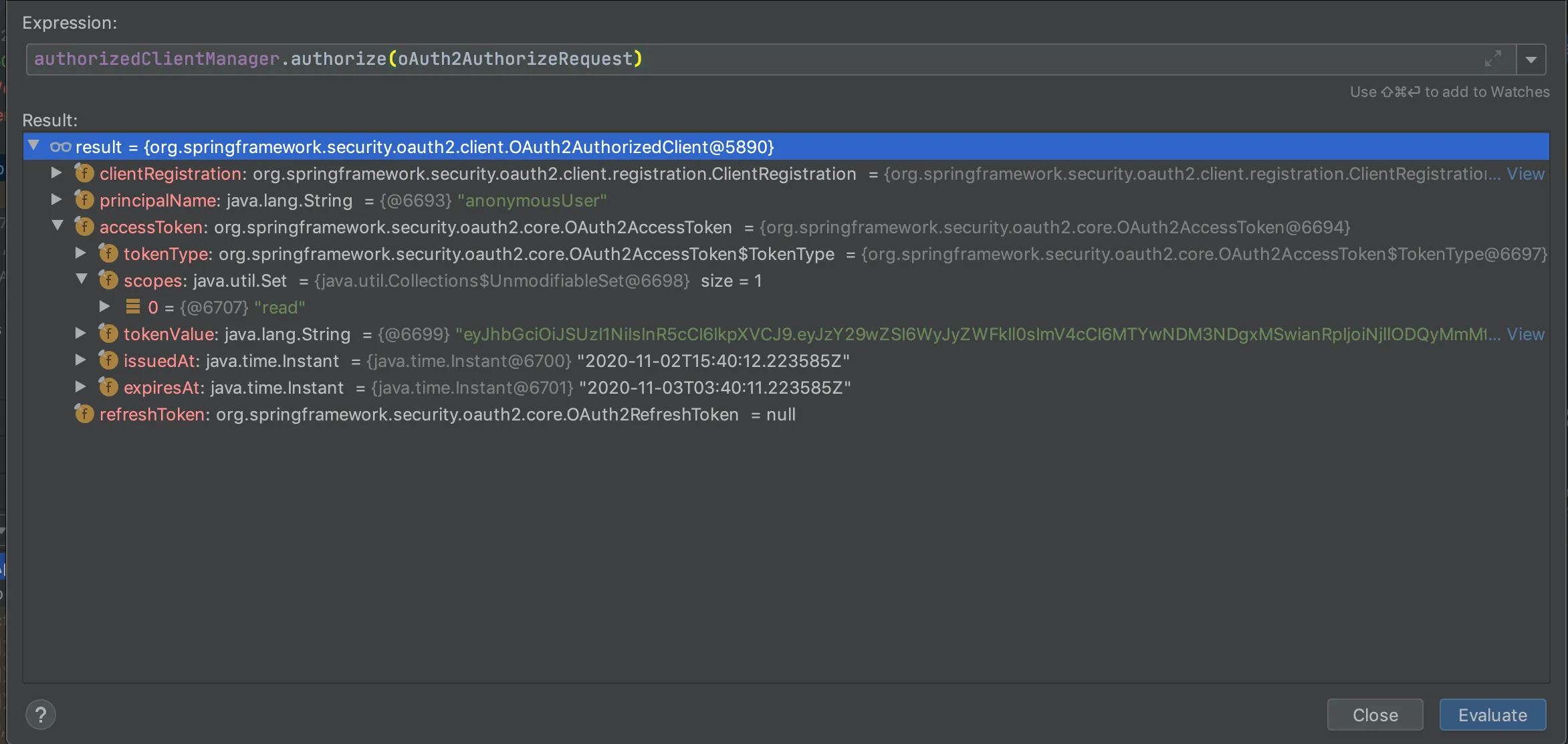
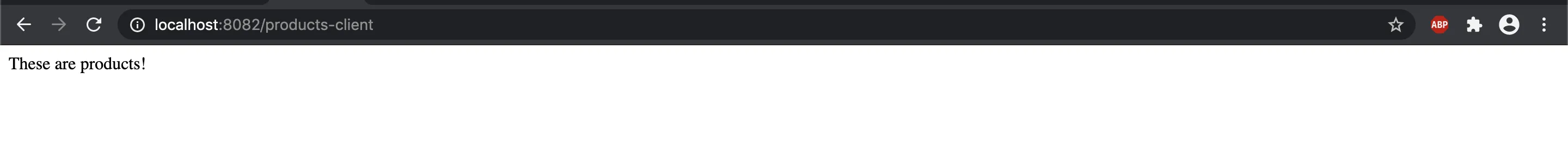
我正在学习如何使用基本身份验证和OAuth2 JWT令牌验证保护微服务。我使用基本身份验证实施了它,现在我想将其转换为OAuth2身份验证。
以下是使用基本身份验证来保护这两个微服务之间通信的实现。
微服务1 - REST API
@Configuration
@Getter
public class DemoApiConfiguration {
@Value("${demo.api.credentials.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${demo.api.credentials.password}")
private String password;
}
SecurityConfigurer类:
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class SecurityConfigurer extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
private final DemoApiConfiguration apiConfig;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http
.csrf().disable()
.authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated()
.and()
.httpBasic();
}
@Bean
public UserDetailsService userDetailsService(PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder) {
UserDetails theUser = User.withUsername(apiConfig.getUsername())
.password(passwordEncoder.encode(apiConfig.getPassword())).roles("USER").build();
InMemoryUserDetailsManager userDetailsManager = new InMemoryUserDetailsManager();
userDetailsManager.createUser(theUser);
return userDetailsManager;
}
@Bean
public PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
}
控制器类:
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/rest/api/v1")
public class HomeController {
@GetMapping("/products")
public String home() {
return "These are products!";
}
}
application.yml:
demo:
api:
credentials:
username: ${demo_api_username:john}
password: ${demo_api_password:test}
微服务2 - REST消费者
@Configuration
@Getter
public class DemoApiConfiguration {
@Value("${demo.api.credentials.username}")
private String username;
@Value("${demo.api.credentials.password}")
private String password;
@Value("${demo.api.credentials.basePath}")
private String basePath;
}
WebConfigurer 类:
@Configuration
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class WebConfigurer {
private final DemoApiConfiguration apiConfig;
@Bean
public ApiClient restTemplate() {
RestTemplate restTemplate = new RestTemplate();
ApiClient apiClient = new ApiClient(restTemplate);
apiClient.setBasePath(apiConfig.getBasePath());
return apiClient;
}
public String getAuthorization() {
return (!StringUtils.isEmpty(apiConfig.getUsername()) &&
!StringUtils.isEmpty(apiConfig.getPassword())) ?
"Basic " + Base64Utils.encodeToString((
apiConfig.getUsername() + ":" + apiConfig.getPassword())
.getBytes()) :
null;
}
}
ApiClient 类:
@Getter
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@Slf4j
public class ApiClient {
private static final String AUTHORIZATION_HEADER = "Authorization";
private final RestTemplate restTemplate;
private String basePath;
public ApiClient setBasePath(String basePath) {
this.basePath = basePath;
return this;
}
public String invokeApi(String path, String credentials) {
UriComponentsBuilder builder = UriComponentsBuilder.fromHttpUrl(basePath).path(path);
RequestEntity.BodyBuilder requestBuilder =
RequestEntity.method(HttpMethod.GET, builder.build().toUri());
requestBuilder.contentType(MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON);
requestBuilder.header(AUTHORIZATION_HEADER, credentials);
RequestEntity<Object> requestEntity = requestBuilder.body(null);
return restTemplate
.exchange(requestEntity, String.class).getBody();
}
}
ConsumeController 类:
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class ConsumeController {
private static final String PATH = "/rest/api/v1/products";
private final WebConfigurer webConfigurer;
private final ApiClient apiClient;
@GetMapping(value = "/products-client")
public String getProductList() {
return apiClient.invokeApi(PATH, webConfigurer.getAuthorization());
}
}
application.yml:
server:
port: 8090
demo:
api:
credentials:
username: ${demo_api_username:john}
password: ${demo_api_password:test}
basePath: ${demo_api_path:http://localhost:8080}
第一个微服务是一个REST API,第二个微服务是一个REST消费者,通信使用Basic Auth进行安全保护。
现在我想要使用OAuth2来实现,并请问您如何使用OAuth2来保障通信的安全性?因此,我想添加另一个端点,例如"/access-token",客户端首先将使用用户名和密码对该端点发出请求,并获取jwt令牌。之后,将使用此jwt令牌向"/products"端点发出带有Authorization头的请求。您能帮助我完成这种实现吗?谢谢!