从一个坐标到另一个坐标的方位和找到北、东、南、西 :)
public class FindBearing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(" Your Result >>> "+FindBearing.bearing(19.2859590, 73.4966430, 19.2861020, 73.4988090));
}
protected static String bearing(double lat1, double lon1, double lat2, double lon2){
double longitude1 = lon1;
double longitude2 = lon2;
double latitude1 = Math.toRadians(lat1);
double latitude2 = Math.toRadians(lat2);
double longDiff= Math.toRadians(longitude2-longitude1);
double y= Math.sin(longDiff)*Math.cos(latitude2);
double x=Math.cos(latitude1)*Math.sin(latitude2)-Math.sin(latitude1)*Math.cos(latitude2)*Math.cos(longDiff);
double resultDegree= (Math.toDegrees(Math.atan2(y, x))+360)%360;
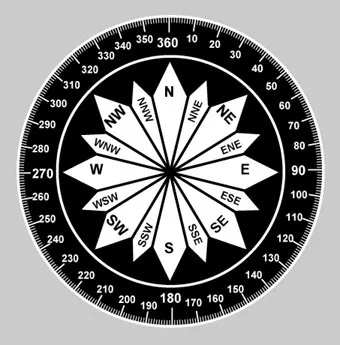
String coordNames[] = {"N","NNE", "NE","ENE","E", "ESE","SE","SSE", "S","SSW", "SW","WSW", "W","WNW", "NW","NNW", "N"};
double directionid = Math.round(resultDegree / 22.5);
if (directionid < 0) {
directionid = directionid + 16;
}
String compasLoc=coordNames[(int) directionid];
return resultDegree+" "+compasLoc;
}
}
