我来这里是寻找答案,但发现所有的答案都包含太多信息或者不足,所以这里是我的答案...
既然你已经创建了一个自定义类,你需要实现GetHashCode和Equals。在这个例子中,我将使用一个名为Student的类代替a,因为它更容易理解,也不会违反任何命名规范。 下面是实现的代码:
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
return obj is Student student && Id == student.Id;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return HashCode.Combine(Id);
}
我发现
这篇来自Microsoft的文章,如果你正在使用Visual Studio,那么实现这些功能的方法非常简单。如果对其他人有帮助的话,下面是在Visual Studio中使用自定义数据类型在HashSet中的完整步骤:
假设有一个类
Student,其中包含2个简单属性和一个初始化器。
public class Student
{
public int Id { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public Student(int id)
{
this.Id = id;
}
}
要实现IComparable,只需添加
: IComparable<Student>即可:
public class Student : IComparable<Student>
您将看到一个红色波浪线,上面显示一个错误消息,说明您的类没有实现IComparable接口。点击建议或按Alt+Enter键,并使用建议来实现它。
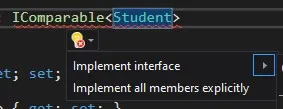
您将看到生成的方法。然后,您可以编写自己的实现,如下所示:
public int CompareTo(Student student)
{
return this.Id.CompareTo(student.Id);
}
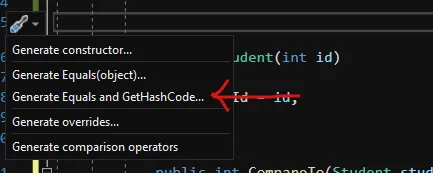
在上述实现中,仅比较了Id属性,忽略了名称。接下来,在您的代码中右键单击并选择“快速操作和重构”,然后选择“生成Equals和GetHashCode”。
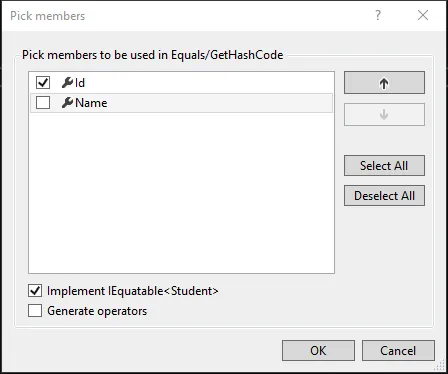
弹出一个窗口,您可以在其中选择用于哈希的属性,甚至可以实现IEquitable(如果您愿意):
这是生成的代码:
public class Student : IComparable<Student>, IEquatable<Student> {
...
public override bool Equals(object obj)
{
return Equals(obj as Student);
}
public bool Equals(Student other)
{
return other != null && Id == other.Id;
}
public override int GetHashCode()
{
return HashCode.Combine(Id);
}
}
现在,如果您尝试添加一个重复的项目,如下所示,它将被跳过:
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Student s1 = new Student(1);
Student s2 = new Student(2);
HashSet<Student> hs = new HashSet<Student>();
hs.Add(s1);
hs.Add(s2);
hs.Add(new Student(1));
hs.Add(new Student(3));
}
现在您可以这样使用
.Contains:
for (int i = 0; i <= 4; i++)
{
if (hs.Contains(new Student(i)))
{
Console.WriteLine($@"Set contains student with Id {i}");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine($@"Set does NOT contain a student with Id {i}");
}
}
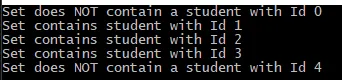
输出:




IEqualityComparer<T>的实现或在类a中实现它。https://msdn.microsoft.com/zh-cn/library/bb301504(v=vs.110).aspx - Jaider