我是一名初学Java编程的人,目前在设置DelayQueue方面遇到了困难。
我想要实现以下功能:
我只是在试图学习所有的基础知识,读过API文档,但似乎无法理解。
我想要实现以下功能:
DelayQueue queue = new DelayQueue();
If (counter > 0){
queue.offer(Integer, *A custom delay*)
} Else {
queue.offer(Integer, *A different custom delay*)
}
我只是在试图学习所有的基础知识,读过API文档,但似乎无法理解。
提前感谢您。
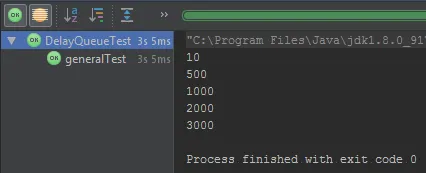
setDelay()方法来手动设置静态延迟,并返回它而不是计算它。 - Kayaman