测量两个不规则图形之间的相似度
8
- pradeepln4
4
有什么相似之处;您是在寻找精确匹配吗?点列表必须按顺序排列,还是可以重新排序? - Shashank Agarwal
不是精确匹配,而是模式匹配测量。必须按顺序进行。 - pradeepln4
你的数据点在x轴上等间距吗? - Sahil M
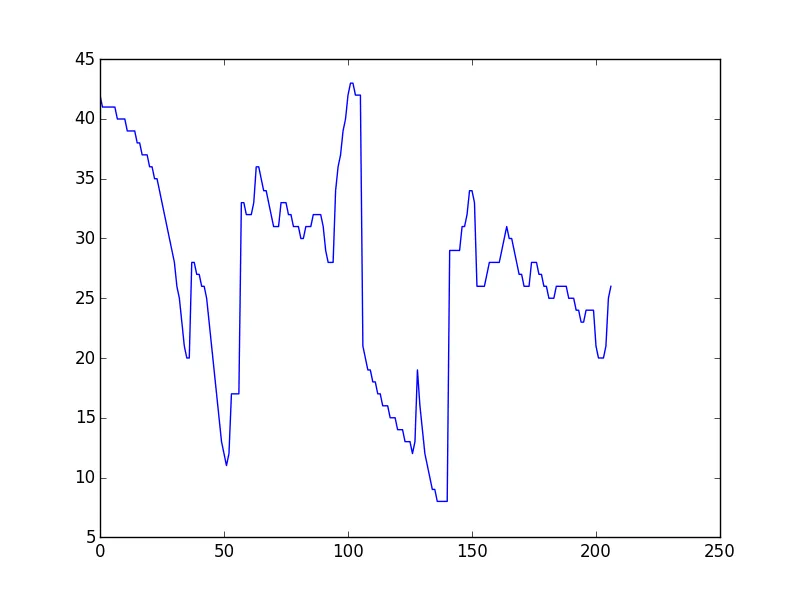
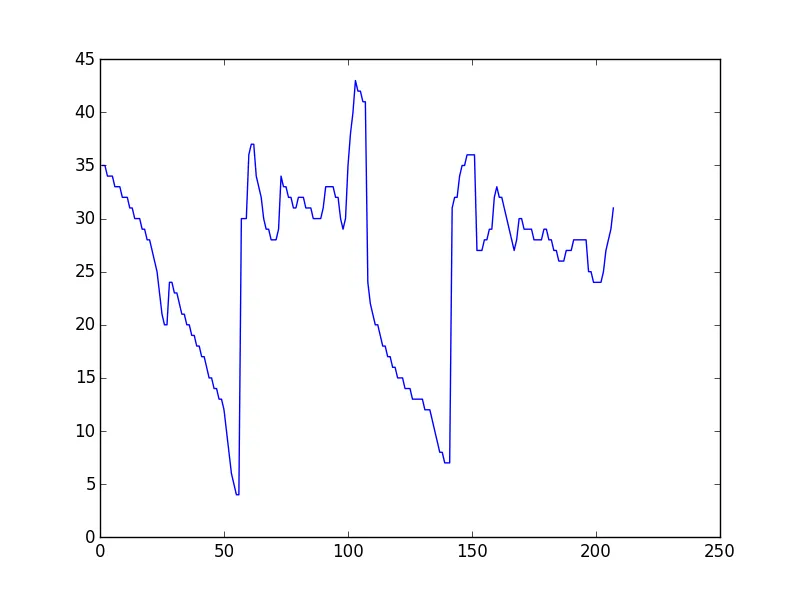
我在问题中发布了两张图片...你能看到它们之间的某种模式吗?如何测量这种模式的相似性? - pradeepln4
3个回答
12
我不知道Python中是否有内置函数可以实现此操作。
我可以给你列出Python生态系统中可能使用的函数列表。这绝不是所有函数的完整列表,可能还有很多我不知道的方法。
如果数据已排序,但您不知道哪个数据点是第一个,哪个数据点是最后一个:
- 使用有向豪斯多夫距离
如果数据已排序,并且您知道第一个和最后一个点是正确的:
- 离散Fréchet距离*
- 动态时间规整(DTW)*
- 部分曲线映射(PCM)**
- 曲线长度距离度量(使用起点到终点的弧长距离)**
- 两条曲线之间的面积**
*通常用于各种机器学习任务的数学方法
**我用来识别唯一材料滞回响应的方法
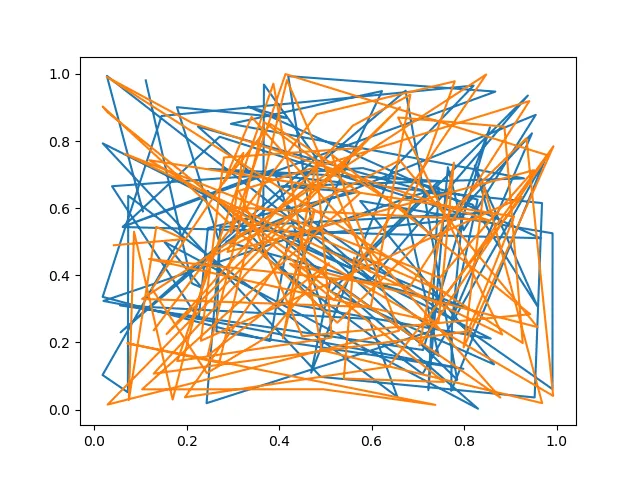
首先,让我们假设我们有两个完全相同的随机X Y数据。请注意,所有这些方法都将返回零。如果您没有安装similaritymeasures,请从pip中安装。
import numpy as np
from scipy.spatial.distance import directed_hausdorff
import similaritymeasures
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# Generate random experimental data
np.random.seed(121)
x = np.random.random(100)
y = np.random.random(100)
P = np.array([x, y]).T
# Generate an exact copy of P, Q, which we will use to compare
Q = P.copy()
dh, ind1, ind2 = directed_hausdorff(P, Q)
df = similaritymeasures.frechet_dist(P, Q)
dtw, d = similaritymeasures.dtw(P, Q)
pcm = similaritymeasures.pcm(P, Q)
area = similaritymeasures.area_between_two_curves(P, Q)
cl = similaritymeasures.curve_length_measure(P, Q)
# all methods will return 0.0 when P and Q are the same
print(dh, df, dtw, pcm, cl, area)
打印输出为0.0、0.0、0.0、0.0、0.0、0.0。这是因为曲线P和Q完全相同!
现在假设P和Q是不同的。
# Generate random experimental data
np.random.seed(121)
x = np.random.random(100)
y = np.random.random(100)
P = np.array([x, y]).T
# Generate random Q
x = np.random.random(100)
y = np.random.random(100)
Q = np.array([x, y]).T
dh, ind1, ind2 = directed_hausdorff(P, Q)
df = similaritymeasures.frechet_dist(P, Q)
dtw, d = similaritymeasures.dtw(P, Q)
pcm = similaritymeasures.pcm(P, Q)
area = similaritymeasures.area_between_two_curves(P, Q)
cl = similaritymeasures.curve_length_measure(P, Q)
# all methods will return 0.0 when P and Q are the same
print(dh, df, dtw, pcm, cl, area)
打印输出是 0.107、0.743、37.69、21.5、6.86、11.8, 根据每种方法量化P与Q之间的差异。
现在,您有很多方法可以比较两条曲线。我建议先从DTW开始,因为在许多时间序列应用程序中,它已经被使用过,并且看起来与您上传的数据相似。
我们可以使用以下代码可视化P和Q的外观。
plt.figure()
plt.plot(P[:, 0], P[:, 1])
plt.plot(Q[:, 0], Q[:, 1])
plt.show()
- Charles Jekel
3
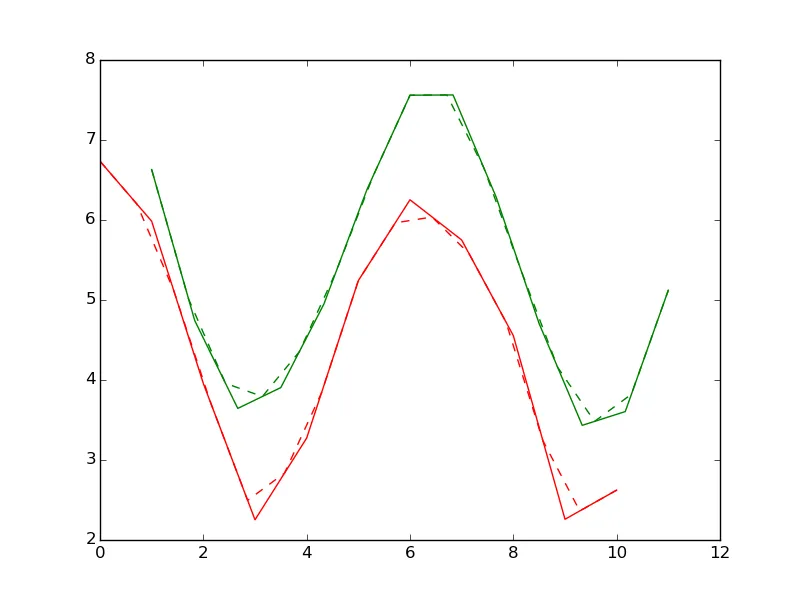
由于你的数组大小不同(我假设你是同时获取的),需要插值以便在相关点上进行比较。以下代码可以执行此操作,并计算相关度量:
#!/usr/bin/python
import numpy as np
from scipy.interpolate import interp1d
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import scipy.spatial.distance as ssd
import scipy.stats as ss
x = np.linspace(0, 10, num=11)
x2 = np.linspace(1, 11, num=13)
y = 2*np.cos( x) + 4 + np.random.random(len(x))
y2 = 2* np.cos(x2) + 5 + np.random.random(len(x2))
# Interpolating now, using linear, but you can do better based on your data
f = interp1d(x, y)
f2 = interp1d(x2,y2)
points = 15
xnew = np.linspace ( min(x), max(x), num = points)
xnew2 = np.linspace ( min(x2), max(x2), num = points)
ynew = f(xnew)
ynew2 = f2(xnew2)
plt.plot(x,y, 'r', x2, y2, 'g', xnew, ynew, 'r--', xnew2, ynew2, 'g--')
plt.show()
# Now compute correlations
print ssd.correlation(ynew, ynew2) # Computes a distance measure based on correlation between the two vectors
print np.correlate(ynew, ynew2, mode='valid') # Does a cross-correlation of same sized arrays and gives back correlation
print np.corrcoef(ynew, ynew2) # Gives back the correlation matrix for the two arrays
print ss.spearmanr(ynew, ynew2) # Gives the spearman correlation for the two arrays
输出:
0.499028272458
[ 363.48984942]
[[ 1. 0.50097173]
[ 0.50097173 1. ]]
SpearmanrResult(correlation=0.45357142857142857, pvalue=0.089485900143027278)
请记住,这里的相关性是参数化和皮尔逊类型,并假定单调性以计算相关性。如果不是这种情况,并且您认为您的数组只是一起改变符号,您可以像最后一个示例中那样使用Spearman's相关性。
- Sahil M
2
我不知道有没有内置函数,但是你可以修改Levenshtein距离。下面的代码来自于wikibooks。
def point_distance(p1, p2):
# Define distance, if they are the same, then the distance should be 0
def levenshtein_point(l1, l2):
if len(l1) < len(l2):
return levenshtein(l2, l1)
# len(l1) >= len(l2)
if len(l2) == 0:
return len(l1)
previous_row = range(len(l2) + 1)
for i, p1 in enumerate(l1):
current_row = [i + 1]
for j, p2 in enumerate(l2):
print('{},{}'.format(p1, p2))
insertions = previous_row[j + 1] + 1 # j+1 instead of j since previous_row and current_row are one character longer
deletions = current_row[j] + 1 # than l2
substitutions = previous_row[j] + point_distance(p1, p2)
current_row.append(min(insertions, deletions, substitutions))
previous_row = current_row
return previous_row[-1]
- Shashank Agarwal
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接