我有许多标本的图像,其中有些图像具有无法控制的背景颜色。一些图像有黑色背景、一些有白色背景、一些有绿色背景等。
我想去除给定图像中仅有一个标本物体的背景颜色。我尝试了这段代码,但它没有按照我的期望工作。
def get_holes(image, thresh):
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
im_bw = cv2.threshold(gray, thresh, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)[1]
im_bw_inv = cv2.bitwise_not(im_bw)
_, contour, _ = cv2.findContours(im_bw_inv, cv2.RETR_CCOMP, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
for cnt in contour:
cv2.drawContours(im_bw_inv, [cnt], 0, 255, -1)
nt = cv2.bitwise_not(im_bw)
im_bw_inv = cv2.bitwise_or(im_bw_inv, nt)
return im_bw_inv
def remove_background(image, thresh, scale_factor=.25, kernel_range=range(1, 15), border=None):
border = border or kernel_range[-1]
holes = get_holes(image, thresh)
small = cv2.resize(holes, None, fx=scale_factor, fy=scale_factor)
bordered = cv2.copyMakeBorder(small, border, border, border, border, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT)
for i in kernel_range:
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (2*i+1, 2*i+1))
bordered = cv2.morphologyEx(bordered, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, kernel)
unbordered = bordered[border: -border, border: -border]
mask = cv2.resize(unbordered, (image.shape[1], image.shape[0]))
fg = cv2.bitwise_and(image, image, mask=mask)
return fg
file = your_file_location
img = cv2.imread(file)
nb_img = dm.remove_background(img, 255)
以下是一些示例图片:
请您给出建议。
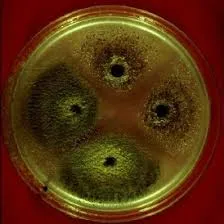
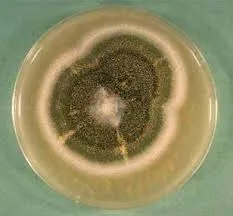
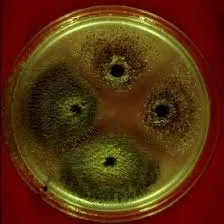






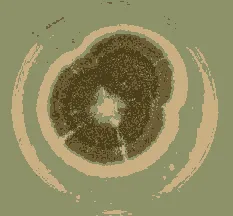

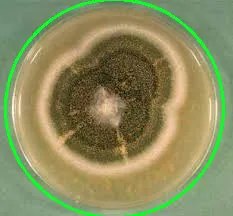

cv2.fitEllipse。 - nathancycv2.findContours查找轮廓,然后使用cv2.drawContours将最大的轮廓绘制到掩码上。这应该适用于任何方向。 - nathancy