我正在设计一种算法,用于找到网格中给定点对的一组非交路径。例如对于这些点对:(9,4) 和 (12,13)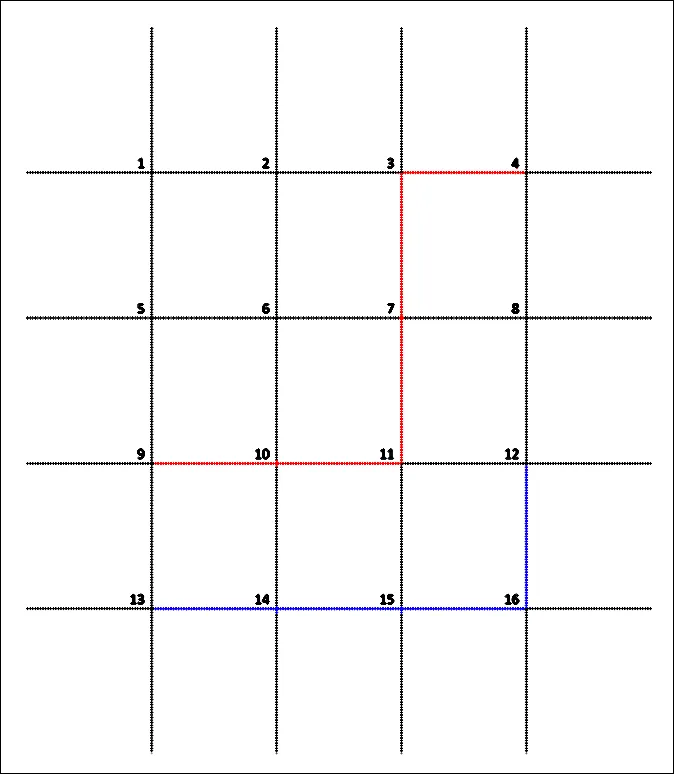 输出应该类似于这样:
输出应该类似于这样:
如果它无法路由所有路径,则打印“Blocked”。
首先,我搜索了已有的算法,以在图形或网格中查找两个点之间的所有简单路径。我在这里找到了@Casey Watson和@svick的一个算法(链接)。它非常有效,但仅适用于小型图形。
我将其转换为C#.NET,并稍微改进了一下,以便能够找到最大长度为X的路径,并建立了我的总算法。
我构建的算法在小型图形中运行良好。这是在8x8网格中的9对路线。
但是,在更大的图形中,如16x16甚至我打算做的最终图形,即16x16x2的3D模型,它需要很长时间才能完成。
该算法开发为深度优先搜索递归算法,但是将值返回给用户需要很长时间。因此,我决定将其转换为循环而不是递归调用,以便我可以从.NET的yield return功能中受益,但仍然没有帮助。
算法的循环版本可以在不到一秒钟内为一对点找到路径,但递归版本需要超过90秒。
当我尝试使用2对时,循环版本需要约342秒,但递归版本需要约200秒。
所以我不知道哪个更快?递归还是循环?
我真的想知道做到这一点的最佳方法。
注意:节点编号中的第一个数字确定层(从1开始)。
以下是代码。
 输出应该类似于这样:
输出应该类似于这样: 9,10,11,7,3,4
13,14,15,16,12
如果它无法路由所有路径,则打印“Blocked”。
首先,我搜索了已有的算法,以在图形或网格中查找两个点之间的所有简单路径。我在这里找到了@Casey Watson和@svick的一个算法(链接)。它非常有效,但仅适用于小型图形。
我将其转换为C#.NET,并稍微改进了一下,以便能够找到最大长度为X的路径,并建立了我的总算法。
我构建的算法在小型图形中运行良好。这是在8x8网格中的9对路线。
但是,在更大的图形中,如16x16甚至我打算做的最终图形,即16x16x2的3D模型,它需要很长时间才能完成。
该算法开发为深度优先搜索递归算法,但是将值返回给用户需要很长时间。因此,我决定将其转换为循环而不是递归调用,以便我可以从.NET的yield return功能中受益,但仍然没有帮助。
算法的循环版本可以在不到一秒钟内为一对点找到路径,但递归版本需要超过90秒。
当我尝试使用2对时,循环版本需要约342秒,但递归版本需要约200秒。
所以我不知道哪个更快?递归还是循环?
我真的想知道做到这一点的最佳方法。
注意:节点编号中的第一个数字确定层(从1开始)。
以下是代码。
using System;
using System.Collections;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
using System.Linq;
namespace AlgorithmTest
{
struct Connection
{
public int FirstNode;
public int SecondNode;
public Connection(int N1,int N2)
{
FirstNode = N1;
SecondNode = N2;
}
}
enum Algorithm
{ Recursion, Loops }
public class Search
{
private const int MAX = 15;
private const int Width = 16;
private const int Length = 16;
private const int Height = 2;
private static void Main(string[] args)
{
var graph = new Graph();
var str = new int[Height,Length, Width];
var level = ((int)Math.Pow(10, (Length * Width).ToString().Length) >= 100) ? (int)Math.Pow(10, (Length * Width).ToString().Length) : 100;
for (var i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
int num = 0;
for (var j = 0; j < Length; j++)
for (var k = 0; k < Width; k++)
{
str[i, j, k] = ++num + level;
}
level += level;
}
for (var i = 0; i < Height; i++)
{
for (var j = 0; j < Length; j++)
{
for (var k = 0; k < Width; k++)
{
if (i < Height - 1) graph.addEdge(str[i, j, k], str[i + 1, j, k]);
if (i > 0) graph.addEdge(str[i, j, k], str[i - 1, j, k]);
if (k < Width - 1) graph.addEdge(str[i, j, k], str[i, j, k + 1]);
if (k > 0) graph.addEdge(str[i, j, k], str[i, j, k - 1]);
if (j < Length - 1) graph.addEdge(str[i, j, k], str[i, j + 1, k]);
if (j > 0) graph.addEdge(str[i, j, k], str[i, j - 1, k]);
}
}
}
var wt = new Stopwatch();
wt.Start();
var connectedNodes = new List<Connection>()
{
new Connection(1030, 1005),
// new Connection(1002, 1044),
// new Connection(1015, 1064),
// new Connection(1041, 1038),
// new Connection(1009, 1027),
// new Connection(1025, 1018),
// new Connection(1037, 1054),
// new Connection(1049, 1060),
// new Connection(1008, 1031),
// new Connection(1001, 1035),
};
wt.Start();
Console.WriteLine("Using Loops:");
Console.WriteLine();
var allPaths = new Search().FindAllPaths(connectedNodes, graph, MAX, Algorithm.Loops);
wt.Stop();
foreach (var path in allPaths)
{
PrintPath(path);
}
Console.WriteLine("Total Seconds: " + wt.Elapsed.TotalSeconds + ", Number of paths: " + allPaths.Count());
Console.WriteLine("***************************************************************************************************");
Console.WriteLine("Using Recursion:");
Console.WriteLine();
wt.Reset();
wt.Start();
allPaths = new Search().FindAllPaths(connectedNodes, graph, MAX, Algorithm.Recursion);
wt.Stop();
foreach (var path in allPaths)
{
PrintPath(path);
}
Console.WriteLine("Total Seconds: " + wt.Elapsed.TotalSeconds + ", Number of paths: " + allPaths.Count());
Console.WriteLine();
}
private IEnumerable<List<int>> FindAllPaths(List<Connection> connectedNodes, Graph graph, int max, Algorithm algorithm)
{
var paths=new Stack<List<int>>();
var blocked=new List<int>();
for (var i = 0; i < connectedNodes.Count; i++)
{
if (!blocked.Contains(connectedNodes[i].FirstNode)) blocked.Add(connectedNodes[i].FirstNode);
if (!blocked.Contains(connectedNodes[i].SecondNode)) blocked.Add(connectedNodes[i].SecondNode);
}
if (algorithm == Algorithm.Recursion)
{
if (FindAllPaths(connectedNodes, 0, max, graph, paths, blocked))
{
Console.WriteLine("BLOCKED");
return new List<List<int>>();
}
}
else if(algorithm==Algorithm.Loops)
{
if (!FindAllPaths2(connectedNodes, 0, max, graph, paths, blocked))
{
Console.WriteLine("BLOCKED");
return new List<List<int>>();
}
}
return paths;
}
private static bool FindAllPaths(List<Connection> connectedNodes,int order,int max, Graph graph, Stack<List<int>> allPaths, List<int> blocked)
{
if (order >= connectedNodes.Count) return false;
var paths = SearchForPaths(graph, connectedNodes[order].FirstNode, connectedNodes[order].SecondNode, max, blocked);
if (paths.Count == 0) return true;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < paths.Count; i++)
{
var path = paths[i];
allPaths.Push(path);
blocked.AddRange(path);
if (!FindAllPaths(connectedNodes, order + 1,max, graph, allPaths, blocked)) break;
allPaths.Pop();
foreach (var j in path)
{
blocked.RemoveAll(num => num==j);
}
paths.RemoveAll(list => IsListsSimilar(list,path));
i--;
}
if (i == paths.Count) return true;
return false;
}
private static bool IsListsSimilar(List<int> L1,List<int> L2)
{
if (L2.Count > L1.Count) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < L2.Count - 1; i++)
{
if (L1[i] != L2[i]) return false;
}
return true;
}
private static List<List<int>> SearchForPaths(Graph graph, int start, int end, int max, List<int> blocked)
{
blocked.Remove(start);
blocked.Remove(end);
var nodePaths = new List<List<int>>();
var visited = new LinkedList<int>();
visited.AddLast(start);
DepthFirstSearch(graph, visited, end, max, blocked, nodePaths);
nodePaths = nodePaths.OrderBy(list => list.Count).ToList();
return nodePaths;
}
private static void DepthFirstSearch(Graph graph, LinkedList<int> visited, int end, int max, List<int> blocked, List<List<int>> paths)
{
var nodes = graph.adjacentNodes(visited.Last.Value);
// examine adjacent nodes
var nodeCount = blocked.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++)
{
if (visited.Contains(blocked[i])) return;
}
if (visited.Count > max) return;
nodeCount = nodes.Count;
for (var i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++)
{
if (visited.Contains(nodes[i]) || nodes[i] != end) continue;
visited.AddLast(nodes[i]);
{
paths.Add(new List<int>(visited));
}
visited.RemoveLast();
break;
}
nodeCount = nodes.Count;
for (var i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++)
{
if (visited.Contains(nodes[i]) || nodes[i] == end) continue;
visited.AddLast(nodes[i]);
DepthFirstSearch(graph, visited, end, max, blocked, paths);
visited.RemoveLast();
}
}
private static bool FindAllPaths2(List<Connection> connectedNodes, int order, int max, Graph graph, Stack<List<int>> allPaths, List<int> blocked)
{
if (order >= connectedNodes.Count) return false;
foreach (var path in SearchForPaths2(graph, connectedNodes[order].FirstNode, connectedNodes[order].SecondNode, max, blocked))
{
allPaths.Push(path);
blocked.AddRange(path);
if (!FindAllPaths2(connectedNodes, order + 1, max, graph, allPaths, blocked)) break;
allPaths.Pop();
foreach (var j in path)
{
blocked.RemoveAll(num => num == j);
}
}
return true;
}
private static IEnumerable<List<int>> SearchForPaths2(Graph graph, int start, int end, int max, List<int> blocked)
{
blocked.Remove(start);
blocked.Remove(end);
var visited = new LinkedList<int>();
visited.AddLast(start);
foreach (var VARIABLE in DepthFirstSearch(graph, visited, end, max, blocked))
{
yield return VARIABLE;
}
}
private static IEnumerable<List<int>> DepthFirstSearch(Graph graph, LinkedList<int> visited, int end, int max, List<int> blocked)
{
var nodes = graph.adjacentNodes(visited.Last.Value);
var nodeCount = blocked.Count;
for (int i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++)
{
if (visited.Contains(blocked[i])) yield break;
}
if (visited.Count > max) yield break;
nodeCount = nodes.Count;
for (var i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++)
{
if (visited.Contains(nodes[i]) || nodes[i] != end) continue;
visited.AddLast(nodes[i]);
yield return (new List<int>(visited));
visited.RemoveLast();
break;
}
nodeCount = nodes.Count;
for (var i = 0; i < nodeCount; i++)
{
if (visited.Contains(nodes[i]) || nodes[i] == end) continue;
visited.AddLast(nodes[i]);
foreach (var P in DepthFirstSearch(graph, visited, end, max, blocked))
{
yield return P;
}
visited.RemoveLast();
}
}
private static void PrintPath(List<int> visited)
{
for (int i = 0; i < visited.Count()-1; i++)
{
Console.Write(visited[i]);
Console.Write(" --> ");
}
Console.Write(visited[visited.Count() - 1]);
Console.WriteLine();
Console.WriteLine();
}
}
public class Graph
{
private readonly Dictionary<int, HashSet<int>> map = new Dictionary<int, HashSet<int>>();
public void addEdge(int node1, int node2)
{
HashSet<int> adjacent = null;
map.TryGetValue(node1, out adjacent);
if (adjacent == null)
{
adjacent = new HashSet<int>();
map.Add(node1, adjacent);
}
adjacent.Add(node2);
}
public List<int> adjacentNodes(int last)
{
HashSet<int> adjacent = null;
map.TryGetValue(last, out adjacent);
if (adjacent == null)
{
return new List<int>();
}
return new List<int>(adjacent);
}
}
}