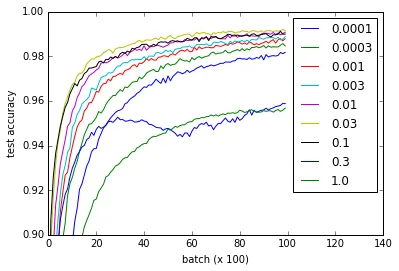
关于TensorFlow网站上的MNIST教程,我进行了一项实验(gist),以查看不同权重初始化对学习的影响。 我注意到,与我在流行的[Xavier, Glorot 2010]论文中所读到的相反,无论权重初始化如何,学习都很好。
不同的曲线代表卷积层和全连接层权重初始化中w的不同取值。请注意,即使0.3和1.0的性能较低并且某些值训练速度更快(特别是0.03和0.1最快),所有w的值都能正常工作。然而,图表显示了一个相当大的w范围可行,表明在权重初始化方面具有“健壮性”。def weight_variable(shape, w=0.1):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=w)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape, w=0.1):
initial = tf.constant(w, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
问题: 为什么这个网络不会受到梯度消失或梯度爆炸的问题?
我建议您阅读要点以了解实现细节,但以下是参考代码。在我的 Nvidia 960m 上大约需要一个小时,尽管我想象它也可以在 CPU 上在合理的时间内运行。
import time
from tensorflow.examples.tutorials.mnist import input_data
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow.python.client import device_lib
import numpy
import matplotlib.pyplot as pyplot
mnist = input_data.read_data_sets('MNIST_data', one_hot=True)
# Weight initialization
def weight_variable(shape, w=0.1):
initial = tf.truncated_normal(shape, stddev=w)
return tf.Variable(initial)
def bias_variable(shape, w=0.1):
initial = tf.constant(w, shape=shape)
return tf.Variable(initial)
# Network architecture
def conv2d(x, W):
return tf.nn.conv2d(x, W, strides=[1, 1, 1, 1], padding='SAME')
def max_pool_2x2(x):
return tf.nn.max_pool(x, ksize=[1, 2, 2, 1],
strides=[1, 2, 2, 1], padding='SAME')
def build_network_for_weight_initialization(w):
""" Builds a CNN for the MNIST-problem:
- 32 5x5 kernels convolutional layer with bias and ReLU activations
- 2x2 maxpooling
- 64 5x5 kernels convolutional layer with bias and ReLU activations
- 2x2 maxpooling
- Fully connected layer with 1024 nodes + bias and ReLU activations
- dropout
- Fully connected softmax layer for classification (of 10 classes)
Returns the x, and y placeholders for the train data, the output
of the network and the dropbout placeholder as a tuple of 4 elements.
"""
x = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 784])
y_ = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 10])
x_image = tf.reshape(x, [-1,28,28,1])
W_conv1 = weight_variable([5, 5, 1, 32], w)
b_conv1 = bias_variable([32], w)
h_conv1 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(x_image, W_conv1) + b_conv1)
h_pool1 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv1)
W_conv2 = weight_variable([5, 5, 32, 64], w)
b_conv2 = bias_variable([64], w)
h_conv2 = tf.nn.relu(conv2d(h_pool1, W_conv2) + b_conv2)
h_pool2 = max_pool_2x2(h_conv2)
W_fc1 = weight_variable([7 * 7 * 64, 1024], w)
b_fc1 = bias_variable([1024], w)
h_pool2_flat = tf.reshape(h_pool2, [-1, 7*7*64])
h_fc1 = tf.nn.relu(tf.matmul(h_pool2_flat, W_fc1) + b_fc1)
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32)
h_fc1_drop = tf.nn.dropout(h_fc1, keep_prob)
W_fc2 = weight_variable([1024, 10], w)
b_fc2 = bias_variable([10], w)
y_conv = tf.matmul(h_fc1_drop, W_fc2) + b_fc2
return (x, y_, y_conv, keep_prob)
# Experiment
def evaluate_for_weight_init(w):
""" Returns an accuracy learning curve for a network trained on
10000 batches of 50 samples. The learning curve has one item
every 100 batches."""
with tf.Session() as sess:
x, y_, y_conv, keep_prob = build_network_for_weight_initialization(w)
cross_entropy = tf.reduce_mean(
tf.nn.softmax_cross_entropy_with_logits(labels=y_, logits=y_conv))
train_step = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(1e-4).minimize(cross_entropy)
correct_prediction = tf.equal(tf.argmax(y_conv,1), tf.argmax(y_,1))
accuracy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct_prediction, tf.float32))
sess.run(tf.global_variables_initializer())
lr = []
for _ in range(100):
for i in range(100):
batch = mnist.train.next_batch(50)
train_step.run(feed_dict={x: batch[0], y_: batch[1], keep_prob: 0.5})
assert mnist.test.images.shape[0] == 10000
# This way the accuracy-evaluation fits in my 2GB laptop GPU.
a = sum(
accuracy.eval(feed_dict={
x: mnist.test.images[2000*i:2000*(i+1)],
y_: mnist.test.labels[2000*i:2000*(i+1)],
keep_prob: 1.0})
for i in range(5)) / 5
lr.append(a)
return lr
ws = [0.0001, 0.0003, 0.001, 0.003, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1.0]
accuracies = [
[evaluate_for_weight_init(w) for w in ws]
for _ in range(3)
]
# Plotting results
pyplot.plot(numpy.array(accuracies).mean(0).T)
pyplot.ylim(0.9, 1)
pyplot.xlim(0,140)
pyplot.xlabel('batch (x 100)')
pyplot.ylabel('test accuracy')
pyplot.legend(ws)
def evaluate_for_weight_init(w)和for i in range(100):中期望一个缩进块,所以代码无法工作。请您检查一下。 - Mario