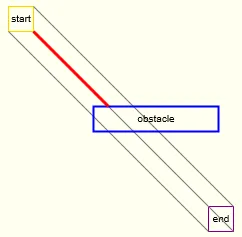
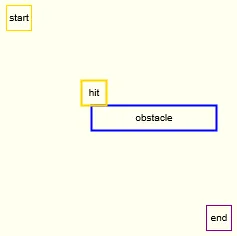
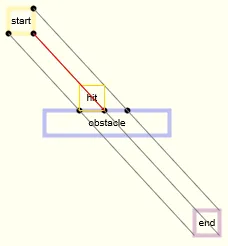
window.onload = function(){
var canvas = document.getElementById('game');
var ctx = canvas.getContext("2d");
var rightKeyPress = false;
var leftKeyPress = false;
var upKeyPress = false;
var downKeyPress = false;
var playerX = canvas.width / 2;
var playerY = -50;
var dx = 3;
var dy = 3;
var dxp = 3;
var dyp = 3;
var dxn = 3;
var dyn = 3;
var prevDxp = dxp;
var prevDyp = dyp;
var prevDxn = dxn;
var prevDyn = dyn;
var playerWidth = 50;
var playerHeight = 50;
var obstacleWidth = 150;
var obstacleHeight = 50;
var obstaclePadding = 10;
var G = .98;
var currentVelocity = 0;
var obstacles = [];
var imageLoaded = false;
document.addEventListener("keyup",keyUp,false);
document.addEventListener("keydown",keyDown,false);
function keyDown(e){
if(e.keyCode == 37){
leftKeyPress = true;
if(currentVelocity > 2){
currentVelocity -= .1;
}
}
if(e.keyCode == 38){
upKeyPress = true;
}
if(e.keyCode == 39){
rightKeyPress = true;
if(currentVelocity < 2){
currentVelocity += .1;
}
}
if(e.keyCode == 40){
downKeyPress = true;
}
}
function keyUp(e){
if(e.keyCode == 37){
leftKeyPress = false;
}
if(e.keyCode == 38){
upKeyPress = false;
}
if(e.keyCode == 39){
rightKeyPress = false;
}
if(e.keyCode == 40){
downKeyPress = false;
}
}
function createObstacles(){
for(x=0;x < 4;x++){
var obX = (200 * x) + Math.round(Math.random() * 150);
var obY = 50 + Math.round(Math.random() * 400);
obstacles.push({"x":obX,"y":obY});
}
}
createObstacles();
function drawObstacles(){
ctx.beginPath();
for(x=0;x < 4;x++){
var obX = obstacles[x].x;
var obY = obstacles[x].y;
ctx.rect(obX,obY,obstacleWidth,obstacleHeight)
}
ctx.fillStyle = "grey";
ctx.fill();
ctx.closePath();
}
function initPlayer(){
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.rect(playerX,playerY,50,50);
ctx.fillStyle="orange";
ctx.fill();
ctx.closePath();
}
function KeyPressAndGravity(){
checkObstacleCollision();
playerX += currentVelocity;
if(rightKeyPress && playerX + 50 < canvas.width){
playerX += dxp;
}
if(leftKeyPress && playerX > 0){
playerX -= dxn;
}
if(upKeyPress && playerY > 0){
playerY -= dyn;
}
if(downKeyPress && playerY + 50 < canvas.height){
playerY += dyp;
}
if(playerY+50 < canvas.height){
playerY += G;
}
if(playerX <= 0){
currentVelocity = 0;
}else if(playerX + 50 >= canvas.width){
currentVelocity = 0;
}
dxp = prevDxp;
dyp = prevDyp;
dxn = prevDxn;
dyn = prevDyn;
G = .98;
if(currentVelocity != 0){
if(currentVelocity > 0){
currentVelocity -= .01;
}else{
currentVelocity += .01;
}
}
}
/*-----------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
---------------------------Check this part-------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
-------------------------------------------------------------
------------------------------------------------------------*/
function checkObstacleCollision(){
var obLen = obstacles.length;
for(var x=0;x<obLen;x++){
var obX = obstacles[x].x;
var obY = obstacles[x].y;
if((playerX + playerWidth > obX && playerX + playerWidth < obX + obstacleWidth || playerX > obX && playerX < obX + obstacleWidth) && playerY + playerHeight > obY - obstaclePadding && playerY + playerHeight < obY){
dyp = 0;
G = 0;
}else if((playerX + playerWidth > obX && playerX + playerWidth < obX + obstacleWidth || playerX > obX && playerX < obX + obstacleWidth) && playerY > obY + obstacleHeight && playerY < obY + obstacleHeight + obstaclePadding){
dyn = 0;
}else if(playerX + playerWidth > obX - obstaclePadding && playerX + playerWidth < obX && ((playerY + playerHeight > obY && playerY + playerHeight < obY + obstacleHeight) || (playerY > obY && playerY < obY + obstacleHeight))){
dxp = 0;
}else if(playerX > obX + obstacleWidth && playerX < obX + obstacleWidth + obstaclePadding && ((playerY + playerHeight > obY && playerY + playerHeight < obY + obstacleHeight) || (playerY > obY && playerY < obY + obstacleHeight))){
dxn = 0;
}
}
}
function draw(){
ctx.clearRect(0,0,canvas.width,canvas.height);
initPlayer();
KeyPressAndGravity();
drawObstacles();
}
setInterval(draw,15);
}<canvas id="game" width="1000" height="600" style="border:1px solid #000;"></canvas>所以我的要求是,当玩家到达障碍物时,应该停止而不是通过它。