3个回答
40
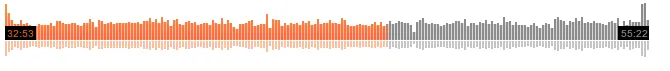
如果你只想要音频样本的可视化,那么可以不用使用库来实现这个功能。
public class PlayerVisualizerView extends View {
/**
* constant value for Height of the bar
*/
public static final int VISUALIZER_HEIGHT = 28;
/**
* bytes array converted from file.
*/
private byte[] bytes;
/**
* Percentage of audio sample scale
* Should updated dynamically while audioPlayer is played
*/
private float denseness;
/**
* Canvas painting for sample scale, filling played part of audio sample
*/
private Paint playedStatePainting = new Paint();
/**
* Canvas painting for sample scale, filling not played part of audio sample
*/
private Paint notPlayedStatePainting = new Paint();
private int width;
private int height;
public PlayerVisualizerView(Context context) {
super(context);
init();
}
public PlayerVisualizerView(Context context, @Nullable AttributeSet attrs) {
super(context, attrs);
init();
}
private void init() {
bytes = null;
playedStatePainting.setStrokeWidth(1f);
playedStatePainting.setAntiAlias(true);
playedStatePainting.setColor(ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), R.color.gray));
notPlayedStatePainting.setStrokeWidth(1f);
notPlayedStatePainting.setAntiAlias(true);
notPlayedStatePainting.setColor(ContextCompat.getColor(getContext(), R.color.colorAccent));
}
/**
* update and redraw Visualizer view
*/
public void updateVisualizer(byte[] bytes) {
this.bytes = bytes;
invalidate();
}
/**
* Update player percent. 0 - file not played, 1 - full played
*
* @param percent
*/
public void updatePlayerPercent(float percent) {
denseness = (int) Math.ceil(width * percent);
if (denseness < 0) {
denseness = 0;
} else if (denseness > width) {
denseness = width;
}
invalidate();
}
@Override
protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int left, int top, int right, int bottom) {
super.onLayout(changed, left, top, right, bottom);
width = getMeasuredWidth();
height = getMeasuredHeight();
}
@Override
protected void onDraw(Canvas canvas) {
super.onDraw(canvas);
if (bytes == null || width == 0) {
return;
}
float totalBarsCount = width / dp(3);
if (totalBarsCount <= 0.1f) {
return;
}
byte value;
int samplesCount = (bytes.length * 8 / 5);
float samplesPerBar = samplesCount / totalBarsCount;
float barCounter = 0;
int nextBarNum = 0;
int y = (height - dp(VISUALIZER_HEIGHT)) / 2;
int barNum = 0;
int lastBarNum;
int drawBarCount;
for (int a = 0; a < samplesCount; a++) {
if (a != nextBarNum) {
continue;
}
drawBarCount = 0;
lastBarNum = nextBarNum;
while (lastBarNum == nextBarNum) {
barCounter += samplesPerBar;
nextBarNum = (int) barCounter;
drawBarCount++;
}
int bitPointer = a * 5;
int byteNum = bitPointer / Byte.SIZE;
int byteBitOffset = bitPointer - byteNum * Byte.SIZE;
int currentByteCount = Byte.SIZE - byteBitOffset;
int nextByteRest = 5 - currentByteCount;
value = (byte) ((bytes[byteNum] >> byteBitOffset) & ((2 << (Math.min(5, currentByteCount) - 1)) - 1));
if (nextByteRest > 0) {
value <<= nextByteRest;
value |= bytes[byteNum + 1] & ((2 << (nextByteRest - 1)) - 1);
}
for (int b = 0; b < drawBarCount; b++) {
int x = barNum * dp(3);
float left = x;
float top = y + dp(VISUALIZER_HEIGHT - Math.max(1, VISUALIZER_HEIGHT * value / 31.0f));
float right = x + dp(2);
float bottom = y + dp(VISUALIZER_HEIGHT);
if (x < denseness && x + dp(2) < denseness) {
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, bottom, notPlayedStatePainting);
} else {
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, bottom, playedStatePainting);
if (x < denseness) {
canvas.drawRect(left, top, right, bottom, notPlayedStatePainting);
}
}
barNum++;
}
}
}
public int dp(float value) {
if (value == 0) {
return 0;
}
return (int) Math.ceil(getContext().getResources().getDisplayMetrics().density * value);
}
}
很抱歉,代码注释较少,但它是一个可工作的可视化程序。您可以将其附加到任何您想要的播放器中。
使用方法:将此视图添加到您的XML布局中,然后使用方法更新可视化状态。
public void updateVisualizer(byte[] bytes) {
playerVisualizerView.updateVisualizer(bytes);
}
public void updatePlayerProgress(float percent) {
playerVisualizerView.updatePlayerPercent(percent);
}
在 updateVisualizer 方法中,您传递了带有音频样本的字节数组,而在 updatePlayerProgress 中,当音频样本正在播放时,您会动态地传递百分比。
要将文件转换为字节数组,您可以使用此辅助方法。
public static byte[] fileToBytes(File file) {
int size = (int) file.length();
byte[] bytes = new byte[size];
try {
BufferedInputStream buf = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(file));
buf.read(bytes, 0, bytes.length);
buf.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return bytes;
}
以 Mosby 库为例(简单介绍):
public class AudioRecorderPresenter extends MvpBasePresenter<AudioRecorderView> {
public void onStopRecord() {
// stopped and released MediaPlayer
// ...
// some preparation and saved audio file in audioFileName variable.
getView().updateVisualizer(FileUtils.fileToBytes(new File(audioFileName)));
}
}
}
UPD: 我创建了一个库来解决这个问题github.com/scrobot/SoundWaveView。它仍处于“WIP”(正在进行中)状态,但很快我就会完成它。
- Scrobot
12
1谢谢,我该如何使用PlayerVisualizerView? - Hamed Ghadirian
1我认为你给出了最好的答案并授予+50奖励,但请添加更多细节并展示用法。 - Hamed Ghadirian
最好能够在每一行代码上进行注释并解释它,特别是字节移动的部分。 - Diego Fernando Murillo Valenci
1@KathanShah 你好!我正在处理这个问题)) 我收集了很多反馈,决定为此功能创建一个库) 因此,Android库将很快发布。)) 特别是,负面波也将被“装箱”。)) - Scrobot
@Scrobot - 我很乐意为你购买一杯咖啡/小吃来感谢你的这个库。越快越好。非常棒的工作。请提供你的联系方式,我有一些自由职业工作需要你的帮助。
谢谢。 - Kathan Shah
显示剩余7条评论
12
JETPACK COMPOSE
AudioWaveform是一个轻量级的Jetpack Compose库,用于绘制音频波形。
XML
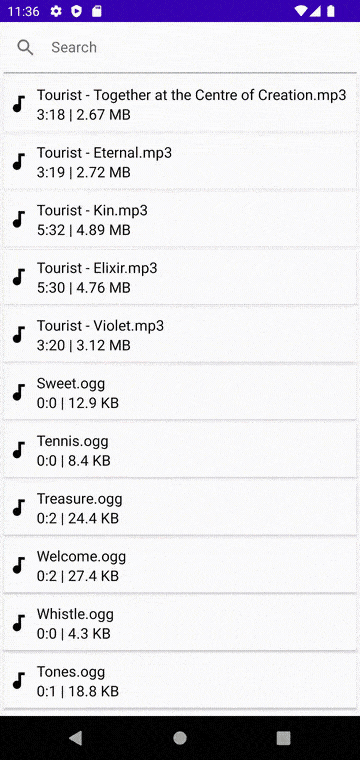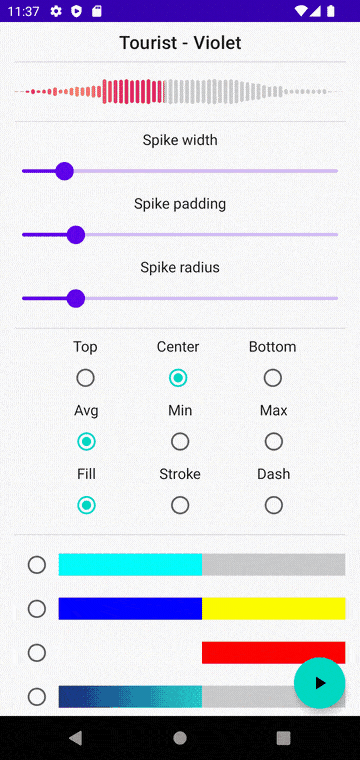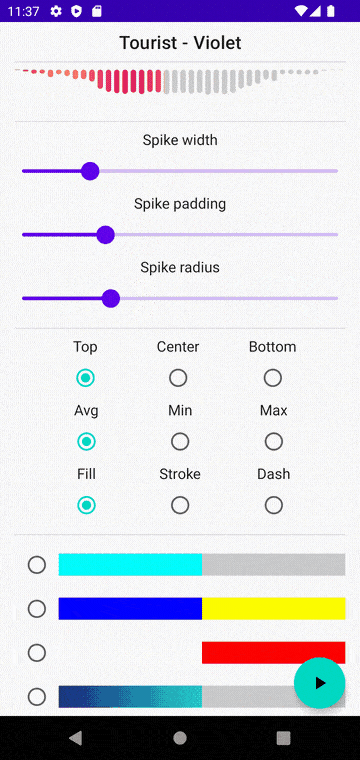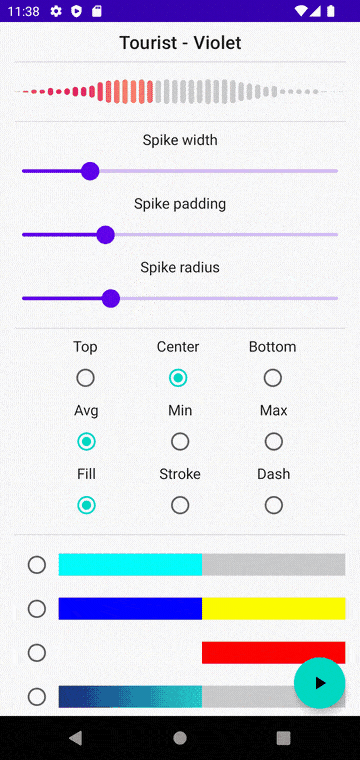
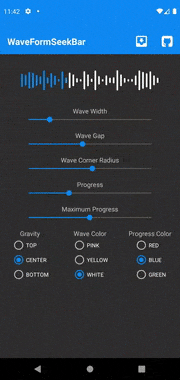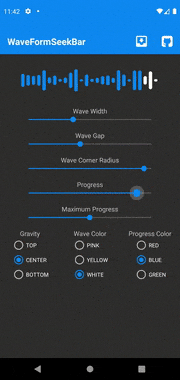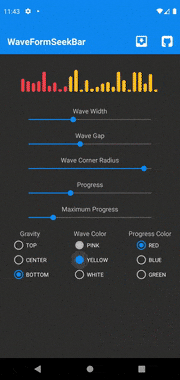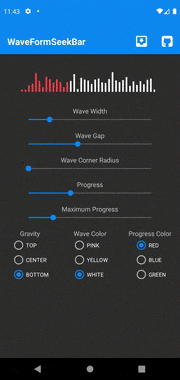
如果想要从本地音频文件、资源和URL绘制音频波形,使用 android.view.View (XML方式)的Android库WaveformSeekBar是一个不错的选择。
AUDIO PROCESSING
如果需要快速的音频处理库,可以使用现有的Amplituda库。 Amplituda还具备开箱即用的缓存和压缩功能。
- lincollincol
9
我认为Scrobot的回答不起作用。它假设输入音频采用某种(相当奇特的)编码方式(单声道/单声道线性PCM,5位深度)。从波函数计算振幅的算法可能存在缺陷。如果您将该算法与任何常用的音频文件格式一起使用,您将得到随机数据。
事实是:情况比那个稍微复杂一些。
以下是需要完成OP目标的步骤:
注意:RMS被认为是一种不太准确的响度测量方法。但它似乎能产生与你实际听到的某些相关结果。对于许多应用程序来说,这应该足够了。
事实是:情况比那个稍微复杂一些。
以下是需要完成OP目标的步骤:
- 使用Android的MediaExtractor读取输入音频文件(支持多种格式/编码)
- 使用Android的MediaCodec将输入音频编码解码为具有特定位深度(通常为16位)的线性PCM编码
- 只有在此步骤之后,您才能获得一个字节数组,您可以从中线性读取并计算振幅。
- 对PCM编码数据应用响度测量。有许多这样的测量方法,有些更复杂(例如LUFS / LKFS),有些更基本(RMS)。我们以RMS(=均方根)为例:
- 确定每个小节的样本数。
- 读取单个小节的所有样本。通常有2个通道,因此对于每个样本,您将获得PCM-16的2个短整数(16位)。
- 对于每个样本,计算所有通道的平均值。
- 也许您希望以某种方式规范化该值,例如获取介于-1和1之间的浮点值,您可以除以(2 /(1 << 16))
- 平方每个样本(因此是“ RMS”中的“ S”)
- 计算一条柱形图的所有样本的平均值(因此是“ RMS”中的“ M”)
- 计算结果值的平方根(因此是RMS中的R)
- 现在您可以基于该值确定柱形图的高度。
- 对所有小节重复步骤2-8。
注意:RMS被认为是一种不太准确的响度测量方法。但它似乎能产生与你实际听到的某些相关结果。对于许多应用程序来说,这应该足够了。
- aax
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接