我建立了一个广义加性混合效应模型,包括一个固定效应和随机截距效应(这是一个分类变量)。在运行模型后,我可以使用
是否有人可以帮助我从“gamm”类中提取我的随机截距的标准误差?我想使用随机截距和标准误差来绘制我的gamm模型的最佳线性无偏预测器。
我的初始模型的形式为:
ranef(m1$lme)$x[[1]]提取每个类别的随机截距。但是,当我尝试使用se.ranef(m1$lme)提取随机效应的标准误差时,该函数无法工作。尝试使用se.ranef(m1)和se.ranef(m1$gam)也不起作用。我不知道是否因为这些函数仅适用于lmer类的模型?是否有人可以帮助我从“gamm”类中提取我的随机截距的标准误差?我想使用随机截距和标准误差来绘制我的gamm模型的最佳线性无偏预测器。
我的初始模型的形式为:
gamm(y ~ s(z), random = list(x = ~1), data = dat)。library(mgcv)
library(arm)
example <- gamm(mag ~ s(depth), random = list(stations = ~1), data = quakes)
summary(example$gam)
#Family: gaussian
#Link function: identity
#Formula:
# mag ~ s(depth)
#Parametric coefficients:
# Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
#(Intercept) 5.02300 0.04608 109 <2e-16 ***
# ---
# Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#Approximate significance of smooth terms:
# edf Ref.df F p-value
#s(depth) 3.691 3.691 43.12 <2e-16 ***
# ---
# Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
#
#R-sq.(adj) = 0.0725
#Scale est. = 0.036163 n = 1000
ranef(example$lme)$stations[[1]] # extract random intercepts
#se.ranef(example$lme) # extract se of random intercepts - Problem line - doesn't work?
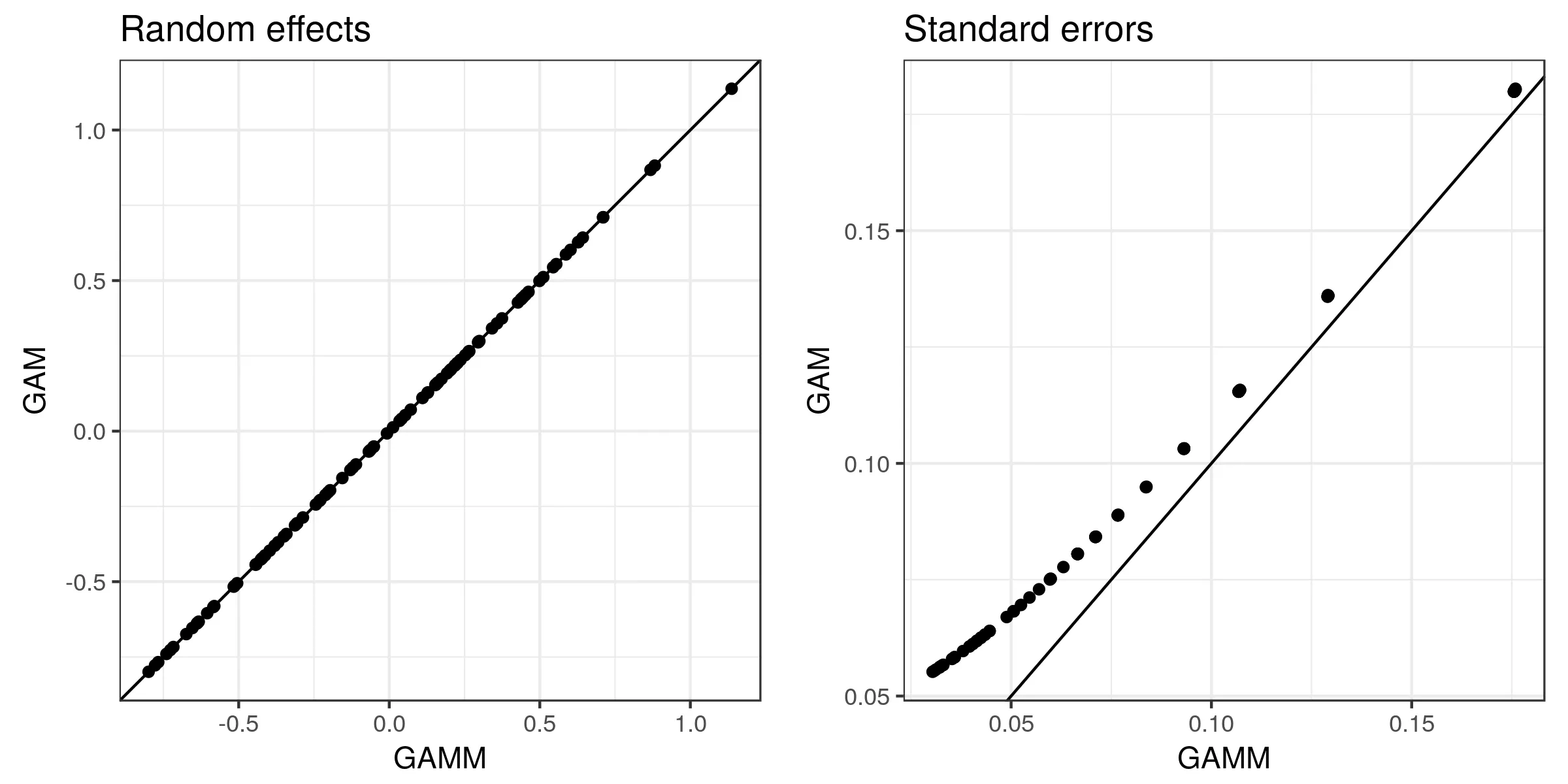
lme中随机效应值的标准误差的所有陈述都是正确的(在?ranef.lme或?intervals.lme中也没有提到可能性)。您可能希望评论一下为什么在“估计值”周围使用引号(即,随机效应的预测/BLUPs/条件模式不是以标准频率学意义上的估计值)。 - Ben Bolker