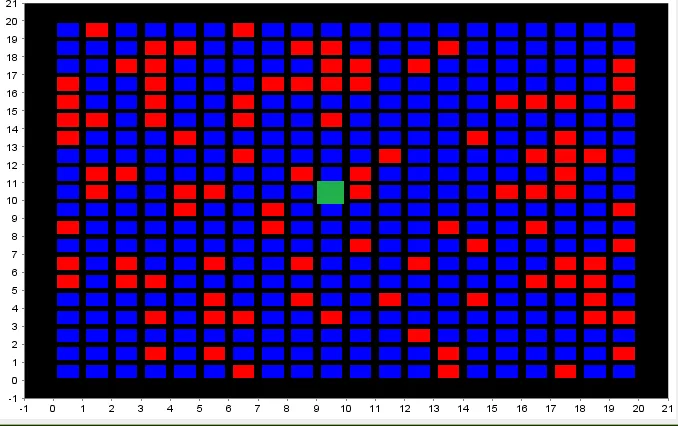
从绿色正方形开始,我希望有一个高效的算法来找到最近的3x3窗口,其中没有红色正方形,只有蓝色正方形。该算法不需要精确地找到最接近的3x3窗口,但它应该找到一个靠近绿色正方形的3x3全蓝窗口(假设存在这样的窗口)。我考虑将其实现为递归广度优先搜索,但该解决方案会涉及多次重新检查同一正方形。发布此内容以查看是否有人知道更有效的解决方案。检查给定正方形的成本是恒定且廉价的,但我希望尽可能减少算法的执行时间(将此实际应用于在更大的2D搜索区域内找到3x3“清除”/全蓝窗口)。
这是一个示例解决方案,但我认为它并不是最优的。实际上,这是一种深度优先搜索,我需要重新构建它以转换为广度优先搜索,但我需要再考虑一下如何做到这一点(一种方法是将每个点作为一个对象扩展到相邻点,然后多次迭代这些点到子节点,访问这些子节点,然后允许这些子节点生成更多的子节点)。重点是我认为有更有效和常见的方法来做到这一点,所以我试图避免重复造轮子。
public class Search2D {
private TreeSet<Point> centerpointscheckedsofar;
private Point Search(Point centerpoint) {
if(centerpointscheckedsofar.contains(centerpoint)) {
return null;
}
if(isWithinBounds(centerpoint)) {
if(checkCenterPoint(centerpoint)) {
centerpointscheckedsofar.add(centerpoint);
return null;
}
Point result = Search(getPoint(-1, -1, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
result = Search(getPoint(-1, 0, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
result = Search(getPoint(-1, 1, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
result = Search(getPoint(0, -1, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
result = Search(getPoint(0, 1, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
result = Search(getPoint(1, -1, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
result = Search(getPoint(1, 0, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
result = Search(getPoint(1, 1, centerpoint));
if(result != null) return result;
}
return null;
}
private Point getPoint(int x, int y, Point centerpoint) {
return new Point(centerpoint.x + x, centerpoint.y + y);
}
private boolean checkCenterPoint(Point centerpoint) {
//check here to see if point is valid
return false;
}
private boolean isWithinBounds(Point startPoint) {
//check here to see if point and all neighboring points of 3 x 3 window falls within bounds
return false;
}
}
更新: 距离度量并不是很重要,但为了简单起见,让我们最小化曼哈顿距离。
这是一个更好的算法,它不使用递归,并且保证能够找到最接近的解(如果有多个相同的解,则找到其中一个)。它需要一个大于5 x 5的网格才能正常工作,但如果您想搜索比那小的网格,则可能可以使用更有效的算法。假设最低的x索引为0,最低的y索引也为0。
import java.awt.Point;
public class Search2D_v2 {
private boolean[][] bitgrid;
public Search2D_v2() {
bitgrid = new boolean[20][20];
}
public Point search(int centerx, int centery, int maxx, int maxy, int maxsearchsteps) {
//check starting point first, if it works, we're done
if(checkPoint(centerx, centery)) {
return new Point(centerx, centery);
}
int westbound = centerx-1;
boolean keepgoingwest = true;
int eastbound = centerx+1;
boolean keepgoingeast = true;
int southbound = centery-1;
boolean keepgoingsouth = true;
int northbound = centery+1;
boolean keepgoingnorth = true;
//stay within bounds, may move initial search square by 1 east and 1 west
if(westbound <= 0) {
eastbound = 3;
westbound = 1;
}
if(eastbound >= maxx) {
eastbound = maxx - 1;
westbound = maxx - 3;
}
if(southbound == 0) {
northbound = 3;
southbound = 1;
}
if(northbound == maxy) {
northbound = maxy - 1;
southbound = maxy - 3;
}
//always search boundary, we've already searched inside the boundary on previous iterations, expand boundary by 1 step / square for each iteration
for(int i = 0; i < maxsearchsteps && (keepgoingwest || keepgoingeast || keepgoingsouth || keepgoingnorth); i++) {
//search top row
if(keepgoingnorth) { //if we have already hit the north bound, stop searching the top row
for(int x = westbound; x <= eastbound; x++) {
if(checkPoint(x, northbound)) {
return new Point(x, northbound);
}
}
}
//search bottom row
if(keepgoingsouth) {
for(int x = westbound; x <= eastbound; x++) {
if(checkPoint(x, southbound)) {
return new Point(x, southbound);
}
}
}
//search westbound
if(keepgoingwest) {
for(int y = southbound; y <= northbound; y++) {
if(checkPoint(westbound, northbound)) {
return new Point(westbound, y);
}
}
}
//search eastbound
if(keepgoingeast) {
for(int y = southbound; y <= northbound; y++) {
if(checkPoint(eastbound, northbound)) {
return new Point(eastbound, y);
}
}
}
//expand search area by one square on each side
if(westbound - 2 >= 0) {
westbound--;
}
else {
keepgoingwest = false;
}
if(eastbound + 2 <= maxx) {
eastbound++;
}
else {
keepgoingeast = false;
}
if(southbound - 2 >= 0) {
southbound--;
}
else {
keepgoingsouth = false;
}
if(northbound + 2 <= maxy) {
northbound++;
}
else {
keepgoingnorth = false;
}
}
return null; //failed to find a point
}
private boolean checkPoint(int centerx, int centery) {
return !bitgrid[centerx][centery] && //center
!bitgrid[centerx-1][centery-1] && //left lower
!bitgrid[centerx-1][centery] && //left middle
!bitgrid[centerx-1][centery+1] && //left upper
!bitgrid[centerx][centery-1] && //middle lower
!bitgrid[centerx][centery+1] && //middle upper
!bitgrid[centerx+1][centery-1] && //right lower
!bitgrid[centerx+1][centery] && //right middle
!bitgrid[centerx+1][centery+1]; //right upper
}
}