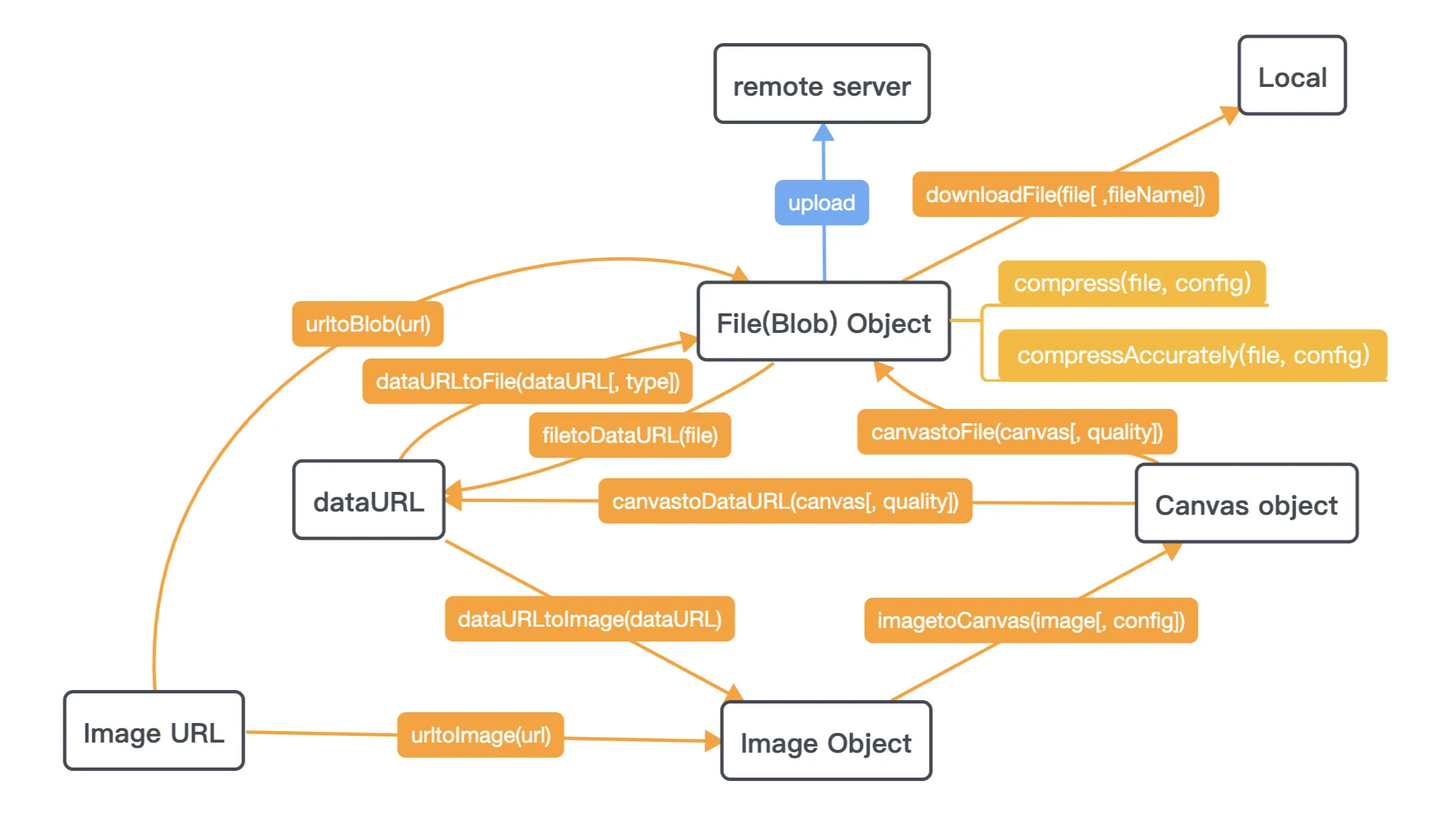
我在其他答案中发现了两个缺失的点:
canvas.toBlob(如果可用)比canvas.toDataURL更高效,而且是异步的。- 文件->图像->画布->文件转换会丢失EXIF数据;特别是由现代手机/平板电脑常见设置的有关图像旋转的数据。
以下脚本解决了这两个问题:
if (!HTMLCanvasElement.prototype.toBlob) {
Object.defineProperty(HTMLCanvasElement.prototype, 'toBlob', {
value: function(callback, type, quality) {
var binStr = atob(this.toDataURL(type, quality).split(',')[1]),
len = binStr.length,
arr = new Uint8Array(len);
for (var i = 0; i < len; i++) {
arr[i] = binStr.charCodeAt(i);
}
callback(new Blob([arr], {type: type || 'image/png'}));
}
});
}
window.URL = window.URL || window.webkitURL;
function getExifOrientation(file, callback) {
if (file.slice) {
file = file.slice(0, 131072);
} else if (file.webkitSlice) {
file = file.webkitSlice(0, 131072);
}
var reader = new FileReader();
reader.onload = function(e) {
var view = new DataView(e.target.result);
if (view.getUint16(0, false) != 0xFFD8) {
callback(-2);
return;
}
var length = view.byteLength, offset = 2;
while (offset < length) {
var marker = view.getUint16(offset, false);
offset += 2;
if (marker == 0xFFE1) {
if (view.getUint32(offset += 2, false) != 0x45786966) {
callback(-1);
return;
}
var little = view.getUint16(offset += 6, false) == 0x4949;
offset += view.getUint32(offset + 4, little);
var tags = view.getUint16(offset, little);
offset += 2;
for (var i = 0; i < tags; i++)
if (view.getUint16(offset + (i * 12), little) == 0x0112) {
callback(view.getUint16(offset + (i * 12) + 8, little));
return;
}
}
else if ((marker & 0xFF00) != 0xFF00) break;
else offset += view.getUint16(offset, false);
}
callback(-1);
};
reader.readAsArrayBuffer(file);
}
function imgToCanvasWithOrientation(img, rawWidth, rawHeight, orientation) {
var canvas = document.createElement('canvas');
if (orientation > 4) {
canvas.width = rawHeight;
canvas.height = rawWidth;
} else {
canvas.width = rawWidth;
canvas.height = rawHeight;
}
if (orientation > 1) {
console.log("EXIF orientation = " + orientation + ", rotating picture");
}
var ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
switch (orientation) {
case 2: ctx.transform(-1, 0, 0, 1, rawWidth, 0); break;
case 3: ctx.transform(-1, 0, 0, -1, rawWidth, rawHeight); break;
case 4: ctx.transform(1, 0, 0, -1, 0, rawHeight); break;
case 5: ctx.transform(0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0); break;
case 6: ctx.transform(0, 1, -1, 0, rawHeight, 0); break;
case 7: ctx.transform(0, -1, -1, 0, rawHeight, rawWidth); break;
case 8: ctx.transform(0, -1, 1, 0, 0, rawWidth); break;
}
ctx.drawImage(img, 0, 0, rawWidth, rawHeight);
return canvas;
}
function reduceFileSize(file, acceptFileSize, maxWidth, maxHeight, quality, callback) {
if (file.size <= acceptFileSize) {
callback(file);
return;
}
var img = new Image();
img.onerror = function() {
URL.revokeObjectURL(this.src);
callback(file);
};
img.onload = function() {
URL.revokeObjectURL(this.src);
getExifOrientation(file, function(orientation) {
var w = img.width, h = img.height;
var scale = (orientation > 4 ?
Math.min(maxHeight / w, maxWidth / h, 1) :
Math.min(maxWidth / w, maxHeight / h, 1));
h = Math.round(h * scale);
w = Math.round(w * scale);
var canvas = imgToCanvasWithOrientation(img, w, h, orientation);
canvas.toBlob(function(blob) {
console.log("Resized image to " + w + "x" + h + ", " + (blob.size >> 10) + "kB");
callback(blob);
}, 'image/jpeg', quality);
});
};
img.src = URL.createObjectURL(file);
}
示例用法:
inputfile.onchange = function() {
reduceFileSize(this.files[0], 500*1024, 1000, Infinity, 0.9, blob => {
let body = new FormData();
body.set('file', blob, blob.name || "file.jpg");
fetch('/upload-image', {method: 'POST', body}).then(...);
});
};