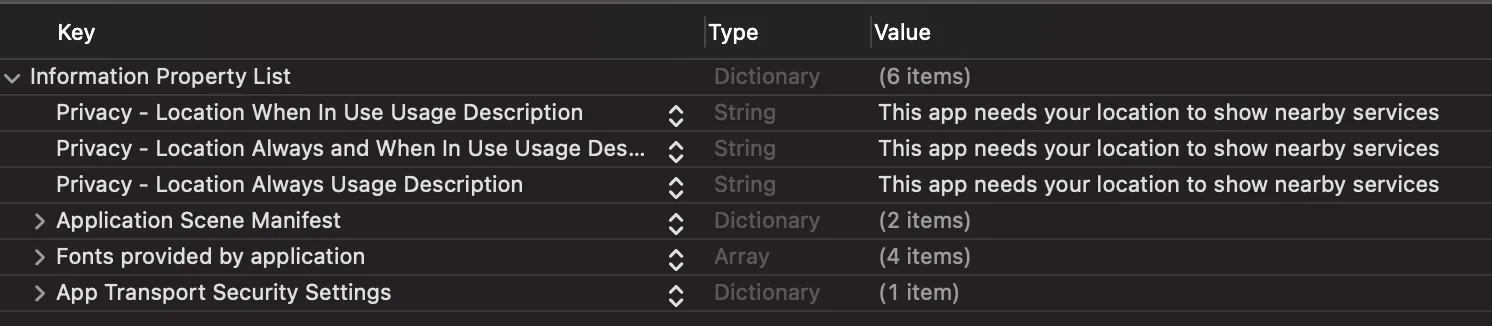
我想使用Swift获取一个位置的当前经纬度,并通过标签显示它们。我尝试过这样做,但标签上什么也没有显示。
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class ViewController: UIViewController, CLLocationManagerDelegate{
@IBOutlet weak var longitude: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var latitude: UILabel!
let locationManager = CLLocationManager()
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
if (CLLocationManager.locationServicesEnabled()) {
locationManager.delegate = self
locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyBest
locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
} else {
println("Location services are not enabled");
}
}
// MARK: - CoreLocation Delegate Methods
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager!, didFailWithError error: NSError!) {
locationManager.stopUpdatingLocation()
removeLoadingView()
if (error) != nil {
print(error)
}
}
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager!, didUpdateLocations locations: [AnyObject]!) {
var locationArray = locations as NSArray
var locationObj = locationArray.lastObject as CLLocation
var coord = locationObj.coordinate
longitude.text = coord.longitude
latitude.text = coord.latitude
longitude.text = "\(coord.longitude)"
latitude.text = "\(coord.latitude)"
}
}