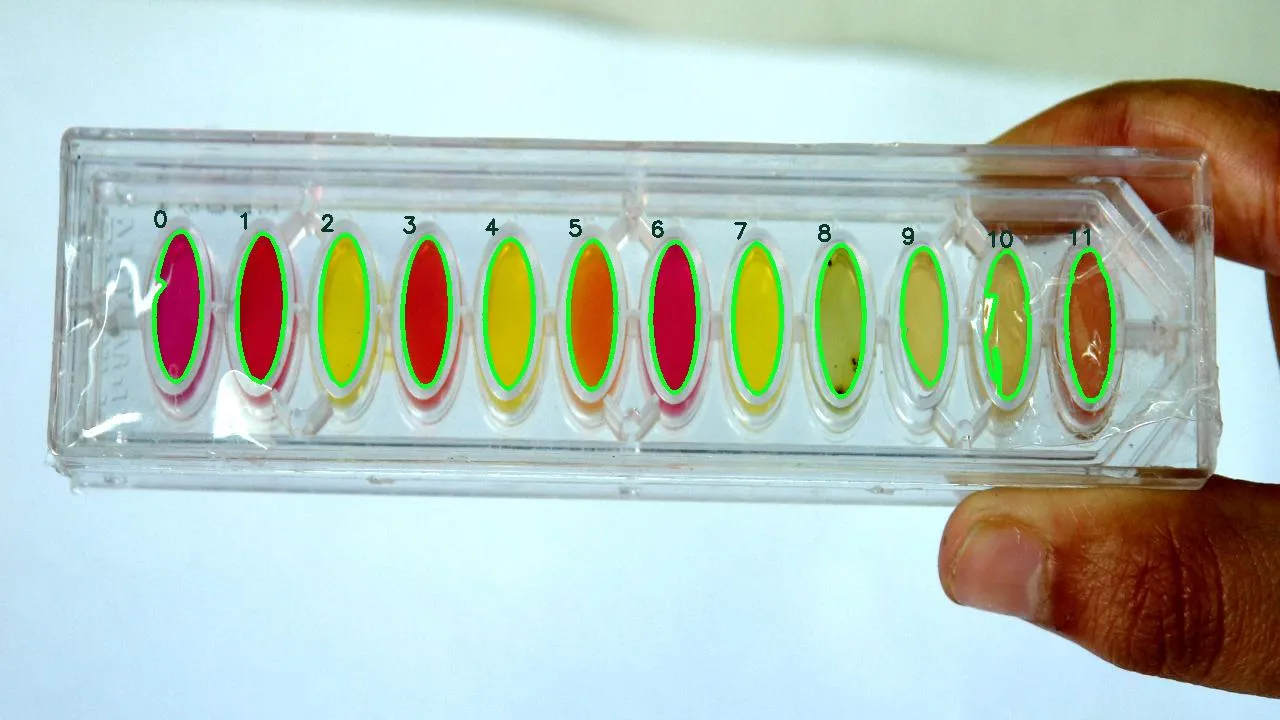
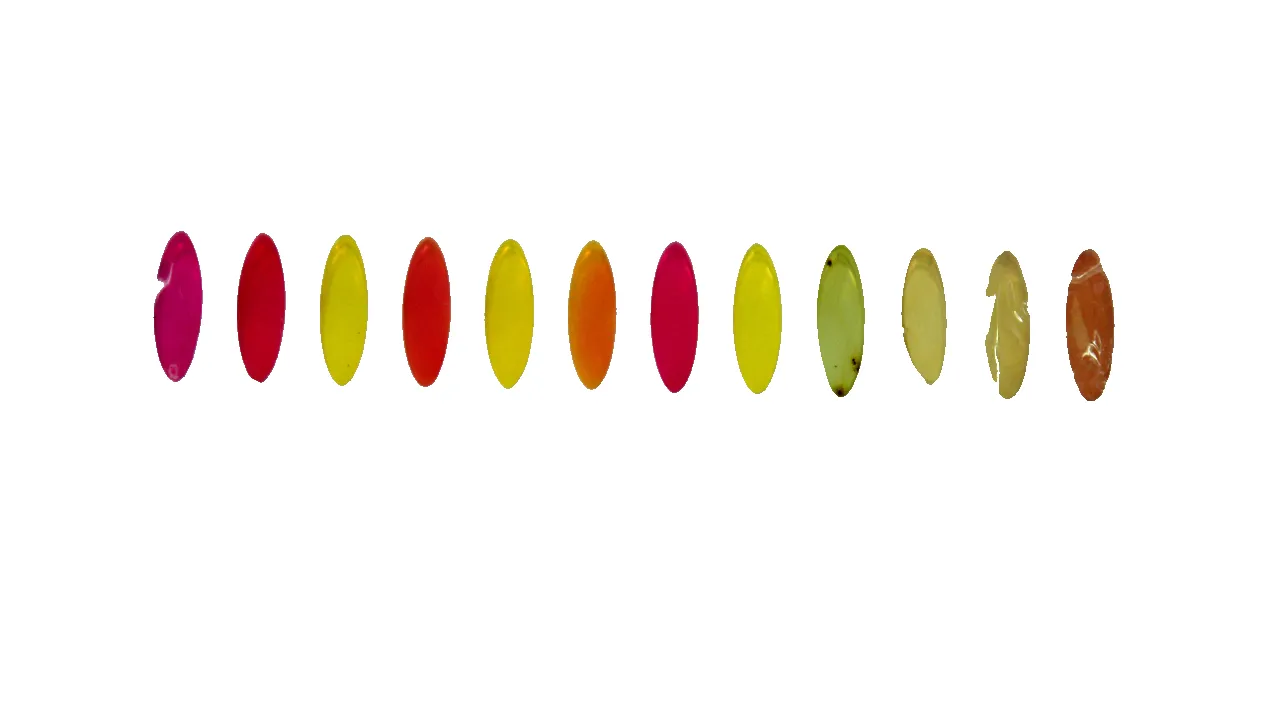
我需要从图像中提取12个椭圆形,并将它们分别存储在变量1到12中。
原始图片如下:
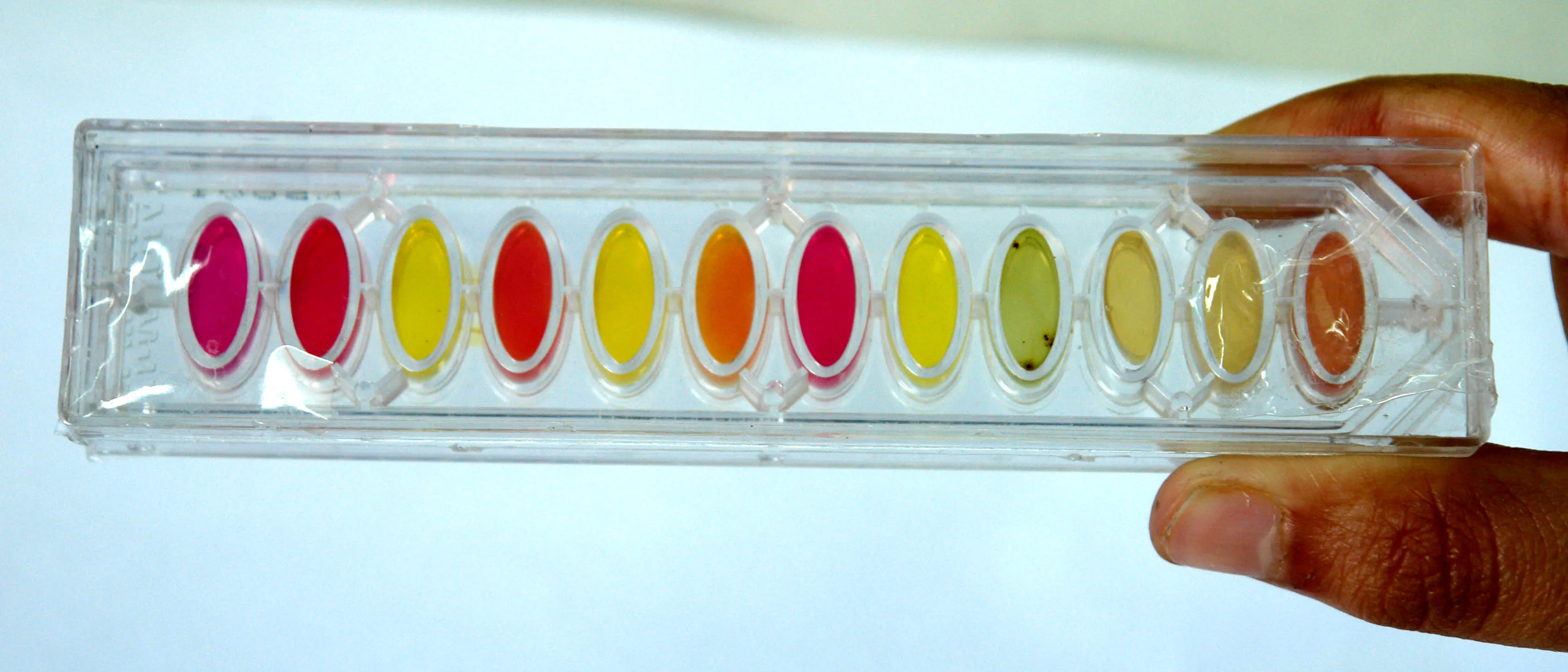

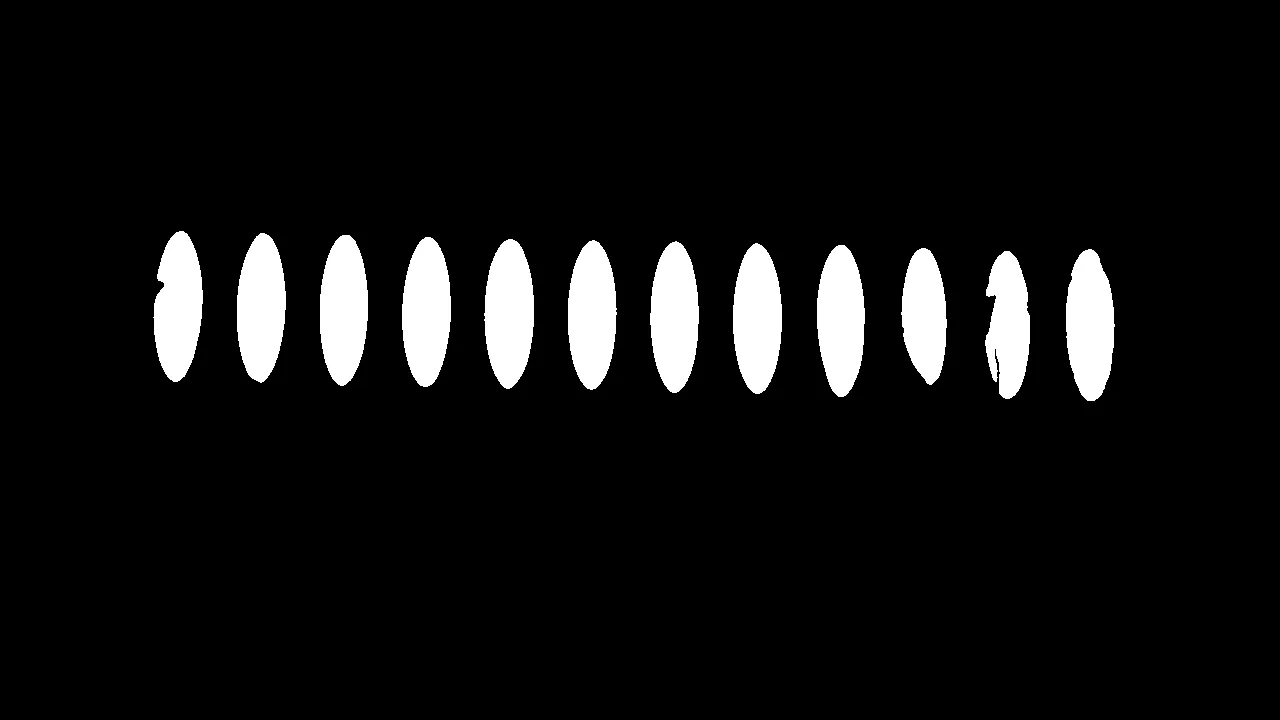
输出图片如下:

有人能帮助我将所有这些椭圆形提取到不同的变量中吗?
我的代码是:
import cv2
import numpy as np
path = r'/home/parallels/Desktop/Opencv/data/test.JPG'
i = cv2.imread(path, -1)
img_rgb = cv2.resize(i, (1280,720))
cv2.namedWindow("Original Image",cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
img = cv2.cvtColor(img_rgb, cv2.COLOR_RGB2HSV)
img = cv2.bilateralFilter(img,9,105,105)
r,g,b=cv2.split(img)
equalize1= cv2.equalizeHist(r)
equalize2= cv2.equalizeHist(g)
equalize3= cv2.equalizeHist(b)
equalize=cv2.merge((r,g,b))
equalize = cv2.cvtColor(equalize,cv2.COLOR_RGB2GRAY)
ret,thresh_image = cv2.threshold(equalize,0,255,cv2.THRESH_OTSU+cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
equalize= cv2.equalizeHist(thresh_image)
canny_image = cv2.Canny(equalize,250,255)
canny_image = cv2.convertScaleAbs(canny_image)
kernel = np.ones((3,3), np.uint8)
dilated_image = cv2.dilate(canny_image,kernel,iterations=1)
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(dilated_image, cv2.RETR_TREE, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
contours= sorted(contours, key = cv2.contourArea, reverse = True)[:10]
c=contours[0]
print(cv2.contourArea(c))
final = cv2.drawContours(img, [c], -1, (255,0, 0), 3)
mask = np.zeros(img_rgb.shape,np.uint8)
new_image = cv2.drawContours(mask,[c],0,255,-1,)
new_image = cv2.bitwise_and(img_rgb, img_rgb, mask=equalize)
cv2.namedWindow("new",cv2.WINDOW_NORMAL)
cv2.imshow("new",new_image)
cv2.waitKey(0)