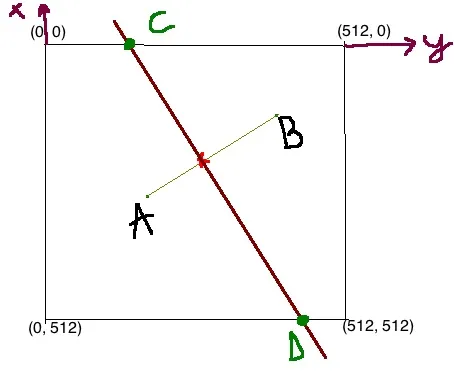
整整一天我都在试图理解这个问题...
基本上,我有两个点的坐标,它们总是在矩形内部。我还知道矩形四个角的位置。这两个点是在运行时给定的。
我需要一个算法来找到这条线段的平分线与矩形相交的2个点。
以下是一些细节:
在上图中,A和B由它们的坐标给出:A(x1, y1)和B(x2, y2)。基本上,我需要找到C和D的位置。 红色X是AB线段的中心点。这个点(让我们称之为中心)必须位于CD线上。
我的做法:
found the center:
center.x = (A.x+B.x)/2; center.y = (A.y+B.y)/2;found CD slope:
AB_slope = A.y - B.y / A.x - B.x; CD_slope = -1/AB_slope;
我知道中心和CD斜率后,得到了CD的方程,然后尝试通过在矩形的4个边界上尝试点的位置来找到解决方案。 但是,出于某种原因它不起作用:每次当我有一个解决方案,比如对于C,D就会被绘制在外面,反之亦然。
以下是我使用的方程:
knowing x:
y = (CD_slope * (x - center.x)) + center.y; if y > 0 && y < 512: #=> solution found!knowing y:
x = (y - center.y + CD_slope*center.x)/CD_slope; if x > 0 && x < 512: #=> solution found!
从这里,我还可以得到另一条线段(假设我已经找到了C并知道中心),但是几何学无法帮助我找到这条线段的延伸,直到它与矩形的另一侧相交。
更新以包括代码片段
(请参见主函数中的注释)
typedef struct { double x; double y; } Point;
Point calculate_center(Point p1, Point p2) {
Point point;
point.x = (p1.x+p2.x)/2;
point.y = (p1.y+p2.y)/2;
return point;
}
double calculate_pslope(Point p1, Point p2) {
double dy = p1.y - p2.y;
double dx = p1.x - p2.x;
double slope = dy/dx; // this is p1 <-> p2 slope
return -1/slope;
}
int calculate_y_knowing_x(double pslope, Point center, double x, Point *point) {
double min= 0.00;
double max= 512.00;
double y = (pslope * (x - center.x)) + center.y;
if(y >= min && y <= max) {
point->x = corner;
point->y = y;
printf("++> found Y for X, point is P(%f, %f)\n", point->x, point->y);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int calculate_x_knowing_y(double pslope, Point center, double y, Point *point) {
double min= 0.00;
double max= 512.00;
double x = (y - center.y + pslope*center.x)/pslope;
if(x >= min && x <= max) {
point->x = x;
point->y = y;
printf("++> found X for Y, point is: P(%f, %f)\n", point->x, point->y);
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv) {
Point A, B;
// parse argv and define A and B
// this code is omitted here, let's assume:
// A.x = 175.00;
// A.y = 420.00;
// B.x = 316.00;
// B.y = 62.00;
Point C;
Point D;
Point center;
double pslope;
center = calculate_center(A, B);
pslope = calculate_pslope(A, B);
// Here's where the fun happens:
// I'll need to find the right succession of calls to calculate_*_knowing_*
// for 4 cases: x=0, X=512 #=> call calculate_y_knowing_x
// y=0, y=512 #=> call calculate_x_knowing_y
// and do this 2 times for both C and D points.
// Also, if point C is found, point D should not be on the same side (thus C != D)
// for the given A and B points the succession is:
calculate_y_knowing_x(pslope, center, 0.00, C);
calculate_y_knowing_x(pslope, center, 512.00, D);
// will yield: C(0.00, 144.308659), D(512.00, 345.962291)
// But if A(350.00, 314.00) and B(106.00, 109.00)
// the succesion should be:
// calculate_y_knowing_x(pslope, center, 0.00, C);
// calculate_x_knowing_y(pslope, center, 512.00, D);
// to yield C(0.00, 482.875610) and D(405.694672, 0.00)
return 0;
}
这是C代码。
注:
- 图片是手绘的。
- 坐标系逆时针旋转90度,但不会对解决方案产生影响。
- 我需要用C语言编写算法,但我也可以阅读其他编程语言。
- 这是一个二维问题。