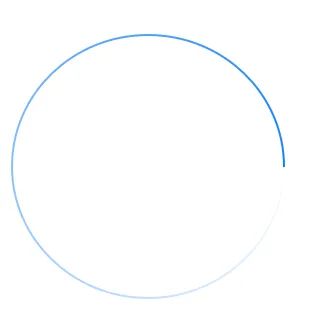
如何用渐变色描绘圆形路径
15
- venj
2
如果您需要这样做,那么我可以帮助您:https://dev59.com/VmIj5IYBdhLWcg3wGRmM - Jitendra Modi
@Jecky 感谢您的评论。我查看了您提供的链接和 CAGradientLayer API,发现它仅支持线性渐变。但是实现上述图片中显示的渐变似乎很困难。请帮忙! - venj
4个回答
25
在macOS 10.14及以上版本(以及iOS 12及以上版本),您可以创建一个
CAGradientLayer,其type为.conic,然后使用圆弧进行遮罩。例如,在macOS中:class GradientArcView: NSView {
var startColor: NSColor = .white { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
var endColor: NSColor = .blue { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
var lineWidth: CGFloat = 3 { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
private let gradientLayer: CAGradientLayer = {
let gradientLayer = CAGradientLayer()
gradientLayer.type = .conic
gradientLayer.startPoint = CGPoint(x: 0.5, y: 0.5)
gradientLayer.endPoint = CGPoint(x: 1, y: 0.5)
return gradientLayer
}()
override init(frame: CGRect = .zero) {
super.init(frame: frame)
configure()
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: aDecoder)
configure()
}
override func layout() {
super.layout()
updateGradient()
}
}
private extension GradientArcView {
func configure() {
wantsLayer = true
layer?.addSublayer(gradientLayer)
}
func updateGradient() {
gradientLayer.frame = bounds
gradientLayer.colors = [startColor, endColor].map { $0.cgColor }
let radius = (min(bounds.width, bounds.height) - lineWidth) / 2
let path = CGPath(ellipseIn: bounds.insetBy(dx: bounds.width / 2 - radius, dy: bounds.height / 2 - radius), transform: nil)
let mask = CAShapeLayer()
mask.fillColor = NSColor.clear.cgColor
mask.strokeColor = NSColor.white.cgColor
mask.lineWidth = lineWidth
mask.path = path
gradientLayer.mask = mask
}
}
或者,在iOS中:
@IBDesignable
class GradientArcView: UIView {
@IBInspectable var startColor: UIColor = .white { didSet { setNeedsLayout() } }
@IBInspectable var endColor: UIColor = .blue { didSet { setNeedsLayout() } }
@IBInspectable var lineWidth: CGFloat = 3 { didSet { setNeedsLayout() } }
private let gradientLayer: CAGradientLayer = {
let gradientLayer = CAGradientLayer()
gradientLayer.type = .conic
gradientLayer.startPoint = CGPoint(x: 0.5, y: 0.5)
gradientLayer.endPoint = CGPoint(x: 1, y: 0.5)
return gradientLayer
}()
override init(frame: CGRect = .zero) {
super.init(frame: frame)
configure()
}
required init?(coder aDecoder: NSCoder) {
super.init(coder: aDecoder)
configure()
}
override func layoutSubviews() {
super.layoutSubviews()
updateGradient()
}
}
private extension GradientArcView {
func configure() {
layer.addSublayer(gradientLayer)
}
func updateGradient() {
gradientLayer.frame = bounds
gradientLayer.colors = [startColor, endColor].map { $0.cgColor }
let center = CGPoint(x: bounds.midX, y: bounds.midY)
let radius = (min(bounds.width, bounds.height) - lineWidth) / 2
let path = UIBezierPath(arcCenter: center, radius: radius, startAngle: 0, endAngle: 2 * .pi, clockwise: true)
let mask = CAShapeLayer()
mask.fillColor = UIColor.clear.cgColor
mask.strokeColor = UIColor.white.cgColor
mask.lineWidth = lineWidth
mask.path = path.cgPath
gradientLayer.mask = mask
}
}
在早期的操作系统版本中,你需要手动完成一些工作,例如用不同颜色描绘一系列弧线。例如,在 macOS 中:
import Cocoa
/// This draws an arc, of length `maxAngle`, ending at `endAngle. This is `@IBDesignable`, so if you
/// put this in a separate framework target, you can use this class in Interface Builder. The only
/// property that is not `@IBInspectable` is the `lineCapStyle` (as IB doesn't know how to show that).
///
/// If you want to make this animated, just use a `CADisplayLink` update the `endAngle` property (and
/// this will automatically re-render itself whenever you change that property).
@IBDesignable
class GradientArcView: NSView {
/// Width of the stroke.
@IBInspectable var lineWidth: CGFloat = 3 { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
/// Color of the stroke (at full alpha, at the end).
@IBInspectable var strokeColor: NSColor = .blue { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
/// Where the arc should end, measured in degrees, where 0 = "3 o'clock".
@IBInspectable var endAngle: CGFloat = 0 { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
/// What is the full angle of the arc, measured in degrees, e.g. 180 = half way around, 360 = all the way around, etc.
@IBInspectable var maxAngle: CGFloat = 360 { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
/// What is the shape at the end of the arc.
var lineCapStyle: NSBezierPath.LineCapStyle = .square { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
override func draw(_ dirtyRect: NSRect) {
super.draw(dirtyRect)
let gradations = 255
let startAngle = -endAngle + maxAngle
let center = NSPoint(x: bounds.midX, y: bounds.midY)
let radius = (min(bounds.width, bounds.height) - lineWidth) / 2
var angle = startAngle
for i in 1 ... gradations {
let percent = CGFloat(i) / CGFloat(gradations)
let endAngle = startAngle - percent * maxAngle
let path = NSBezierPath()
path.lineWidth = lineWidth
path.lineCapStyle = lineCapStyle
path.appendArc(withCenter: center, radius: radius, startAngle: angle, endAngle: endAngle, clockwise: true)
strokeColor.withAlphaComponent(percent).setStroke()
path.stroke()
angle = endAngle
}
}
}
- Rob
3
这是一个很好的想法。谢谢你。我会尝试一下。 - venj
答案涉及macOS的实现。我能否在iOS中将NSView替换为UIView? - Hans Bondoka
1@HansBondoka -
NSView 与 UIView,NSBezierPath 与 UIBezierPath,layout 与 layoutSubviews 等等。有许多微小的语法差异,但它们基本上是相同的。我已经修改了我的答案,添加了第一个锥形渐变层实现的 iOS 版本。你可以看到它们之间的相似之处。后面例子的翻译也很简单,但我会留给读者自行理解。原始问题虽然标记了两个平台,但提到了 NSBezierPath 等等,所以我专注于 macOS 的版本。希望 Marzipan 能够让这种愚蠢的事情过去。 - Rob13
这是一些对我有效的代码。其中有一些动画,但您可以使用相同的原理来使渐变具有“strokeEnd”。
A. 创建一个自定义视图'Donut'并将其放在标题中:
@interface Donut : UIView
@property UIColor * fromColour;
@property UIColor * toColour;
@property UIColor * baseColour;
@property float lineWidth;
@property float duration;
-(void)layout;
-(void)animateTo:(float)percentage;
B. 然后进行了基本的视图设置,并编写了这两种方法:
-(void)layout{
//vars
float dimension = self.frame.size.width;
//1. layout views
//1.1 layout base track
UIBezierPath * donut = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithOvalInRect:CGRectMake(lineWidth/2, lineWidth/2, dimension-lineWidth, dimension-lineWidth)];
CAShapeLayer * baseTrack = [CAShapeLayer layer];
baseTrack.path = donut.CGPath;
baseTrack.lineWidth = lineWidth;
baseTrack.fillColor = [UIColor clearColor].CGColor;
baseTrack.strokeStart = 0.0f;
baseTrack.strokeEnd = 1.0f;
baseTrack.strokeColor = baseColour.CGColor;
baseTrack.lineCap = kCALineCapButt;
[self.layer addSublayer:baseTrack];
//1.2 clipView has mask applied to it
UIView * clipView = [UIView new];
clipView.frame = self.bounds;
[self addSubview:clipView];
//1.3 rotateView transforms with strokeEnd
rotateView = [UIView new];
rotateView.frame = self.bounds;
[clipView addSubview:rotateView];
//1.4 radialGradient holds an image of the colours
UIImageView * radialGradient = [UIImageView new];
radialGradient.frame = self.bounds;
[rotateView addSubview:radialGradient];
//2. create colours fromColour --> toColour and add to an array
//2.1 holds all colours between fromColour and toColour
NSMutableArray * spectrumColours = [NSMutableArray new];
//2.2 get RGB values for both colours
double fR, fG, fB; //fromRed, fromGreen etc
double tR, tG, tB; //toRed, toGreen etc
[fromColour getRed:&fR green:&fG blue:&fB alpha:nil];
[toColour getRed:&tR green:&tG blue:&tB alpha:nil];
//2.3 determine increment between fromRed and toRed etc.
int numberOfColours = 360;
double dR = (tR-fR)/(numberOfColours-1);
double dG = (tG-fG)/(numberOfColours-1);
double dB = (tB-fB)/(numberOfColours-1);
//2.4 loop through adding incrementally different colours
//this is a gradient fromColour --> toColour
for (int n = 0; n < numberOfColours; n++){
[spectrumColours addObject:[UIColor colorWithRed:(fR+n*dR) green:(fG+n*dG) blue:(fB+n*dB) alpha:1.0f]];
}
//3. create a radial image using the spectrum colours
//go through adding the next colour at an increasing angle
//3.1 setup
float radius = MIN(dimension, dimension)/2;
float angle = 2 * M_PI/numberOfColours;
UIBezierPath * bezierPath;
CGPoint center = CGPointMake(dimension/2, dimension/2);
UIGraphicsBeginImageContextWithOptions(CGSizeMake(dimension, dimension), true, 0.0);
UIRectFill(CGRectMake(0, 0, dimension, dimension));
//3.2 loop through pulling the colour and adding
for (int n = 0; n<numberOfColours; n++){
UIColor * colour = spectrumColours[n]; //colour for increment
bezierPath = [UIBezierPath bezierPathWithArcCenter:center radius:radius startAngle:n * angle endAngle:(n + 1) * angle clockwise:YES];
[bezierPath addLineToPoint:center];
[bezierPath closePath];
[colour setFill];
[colour setStroke];
[bezierPath fill];
[bezierPath stroke];
}
//3.3 create image, add to the radialGradient and end
[radialGradient setImage:UIGraphicsGetImageFromCurrentImageContext()];
UIGraphicsEndImageContext();
//4. create a dot to add to the rotating view
//this covers the connecting line between the two colours
//4.1 set up vars
float containsDots = (M_PI * dimension) /*circumference*/ / lineWidth; //number of dots in circumference
float colourIndex = roundf((numberOfColours / containsDots) * (containsDots-0.5f)); //the nearest colour for the dot
UIColor * closestColour = spectrumColours[(int)colourIndex]; //the closest colour
//4.2 create dot
UIImageView * dot = [UIImageView new];
dot.frame = CGRectMake(dimension-lineWidth, (dimension-lineWidth)/2, lineWidth, lineWidth);
dot.layer.cornerRadius = lineWidth/2;
dot.backgroundColor = closestColour;
[rotateView addSubview:dot];
//5. create the mask
mask = [CAShapeLayer layer];
mask.path = donut.CGPath;
mask.lineWidth = lineWidth;
mask.fillColor = [UIColor clearColor].CGColor;
mask.strokeStart = 0.0f;
mask.strokeEnd = 0.0f;
mask.strokeColor = [UIColor blackColor].CGColor;
mask.lineCap = kCALineCapRound;
//5.1 apply the mask and rotate all by -90 (to move to the 12 position)
clipView.layer.mask = mask;
clipView.transform = CGAffineTransformMakeRotation(DEGREES_TO_RADIANS(-90.0f));
}
-(void)animateTo:(float)percentage {
float difference = fabsf(fromPercentage - percentage);
float fixedDuration = difference * duration;
//1. animate stroke End
CABasicAnimation * strokeEndAnimation = [CABasicAnimation animationWithKeyPath:@"strokeEnd"];
strokeEndAnimation.duration = fixedDuration;
strokeEndAnimation.fromValue = @(fromPercentage);
strokeEndAnimation.toValue = @(percentage);
strokeEndAnimation.fillMode = kCAFillModeForwards;
strokeEndAnimation.removedOnCompletion = false;
strokeEndAnimation.timingFunction = [CAMediaTimingFunction functionWithName:kCAMediaTimingFunctionLinear];
[mask addAnimation:strokeEndAnimation forKey:@"strokeEndAnimation"];
//2. animate rotation of rotateView
CABasicAnimation * viewRotationAnimation = [CABasicAnimation animationWithKeyPath:@"transform.rotation.z"];
viewRotationAnimation.duration = fixedDuration;
viewRotationAnimation.fromValue = @(DEGREES_TO_RADIANS(360 * fromPercentage));
viewRotationAnimation.toValue = @(DEGREES_TO_RADIANS(360 * percentage));
viewRotationAnimation.fillMode = kCAFillModeForwards;
viewRotationAnimation.removedOnCompletion = false;
viewRotationAnimation.timingFunction = [CAMediaTimingFunction functionWithName:kCAMediaTimingFunctionLinear];
[rotateView.layer addAnimation:viewRotationAnimation forKey:@"viewRotationAnimation"];
//3. update from percentage
fromPercentage = percentage;
}
C. 创建视图:
Donut * donut = [Donut new];
donut.frame = CGRectMake(20, 100, 140, 140);
donut.baseColour = [[UIColor blackColor] colorWithAlphaComponent:0.2f];
donut.fromColour = [UIColor redColor];
donut.toColour = [UIColor blueColor];
donut.lineWidth = 20.0f;
donut.duration = 2.0f;
[donut layout];
[tasteView addSubview:donut];
D. 动画视图:
[donut animateTo:0.5f];
当掩码的strokeEnd发生变化时,它下面的视图“rotateView”也会随之旋转。这给人留下了线条正在增长/缩小的印象,只要它们同步。
#define DEGREES_TO_RADIANS(x) (M_PI * (x) / 180.0)
- Johnny Rockex
3
由于您的路径是一个圆,您所要求的就是一种角度梯度,也就是说,随着我们在饼图周围扫过一个半径,它会改变颜色的一种饼图。没有内置的方法可以做到这一点,但有一个很棒的库可以为您完成:https://github.com/paiv/AngleGradientLayer。诀窍在于,您将角度梯度与其中心绘制在圆的中心,并在其上放置一个蒙版,以使其仅出现在您的圆形描边应该出现的位置。
- matt
1
这看起来是一个很有前途的解决方案!非常感谢你。 - venj
2
使用以下代码。测试通过并可在iOS10+上运行。
import UIKit
class MMTGradientArcView: UIView {
var lineWidth: CGFloat = 3 { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
var startColor = UIColor.green { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
var endColor = UIColor.clear { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
var startAngle:CGFloat = 0 { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
var endAngle:CGFloat = 360 { didSet { setNeedsDisplay(bounds) } }
override func draw(_ rect: CGRect) {
let gradations = 289 //My School Number
var startColorR:CGFloat = 0
var startColorG:CGFloat = 0
var startColorB:CGFloat = 0
var startColorA:CGFloat = 0
var endColorR:CGFloat = 0
var endColorG:CGFloat = 0
var endColorB:CGFloat = 0
var endColorA:CGFloat = 0
startColor.getRed(&startColorR, green: &startColorG, blue: &startColorB, alpha: &startColorA)
endColor.getRed(&endColorR, green: &endColorG, blue: &endColorB, alpha: &endColorA)
let startAngle:CGFloat = 0
let endAngle:CGFloat = 270
let center = CGPoint(x: bounds.midX, y: bounds.midY)
let radius = (min(bounds.width, bounds.height) - lineWidth) / 2
var angle = startAngle
for i in 1 ... gradations {
let extraAngle = (endAngle - startAngle) / CGFloat(gradations)
let currentStartAngle = angle
let currentEndAngle = currentStartAngle + extraAngle
let currentR = ((endColorR - startColorR) / CGFloat(gradations - 1)) * CGFloat(i - 1) + startColorR
let currentG = ((endColorG - startColorG) / CGFloat(gradations - 1)) * CGFloat(i - 1) + startColorG
let currentB = ((endColorB - startColorB) / CGFloat(gradations - 1)) * CGFloat(i - 1) + startColorB
let currentA = ((endColorA - startColorA) / CGFloat(gradations - 1)) * CGFloat(i - 1) + startColorA
let currentColor = UIColor.init(red: currentR, green: currentG, blue: currentB, alpha: currentA)
let path = UIBezierPath()
path.lineWidth = lineWidth
path.lineCapStyle = .round
path.addArc(withCenter: center, radius: radius, startAngle: currentStartAngle * CGFloat(Double.pi / 180.0), endAngle: currentEndAngle * CGFloat(Double.pi / 180.0), clockwise: true)
currentColor.setStroke()
path.stroke()
angle = currentEndAngle
}
}
}
- santhu
1
在我看来,这是唯一真正的答案(即使它是一个棘手的方式)。即使循环进度超过单个旋转(例如
endAngle可能是400),它也能正常工作。 - superpuccio网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接