我在鼠标进入/离开事件上遇到了问题。当鼠标按钮被按下并保持在控件内部时,如果光标足够快地移出控件,则这些事件不会触发。
请问为什么会出现这种情况?有没有方法可以正确地获取这些事件?
请检查示例项目以查看其实际效果:https://www.dropbox.com/s/w5ra2vzegjtauso/SampleApp.zip
更新。我在这里发现同样的问题,但没有答案。我在那里启动了悬赏。
我在鼠标进入/离开事件上遇到了问题。当鼠标按钮被按下并保持在控件内部时,如果光标足够快地移出控件,则这些事件不会触发。
请问为什么会出现这种情况?有没有方法可以正确地获取这些事件?
请检查示例项目以查看其实际效果:https://www.dropbox.com/s/w5ra2vzegjtauso/SampleApp.zip
更新。我在这里发现同样的问题,但没有答案。我在那里启动了悬赏。
编辑:在Sisyphe正确指出该行为不适用于具有鼠标交互的元素之后,我已经重写了代码。
此行为可以附加到窗口或任何其他FrameworkElement。默认情况下,所有包含的元素将在鼠标左键按下时监视MouseLeave,并执行处理程序。通过设置MonitorSubControls="False",也可以将该行为应用于其关联的元素。
基本上,该行为所做的事情是(请参阅代码中的注释以获取更多细节):
已知限制(我认为都可以通过更多的努力解决,但似乎并不太重要):
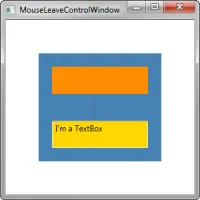

Xaml(示例):
<Window x:Class="WpfApplication1.MouseLeaveControlWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
xmlns:i="http://schemas.microsoft.com/expression/2010/interactivity"
xmlns:beh="clr-namespace:WpfApplication1.Behavior"
Title="MouseLeaveControlWindow" Height="300" Width="300" x:Name="window" MouseLeave="OnMouseLeave">
<i:Interaction.Behaviors>
<beh:MonitorMouseLeaveBehavior />
</i:Interaction.Behaviors>
<Grid x:Name="grid" MouseLeave="OnMouseLeave" Background="Transparent">
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
<RowDefinition Height="*" />
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Border x:Name="blueBorder" MouseLeave="OnMouseLeave" Background="SteelBlue" Margin="50" Grid.RowSpan="2" />
<Border x:Name="orangeBorder" MouseLeave="OnMouseLeave" Background="DarkOrange" Margin="70, 70, 70, 20" />
<TextBox x:Name="goldTextBox" MouseLeave="OnMouseLeave" Background="Gold" Margin="70, 20, 70, 70" Grid.Row="1" Text="I'm a TextBox" />
</Grid>
</Window>
代码后端(仅用于调试目的):
public partial class MouseLeaveControlWindow : Window
{
public MouseLeaveControlWindow()
{
InitializeComponent();
}
private int i = 0;
private void OnMouseLeave(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
FrameworkElement fe = (FrameworkElement)sender;
if (e.LeftButton == MouseButtonState.Pressed)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}: Left {1}.", i, fe.Name)); i++;
}
else
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine(string.Format("{0}: Left {1} (Released).", i, fe.Name)); i++;
}
}
}
MonitorMouseLeaveBehavior:
using System;
using System.Linq;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Reflection;
using System.Runtime.InteropServices;
using System.Timers;
using System.Windows;
using System.Windows.Controls;
using System.Windows.Input;
using System.Windows.Interactivity;
using System.Windows.Interop;
using System.ComponentModel;
using System.Windows.Media;
using WpfApplication1.Helpers;
namespace WpfApplication1.Behavior
{
public class MonitorMouseLeaveBehavior : Behavior<FrameworkElement>
{
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
[return: MarshalAs(UnmanagedType.Bool)]
internal static extern bool GetCursorPos(ref Win32Point pt);
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
internal struct Win32Point
{
public Int32 X;
public Int32 Y;
};
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern short GetAsyncKeyState(UInt16 virtualKeyCode);
private enum VK
{
LBUTTON = 0x01
}
private bool _tracking;
private const int _interval = 1;
private Timer _checkPosTimer = new Timer(_interval);
private Dictionary<FrameworkElement, RoutedEventHandlerInfo[]> _leaveHandlersForElement = new Dictionary<FrameworkElement, RoutedEventHandlerInfo[]>();
private Window _window;
private Dictionary<FrameworkElement, Rect> _boundsByElement = new Dictionary<FrameworkElement, Rect>();
private Dictionary<FrameworkElement, bool> _wasInside = new Dictionary<FrameworkElement, bool>();
private List<FrameworkElement> _elements = new List<FrameworkElement>();
/// <summary>
/// If true, all subcontrols are monitored for the mouseleave event when left mousebutton is down.
/// True by default.
/// </summary>
public bool MonitorSubControls { get { return (bool)GetValue(MonitorSubControlsProperty); } set { SetValue(MonitorSubControlsProperty, value); } }
public static readonly DependencyProperty MonitorSubControlsProperty = DependencyProperty.Register("MonitorSubControls", typeof(bool), typeof(MonitorMouseLeaveBehavior), new PropertyMetadata(true, OnMonitorSubControlsChanged));
private static void OnMonitorSubControlsChanged(DependencyObject d, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
MonitorMouseLeaveBehavior beh = (MonitorMouseLeaveBehavior)d;
beh.AddOrRemoveLogicalChildren((bool)e.NewValue);
}
/// <summary>
/// Initial actions
/// </summary>
protected override void OnAttached()
{
_window = this.AssociatedObject is Window ? (Window)this.AssociatedObject : Window.GetWindow(this.AssociatedObject); // get window
_window.SourceInitialized += (s, e) =>
{
this.AddOrRemoveLogicalChildren(this.MonitorSubControls); // get all monitored elements
this.AttachHandlers(true); // attach mousedown and sizechanged handlers
this.GetAllBounds(); // determine bounds of all elements
_checkPosTimer.Elapsed += (s1, e1) => Dispatcher.BeginInvoke((Action)(() => { CheckPosition(); }));
};
base.OnAttached();
}
protected override void OnDetaching()
{
this.AttachHandlers(false);
base.OnDetaching();
}
/// <summary>
/// Starts or stops monitoring of the AssociatedObject's logical children.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="add"></param>
private void AddOrRemoveLogicalChildren(bool add)
{
if (_window != null && _window.IsInitialized)
{
AddOrRemoveSizeChangedHandlers(false);
_elements.Clear();
if (add)
_elements.AddRange(VisualHelper.FindLogicalChildren<FrameworkElement>(this.AssociatedObject));
_elements.Add(this.AssociatedObject);
AddOrRemoveSizeChangedHandlers(true);
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Attaches/detaches size changed handlers to the monitored elements
/// </summary>
/// <param name="add"></param>
private void AddOrRemoveSizeChangedHandlers(bool add)
{
foreach (var element in _elements)
{
element.SizeChanged -= element_SizeChanged;
if (add) element.SizeChanged += element_SizeChanged;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Adjusts the stored bounds to the changed size
/// </summary>
void element_SizeChanged(object sender, SizeChangedEventArgs e)
{
FrameworkElement fe = sender as FrameworkElement;
if (fe != null)
GetBounds(fe);
}
/// <summary>
/// Attaches/Detaches MouseLeftButtonDown and SizeChanged handlers
/// </summary>
/// <param name="attach">true: attach, false: detach</param>
private void AttachHandlers(bool attach)
{
AddOrRemoveSizeChangedHandlers(attach);
if (attach)
_window.PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown += window_PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown;
else // detach
_window.PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown -= window_PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the bounds for all monitored elements
/// </summary>
private void GetAllBounds()
{
_boundsByElement.Clear();
foreach (var element in _elements)
GetBounds(element);
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the bounds of the control, which are used to check if the mouse position
/// is located within. Note that this only covers rectangular control shapes.
/// </summary>
private void GetBounds(FrameworkElement element)
{
Point p1 = new Point(0, 0);
Point p2 = new Point(element.ActualWidth, element.ActualHeight);
p1 = element.TransformToVisual(_window).Transform(p1);
p2 = element.TransformToVisual(_window).Transform(p2);
if (element == _window) // window bounds need to account for the border
{
var titleHeight = SystemParameters.WindowCaptionHeight + 2 * SystemParameters.ResizeFrameHorizontalBorderHeight; // not sure about that one
var verticalBorderWidth = SystemParameters.ResizeFrameVerticalBorderWidth;
p1.Offset(-verticalBorderWidth, -titleHeight);
p2.Offset(-verticalBorderWidth, -titleHeight);
}
Rect bounds = new Rect(p1, p2);
if (_boundsByElement.ContainsKey(element))
_boundsByElement[element] = bounds;
else
_boundsByElement.Add(element, bounds);
}
/// <summary>
/// For all monitored elements, detach the MouseLeave event handlers and store them locally,
/// to be executed manually.
/// </summary>
private void RerouteLeaveHandlers()
{
foreach (var element in _elements)
{
if (!_leaveHandlersForElement.ContainsKey(element))
{
var handlers = ReflectionHelper.GetRoutedEventHandlers(element, UIElement.MouseLeaveEvent);
if (handlers != null)
{
_leaveHandlersForElement.Add(element, handlers);
foreach (var handler in handlers)
element.MouseLeave -= (MouseEventHandler)handler.Handler; // detach handlers
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Reattach all leave handlers that were detached in window_PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown.
/// </summary>
private void ReattachLeaveHandlers()
{
foreach (var kvp in _leaveHandlersForElement)
{
FrameworkElement fe = kvp.Key;
foreach (var handler in kvp.Value)
{
if (handler.Handler is MouseEventHandler)
fe.MouseLeave += (MouseEventHandler)handler.Handler;
}
}
_leaveHandlersForElement.Clear();
}
/// <summary>
/// Checks if the mouse position is inside the bounds of the elements
/// If there is a transition from inside to outside, the leave event handlers are executed
/// </summary>
private void DetermineIsInside()
{
Point p = _window.PointFromScreen(GetMousePosition());
foreach (var element in _elements)
{
if (_boundsByElement.ContainsKey(element))
{
bool isInside = _boundsByElement[element].Contains(p);
bool wasInside = _wasInside.ContainsKey(element) && _wasInside[element];
if (wasInside && !isInside)
ExecuteLeaveHandlers(element);
if (_wasInside.ContainsKey(element))
_wasInside[element] = isInside;
else
_wasInside.Add(element, isInside);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the mouse position relative to the screen
/// </summary>
public static Point GetMousePosition()
{
Win32Point w32Mouse = new Win32Point();
GetCursorPos(ref w32Mouse);
return new Point(w32Mouse.X, w32Mouse.Y);
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the mouse button state. MouseEventArgs.LeftButton is notoriously unreliable.
/// </summary>
private bool IsMouseLeftButtonPressed()
{
short leftMouseKeyState = GetAsyncKeyState((ushort)VK.LBUTTON);
bool ispressed = leftMouseKeyState < 0;
return ispressed;
}
/// <summary>
/// Executes the leave handlers that were attached to the controls.
/// They have been detached previously by this behavior (see window_PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown), to prevent double execution.
/// After mouseup, they are reattached (see CheckPosition)
/// </summary>
private void ExecuteLeaveHandlers(FrameworkElement fe)
{
MouseDevice mouseDev = InputManager.Current.PrimaryMouseDevice;
MouseEventArgs mouseEvent = new MouseEventArgs(mouseDev, 0) { RoutedEvent = Control.MouseLeaveEvent };
if (_leaveHandlersForElement.ContainsKey(fe))
{
foreach (var handler in _leaveHandlersForElement[fe])
{
if (handler.Handler is MouseEventHandler)
((MouseEventHandler)handler.Handler).Invoke(fe, mouseEvent);
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Sets the mouse capture (events outside the window are still directed to it),
/// and tells the behavior to watch out for a missed leave event
/// </summary>
private void window_PreviewMouseLeftButtonDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("--- left mousebutton down ---"); // todo remove
this.RerouteLeaveHandlers();
_tracking = true;
_checkPosTimer.Start();
}
/// <summary>
/// Uses the _tracking field as well as left mouse button state to determine if either
/// leave event handlers should be executed, or monitoring should be stopped.
/// </summary>
private void CheckPosition()
{
if (_tracking)
{
if (IsMouseLeftButtonPressed())
{
this.DetermineIsInside();
}
else
{
_wasInside.Clear();
_tracking = false;
_checkPosTimer.Stop();
System.Diagnostics.Debug.WriteLine("--- left mousebutton up ---"); // todo remove
// invoking ReattachLeaveHandlers() immediately would rethrow MouseLeave for top grid/window
// if both a) mouse is outside window and b) mouse moves. Wait with reattach until mouse is inside window again and moves.
_window.MouseMove += ReattachHandler;
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// Handles the first _window.MouseMove event after left mouse button was released,
/// and reattaches the MouseLeaveHandlers. Detaches itself to be executed only once.
/// </summary>
private void ReattachHandler(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
ReattachLeaveHandlers();
_window.MouseMove -= ReattachHandler; // only once
}
}
}
VisualHelper.FindLogicalChildren,ReflectionHelper.获取路由事件处理程序:
public static List<T> FindLogicalChildren<T>(DependencyObject obj) where T : DependencyObject
{
List<T> children = new List<T>();
foreach (var child in LogicalTreeHelper.GetChildren(obj))
{
if (child != null)
{
if (child is T)
children.Add((T)child);
if (child is DependencyObject)
children.AddRange(FindLogicalChildren<T>((DependencyObject)child)); // recursive
}
}
return children;
}
/// <summary>
/// Gets the list of routed event handlers subscribed to the specified routed event.
/// </summary>
/// <param name="element">The UI element on which the event is defined.</param>
/// <param name="routedEvent">The routed event for which to retrieve the event handlers.</param>
/// <returns>The list of subscribed routed event handlers.</returns>
public static RoutedEventHandlerInfo[] GetRoutedEventHandlers(UIElement element, RoutedEvent routedEvent)
{
var routedEventHandlers = default(RoutedEventHandlerInfo[]);
// Get the EventHandlersStore instance which holds event handlers for the specified element.
// The EventHandlersStore class is declared as internal.
var eventHandlersStoreProperty = typeof(UIElement).GetProperty("EventHandlersStore", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
object eventHandlersStore = eventHandlersStoreProperty.GetValue(element, null);
if (eventHandlersStore != null)
{
// Invoke the GetRoutedEventHandlers method on the EventHandlersStore instance
// for getting an array of the subscribed event handlers.
var getRoutedEventHandlers = eventHandlersStore.GetType().GetMethod("GetRoutedEventHandlers", BindingFlags.Instance | BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.NonPublic);
routedEventHandlers = (RoutedEventHandlerInfo[])getRoutedEventHandlers.Invoke(eventHandlersStore, new object[] { routedEvent });
}
return routedEventHandlers;
}
方法一 - 仍然是有效的(作为一个纯管理解决方案),如果你能解决具体问题。(可以将捕获给特定控件,以避免问题,但我尚未尝试过)
这应该可以帮助您获取事件(“固定”事件)。
关键是在窗口外部跟踪鼠标移动(只在鼠标按下时跟踪)。
为此,您需要执行capture(但略有不同,因为建议的做法行不通 - 在按下/放开时无法工作)。
private void Window_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
this.CaptureMouse();
}
private void Window_MouseUp(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
this.ReleaseMouseCapture();
}
private void Window_MouseLeave(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
test1.Content = "Mouse left";
}
private void Window_MouseEnter(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
test1.Content = "Mouse entered";
}
private void Window_MouseMove(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
if (Mouse.Captured == this)
{
if (!this.IsMouseInBounds(e))
Window_MouseLeave(sender, e);
else
Window_MouseEnter(sender, e);
}
test2.Content = e.GetPosition(this).ToString();
}
private bool IsMouseInBounds(MouseEventArgs e)
{
var client = ((FrameworkElement)this.Content);
Rect bounds = new Rect(0, 0, client.ActualWidth, client.ActualHeight);
return bounds.Contains(e.GetPosition(this));
}
private Point GetRealPosition(Point mousePoint)
{
return Application.Current.MainWindow.PointFromScreen(mousePoint);
}
Enter和Leave,并没有智能算法(即生成的 enter/leave 将继续触发)。即添加一些标志来正确保存 state 的 enter/leave 状态。
另外,我正在测量鼠标是否在窗口的“客户区域”内。如果需要考虑边框等因素,则需要进行调整。
还有,我忘记添加显而易见的-连接新事件 MouseDown="Window_MouseDown" MouseUp="Window_MouseUp"
Mouse.Capture(yourUIElement);
并在鼠标离开时释放它。
Mouse.Capture(null);
如果您需要,我已经编辑了一个简化的包装器,以便于使用(只需在您的视图模型中添加命令)。
方法二 - 使用全局鼠标钩子来跟踪鼠标移动 - 其余步骤与方法一类似。
实际上,这更多是一个从C#中执行全局挂钩的示例。
在XAML中,您可以连接所有三个事件或仅连接其中一个或两个事件。
my:Hooks.EnterCommand="{Binding EnterCommand}"
my:Hooks.LeaveCommand="{Binding LeaveCommand}"
my:Hooks.MouseMoveCommand="{Binding MoveCommand}"
在你的视图模型中定义命令
RelayCommand _enterCommand;
public RelayCommand EnterCommand
{
get
{
return _enterCommand ?? (_enterCommand = new RelayCommand(param =>
{
var point = (Point)param;
test1.Content = "Mouse entered";
// test2.Content = point.ToString();
},
param => true));
}
}
附加属性(即“好”的包装器)……
public static class Hooks
{
private static Dictionary<ContentControl, Action> _hash = new Dictionary<ContentControl, Action>();
#region MouseMoveCommand
public static ICommand GetMouseMoveCommand(ContentControl control) { return (ICommand)control.GetValue(MouseMoveCommandProperty); }
public static void SetMouseMoveCommand(ContentControl control, ICommand value) { control.SetValue(MouseMoveCommandProperty, value); }
public static readonly DependencyProperty MouseMoveCommandProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("MouseMoveCommand", typeof(ICommand), typeof(Hooks), new UIPropertyMetadata(null, OnMouseMoveCommandChanged));
static void OnMouseMoveCommandChanged(DependencyObject depObj, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
ContentControl control = depObj as ContentControl;
if (control != null && e.NewValue is ICommand)
SetupMouseMove(control);
}
static void Instance_MouseMoveLL(object sender, WinHook.MouseLLMessageArgs e)
{
}
static void OnAutoGeneratingColumn(ICommand command, object sender, DataGridAutoGeneratingColumnEventArgs e)
{
if (command.CanExecute(e)) command.Execute(e);
}
#endregion
#region EnterCommand
public static ICommand GetEnterCommand(ContentControl control) { return (ICommand)control.GetValue(EnterCommandProperty); }
public static void SetEnterCommand(ContentControl control, ICommand value) { control.SetValue(EnterCommandProperty, value); }
public static readonly DependencyProperty EnterCommandProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("EnterCommand", typeof(ICommand), typeof(Hooks), new UIPropertyMetadata(null, OnEnterCommandChanged));
static void OnEnterCommandChanged(DependencyObject depObj, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
ContentControl control = depObj as ContentControl;
if (control != null && e.NewValue is ICommand)
SetupMouseMove(control);
}
#endregion
#region LeaveCommand
public static ICommand GetLeaveCommand(ContentControl control) { return (ICommand)control.GetValue(LeaveCommandProperty); }
public static void SetLeaveCommand(ContentControl control, ICommand value) { control.SetValue(LeaveCommandProperty, value); }
public static readonly DependencyProperty LeaveCommandProperty =
DependencyProperty.RegisterAttached("LeaveCommand", typeof(ICommand), typeof(Hooks), new UIPropertyMetadata(null, OnLeaveCommandChanged));
static void OnLeaveCommandChanged(DependencyObject depObj, DependencyPropertyChangedEventArgs e)
{
ContentControl control = depObj as ContentControl;
if (control != null && e.NewValue is ICommand)
SetupMouseMove(control);
}
#endregion
static void SetupMouseMove(ContentControl control)
{
Action onmove;
if (_hash.TryGetValue(control, out onmove) == false)
{
onmove = () =>
{
var entered = false;
var moveCommand = control.GetValue(Hooks.MouseMoveCommandProperty) as ICommand;
var enterCommand = control.GetValue(Hooks.EnterCommandProperty) as ICommand;
var leaveCommand = control.GetValue(Hooks.LeaveCommandProperty) as ICommand;
// hook is invoked on the 'caller thread' (i.e. your GUI one) so it's safe
// don't forget to unhook and dispose / release it, handle unsubscribe for events
WinHook.Instance.MouseMoveLL += (s, e) =>
{
Point point = control.PointFromScreen(new Point(e.Message.Pt.X, e.Message.Pt.Y));
if (moveCommand != null && moveCommand.CanExecute(point))
moveCommand.Execute(point);
var newEntered = control.IsMouseInBounds(point); // don't use 'IsMouseOver'
if (newEntered != entered)
{
entered = newEntered;
if (entered)
{
if (enterCommand != null && enterCommand.CanExecute(point))
enterCommand.Execute(point);
}
else
{
if (leaveCommand != null && leaveCommand.CanExecute(point))
leaveCommand.Execute(point);
}
}
};
};
control.Loaded += (s, e) => onmove();
_hash[control] = onmove;
}
}
private static bool IsMouseInBounds(this ContentControl control, Point point)
{
var client = ((FrameworkElement)control.Content);
Rect bounds = new Rect(0, 0, client.ActualWidth, client.ActualHeight);
return bounds.Contains(point);
}
}
您可以使用HookManager来处理。
或者使用最小的钩子代码(请注意,需要适当的IDisoposable、异常处理等):
public sealed class WinHook : IDisposable
{
public static readonly WinHook Instance = new WinHook();
public const int WH_MOUSE_LL = 14;
public const uint WM_MOUSEMOVE = 0x0200;
public delegate void MouseLLMessageHandler(object sender, MouseLLMessageArgs e);
public delegate int HookProc(int nCode, IntPtr wParam, IntPtr lParam);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", ExactSpelling = true, CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern int GetCurrentThreadId();
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto, CallingConvention = CallingConvention.StdCall, SetLastError = true)]
public static extern int SetWindowsHookEx(int idHook, HookProc lpfn, IntPtr hInstance, int threadId);
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto, CallingConvention = CallingConvention.StdCall, SetLastError = true)]
public static extern bool UnhookWindowsHookEx(int idHook);
[DllImport("user32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto, CallingConvention = CallingConvention.StdCall, SetLastError = true)]
public static extern int CallNextHookEx(int idHook, int nCode, IntPtr wParam, IntPtr lParam);
[DllImport("kernel32.dll", CharSet = CharSet.Auto)]
public static extern IntPtr GetModuleHandle(string lpModuleName);
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public struct POINT
{
public int X;
public int Y;
}
[StructLayout(LayoutKind.Sequential)]
public class MouseLLHookStruct
{
public POINT Pt;
public uint mouseData;
public uint flags;
public uint time;
public uint dwExtraInfo;
}
public class MouseLLMessageArgs : EventArgs
{
public bool IsProcessed { get; set; }
public MouseLLHookStruct Message { get; private set; }
public MouseLLMessageArgs(MouseLLHookStruct message) { this.Message = message; }
}
static IntPtr GetModuleHandle()
{
using (Process process = Process.GetCurrentProcess())
using (ProcessModule module = process.MainModule)
return GetModuleHandle(module.ModuleName);
}
public event MouseLLMessageHandler MouseMoveLL;
int _hLLMouseHook = 0;
HookProc LLMouseHook;
private WinHook()
{
IntPtr hModule = GetModuleHandle();
LLMouseHook = LowLevelMouseProc;
_hLLMouseHook = SetWindowsHookEx(WH_MOUSE_LL, LLMouseHook, hModule, 0);
if (_hLLMouseHook == 0) { } // "failed w/ an error code: {0}", new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()).Message
}
public void Release()
{
if (_hLLMouseHook == 0) return;
int hhook = _hLLMouseHook;
_hLLMouseHook = 0;
bool ret = UnhookWindowsHookEx(hhook);
if (ret == false) { } // "failed w/ an error code: {0}", new Win32Exception(Marshal.GetLastWin32Error()).Message
}
public int LowLevelMouseProc(int nCode, IntPtr wParam, IntPtr lParam)
{
if (nCode >= 0 && lParam.ToInt32() > 0
&& wParam.ToInt32() == (int)WM_MOUSEMOVE)
{
MouseLLHookStruct msg = (MouseLLHookStruct)Marshal.PtrToStructure(lParam, typeof(MouseLLHookStruct));
MouseLLMessageArgs args = new MouseLLMessageArgs(msg);
if (MouseMoveLL != null)
MouseMoveLL(this, args);
if (args.IsProcessed)
return -1; // return 1;
}
return CallNextHookEx(_hLLMouseHook, nCode, wParam, lParam);
}
// implement IDisposable properly and call `Release` for unmanaged resources / hook
public void Dispose() { }
}
此外,避免在事件中放置任何“重”的内容 - 或者从中产生的任何内容。实际上,你可以花费一定的时间来处理事件 - 或者钩子将被删除,即停止工作。如果需要从事件中进行一些处理,请弹出新线程并进行调用。
我最喜欢的解决方案是将钩子分配到自己的线程中,然后需要调用事件 - 但这超出了范围,有点更复杂(需要一个“泵”等)。
至于“为什么”需要这样做:
我不喜欢猜测,但似乎事件会被限制 - 当“越过边境”时会错过关键的“一个”。无论怎么看,这都与鼠标移动事件有关。
text.AddHandler(MouseMoveEvent, new MouseEventHandler(Window_MouseMove), true);,我就会得到鼠标移动的调用。但对于Enter和Leave则不起作用。您可能需要在MouseMove中检查光标位置以获取窗口坐标,并显式调用此类控件的LostFocus。 - Viv