这个答案是从这个问题复制过来的。我还将其制作成了博客文章
使用正则表达式验证数字范围
明确一点:当简单的if语句足以满足要求时
if(num < -2055 || num > 2055) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("num (" + num + ") must be between -2055 and 2055");
}
不建议使用正则表达式来验证数字范围。
此外,由于正则表达式分析字符串,因此在测试之前必须先将数字转换为字符串(一个例外是当数字恰好已经是字符串时,例如从控制台获取用户输入时)。
(为确保字符串本身就是数字,您可以使用org.apache.commons.lang3.math.NumberUtils#isNumber(s))
尽管如此,了解如何使用正则表达式验证数字范围是有趣且有教育意义的。
一个数字范围
规则:一个数字必须恰好为15。
The simplest range there is. A regex to match this is
\b15\b
Word boundaries are necessary to avoid matching the 15 inside of 8215242.
A two number range
The rule: The number must be between 15 and 16. Three possible regexes:
\b(15|16)\b
\b1(5|6)\b
\b1[5-6]\b
A number range "mirrored" around zero
The rule: The number must be between -12 and 12.
Here is a regex for 0 through 12, positive-only:
\b(\d|1[0-2])\b
Free-spaced:
\b( //The beginning of a word (or number), followed by either
\d // Any digit 0 through 9
| //Or
1[0-2] // A 1 followed by any digit between 0 and 2.
)\b //The end of a word
Making this work for both negative and positive is as simple as adding an optional dash at the start:
-?\b(\d|1[0-2])\b
(This assumes no inappropriate characters precede the dash.)
To forbid negative numbers, a negative lookbehind is necessary:
(?<!-)\b(\d|1[0-2])\b
Leaving the lookbehind out would cause the 11 in -11 to match. (The first example in this post should have this added.)
Note: \d versus [0-9]
In order to be compatible with all regex flavors, all \d-s should be changed to [0-9]. For example, .NET considers non ASCII numbers, such as those in different languages, as legal values for \d. Except for in the last example, for brevity, it's left as \d.
(With thanks to TimPietzcker at stackoverflow)
Three digits, with all but the first digit equal to zero
Rule: Must be between 0 and 400.
A possible regex:
(?<!-)\b([1-3]?\d{1,2}|400)\b
Free spaced:
(?<!-) //Something not preceded by a dash
\b( //Word-start, followed by either
[1-3]? // No digit, or the digit 1, 2, or 3
\d{1,2} // Followed by one or two digits (between 0 and 9)
| //Or
400 // The number 400
)\b //Word-end
Another possibility that should never be used:
\b(0|1|2|3|4|5|6|7|8|9|10|11|12|13|14|15|16|17|18|19|20|21|22|23|24|25|26|27|28|29|30|31|32|33|34|35|36|37|38|39|40|41|42|43|44|45|46|47|48|49|50|51|52|53|54|55|56|57|58|59|60|61|62|63|64|65|66|67|68|69|70|71|72|73|74|75|76|77|78|79|80|81|82|83|84|85|86|87|88|89|90|91|92|93|94|95|96|97|98|99|100|101|102|103|104|105|106|107|108|109|110|111|112|113|114|115|116|117|118|119|120|121|122|123|124|125|126|127|128|129|130|131|132|133|134|135|136|137|138|139|140|141|142|143|144|145|146|147|148|149|150|151|152|153|154|155|156|157|158|159|160|161|162|163|164|165|166|167|168|169|170|171|172|173|174|175|176|177|178|179|180|181|182|183|184|185|186|187|188|189|190|191|192|193|194|195|196|197|198|199|200|201|202|203|204|205|206|207|208|209|210|211|212|213|214|215|216|217|218|219|220|221|222|223|224|225|226|227|228|229|230|231|232|233|234|235|236|237|238|239|240|241|242|243|244|245|246|247|248|249|250|251|252|253|254|255|256|257|258|259|260|261|262|263|264|265|266|267|268|269|270|271|272|273|274|275|276|277|278|279|280|281|282|283|284|285|286|287|288|289|290|291|292|293|294|295|296|297|298|299|300|301|302|303|304|305|306|307|308|309|310|311|312|313|314|315|316|317|318|319|320|321|322|323|324|325|326|327|328|329|330|331|332|333|334|335|336|337|338|339|340|341|342|343|344|345|346|347|348|349|350|351|352|353|354|355|356|357|358|359|360|361|362|363|364|365|366|367|368|369|370|371|372|373|374|375|376|377|378|379|380|381|382|383|384|385|386|387|388|389|390|391|392|393|394|395|396|397|398|399|400)\b
Final example: Four digits, mirrored around zero, that does not end with zeros.
Rule: Must be between -2055 and 2055
This is from a question on stackoverflow.
Regex:
-?\b(20(5[0-5]|[0-4][0-9])|1?[0-9]{1,3})\b
Free-spaced:
-? //Optional dash
\b( //Followed by word boundary, followed by either of the following
20( // "20", followed by either
5[0-5] // A "5" followed by a digit 0-5
| // or
[0-4][0-9] // A digit 0-4, followed by any digit
)
| //OR
1?[0-9]{1,3} // An optional "1", followed by one through three digits (0-9)
)\b //Followed by a word boundary.
Here is a visual representation of this regex:
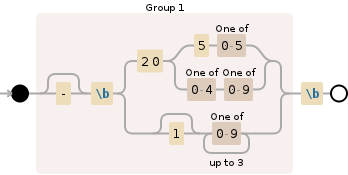
And here you can try it out yourself: Debuggex demonstration
(With thanks to PlasmaPower on stackoverflow for the debugging assistance.)
Final note
Depending on what you are capturing, it is likely that all sub-groups should be made into non-capture groups. For example, this:
(-?\b(?:20(?:5[0-5]|[0-4][0-9])|1?[0-9]{1,3})\b)
Instead of this:
-?\b(20(5[0-5]|[0-4][0-9])|1?[0-9]{1,3})\b
Example Java implementation
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import org.apache.commons.lang.math.NumberUtils;
public class UserInputNumInRangeWRegex {
public static final void main(String[] ignored) {
int num = -1;
boolean isNum = false;
int iRangeMax = 2055;
Matcher mtchrNumNegThrPos = Pattern.compile("-?\\b(20(5[0-5]|[0-4][0-9])|1?[0-9]{1,3})\\b").matcher("");
do {
System.out.print("Enter a number between -" + iRangeMax + " and " + iRangeMax + ": ");
String strInput = (new Scanner(System.in)).next();
if(!NumberUtils.isNumber(strInput)) {
System.out.println("Not a number. Try again.");
} else if(!mtchrNumNegThrPos.reset(strInput).matches()) {
System.out.println("Not in range. Try again.");
} else {
num = Integer.parseInt(strInput);
isNum = true;
}
} while(!isNum);
System.out.println("Number: " + num);
}
}
Output
[C:\java_code\]java UserInputNumInRangeWRegex
Enter a number between -2055 and 2055: tuhet
Not a number. Try again.
Enter a number between -2055 and 2055: 283837483
Not in range. Try again.
Enter a number between -2055 and 2055: -200000
Not in range. Try again.
Enter a number between -2055 and 2055: -300
Number: -300

180-195返回了一个不正确的正则表达式)。我已经修复了它(同样的答案)。 - Bart Kiers