我想使用GZIP压缩我的文件。你能分享一下用于使用GZIP压缩文件的web.config代码吗?
上传完web.config文件后,还有其他需要做的事情吗?
我想使用GZIP压缩我的文件。你能分享一下用于使用GZIP压缩文件的web.config代码吗?
上传完web.config文件后,还有其他需要做的事情吗?
可以直接通过IIS启用GZip压缩。
首先,打开IIS,
进入您希望进行调整的网站并点击“Compression”页面。 如果未安装Gzip,则会看到以下内容:
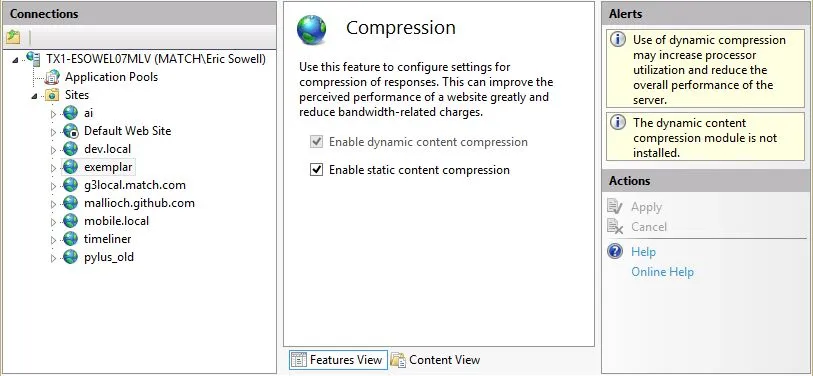
“未安装动态内容压缩模块。”我们需要解决这个问题。所以我们去“打开或关闭Windows功能”并选择“动态内容压缩”,然后点击确定按钮。
现在,如果我们返回到IIS,应该会看到压缩页面已更改。此时,我们需要确保选中了动态压缩复选框,然后就可以启用压缩了。我们的动态内容将被Gzipped。
测试-检查是否启用GZIP压缩
要测试压缩是否起作用,请使用Chrome的开发人员工具或Firefox的Firebug,并确保设置了HTTP响应标头:
Content-Encoding: gzip
cmd 或 64位编辑器 进行这些更改,然后重新启动 Windows进程激活服务 服务。 - KuN谷歌提供了一个相当可靠、易于理解的介绍,介绍了这个工具是如何工作以及其优缺点。https://developers.google.com/web/fundamentals/performance/optimizing-content-efficiency/optimize-encoding-and-transfer 他们推荐使用 HTML5 Boilerplate 项目,该项目针对不同版本的 IIS 提供了解决方案:
可以在此处下载:https://github.com/h5bp/server-configs-iis 他们提供了 web.config 文件,您可以从他们的文件中复制和粘贴更改,并查看更改,这比查阅一堆博客文章要容易得多。
以下是.NET版本4.5的web.config设置: https://github.com/h5bp/server-configs-iis/blob/master/dotnet%204.5/MVC5/Web.config<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<configuration>
<appSettings>
<add key="webpages:Version" value="3.0.0.0" />
<add key="webpages:Enabled" value="false" />
<add key="ClientValidationEnabled" value="true" />
<add key="UnobtrusiveJavaScriptEnabled" value="true" />
</appSettings>
<system.web>
<!--
Set compilation debug="true" to insert debugging
symbols into the compiled page. Because this
affects performance, set this value to true only
during development.
-->
<compilation debug="true" targetFramework="4.5" />
<!-- Security through obscurity, removes X-AspNet-Version HTTP header from the response -->
<!-- Allow zombie DOS names to be captured by ASP.NET (/con, /com1, /lpt1, /aux, /prt, /nul, etc) -->
<httpRuntime targetFramework="4.5" requestValidationMode="2.0" requestPathInvalidCharacters="" enableVersionHeader="false" relaxedUrlToFileSystemMapping="true" />
<!-- httpCookies httpOnlyCookies setting defines whether cookies
should be exposed to client side scripts
false (Default): client side code can access cookies
true: client side code cannot access cookies
Require SSL is situational, you can also define the
domain of cookies with optional "domain" property -->
<httpCookies httpOnlyCookies="true" requireSSL="false" />
<trace writeToDiagnosticsTrace="false" enabled="false" pageOutput="false" localOnly="true" />
</system.web>
<system.webServer>
<!-- GZip static file content. Overrides the server default which only compresses static files over 2700 bytes -->
<httpCompression directory="%SystemDrive%\websites\_compressed" minFileSizeForComp="1024">
<scheme name="gzip" dll="%Windir%\system32\inetsrv\gzip.dll" />
<staticTypes>
<add mimeType="text/*" enabled="true" />
<add mimeType="message/*" enabled="true" />
<add mimeType="application/javascript" enabled="true" />
<add mimeType="application/json" enabled="true" />
<add mimeType="*/*" enabled="false" />
</staticTypes>
</httpCompression>
<httpErrors existingResponse="PassThrough" errorMode="Custom">
<!-- Catch IIS 404 error due to paths that exist but shouldn't be served (e.g. /controllers, /global.asax) or IIS request filtering (e.g. bin, web.config, app_code, app_globalresources, app_localresources, app_webreferences, app_data, app_browsers) -->
<remove statusCode="404" subStatusCode="-1" />
<error statusCode="404" subStatusCode="-1" path="/notfound" responseMode="ExecuteURL" />
<remove statusCode="500" subStatusCode="-1" />
<error statusCode="500" subStatusCode="-1" path="/error" responseMode="ExecuteURL" />
</httpErrors>
<directoryBrowse enabled="false" />
<validation validateIntegratedModeConfiguration="false" />
<!-- Microsoft sets runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests to true by default
You should handle this according to need but consider the performance hit.
Good source of reference on this matter: http://www.west-wind.com/weblog/posts/2012/Oct/25/Caveats-with-the-runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests-in-IIS-78
-->
<modules runAllManagedModulesForAllRequests="false" />
<urlCompression doStaticCompression="true" doDynamicCompression="true" />
<staticContent>
<!-- Set expire headers to 30 days for static content-->
<clientCache cacheControlMode="UseMaxAge" cacheControlMaxAge="30.00:00:00" />
<!-- use utf-8 encoding for anything served text/plain or text/html -->
<remove fileExtension=".css" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".css" mimeType="text/css" />
<remove fileExtension=".js" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".js" mimeType="text/javascript" />
<remove fileExtension=".json" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".json" mimeType="application/json" />
<remove fileExtension=".rss" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".rss" mimeType="application/rss+xml; charset=UTF-8" />
<remove fileExtension=".html" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".html" mimeType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" />
<remove fileExtension=".xml" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".xml" mimeType="application/xml; charset=UTF-8" />
<!-- HTML5 Audio/Video mime types-->
<remove fileExtension=".mp3" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".mp3" mimeType="audio/mpeg" />
<remove fileExtension=".mp4" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".mp4" mimeType="video/mp4" />
<remove fileExtension=".ogg" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".ogg" mimeType="audio/ogg" />
<remove fileExtension=".ogv" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".ogv" mimeType="video/ogg" />
<remove fileExtension=".webm" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".webm" mimeType="video/webm" />
<!-- Proper svg serving. Required for svg webfonts on iPad -->
<remove fileExtension=".svg" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".svg" mimeType="image/svg+xml" />
<remove fileExtension=".svgz" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".svgz" mimeType="image/svg+xml" />
<!-- HTML4 Web font mime types -->
<!-- Remove default IIS mime type for .eot which is application/octet-stream -->
<remove fileExtension=".eot" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".eot" mimeType="application/vnd.ms-fontobject" />
<remove fileExtension=".ttf" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".ttf" mimeType="application/x-font-ttf" />
<remove fileExtension=".ttc" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".ttc" mimeType="application/x-font-ttf" />
<remove fileExtension=".otf" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".otf" mimeType="font/opentype" />
<remove fileExtension=".woff" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".woff" mimeType="application/font-woff" />
<remove fileExtension=".crx" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".crx" mimeType="application/x-chrome-extension" />
<remove fileExtension=".xpi" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".xpi" mimeType="application/x-xpinstall" />
<remove fileExtension=".safariextz" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".safariextz" mimeType="application/octet-stream" />
<!-- Flash Video mime types-->
<remove fileExtension=".flv" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".flv" mimeType="video/x-flv" />
<remove fileExtension=".f4v" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".f4v" mimeType="video/mp4" />
<!-- Assorted types -->
<remove fileExtension=".ico" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".ico" mimeType="image/x-icon" />
<remove fileExtension=".webp" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".webp" mimeType="image/webp" />
<remove fileExtension=".htc" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".htc" mimeType="text/x-component" />
<remove fileExtension=".vcf" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".vcf" mimeType="text/x-vcard" />
<remove fileExtension=".torrent" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".torrent" mimeType="application/x-bittorrent" />
<remove fileExtension=".cur" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".cur" mimeType="image/x-icon" />
<remove fileExtension=".webapp" />
<mimeMap fileExtension=".webapp" mimeType="application/x-web-app-manifest+json; charset=UTF-8" />
</staticContent>
<httpProtocol>
<customHeaders>
<!--#### SECURITY Related Headers ###
More information: https://www.owasp.org/index.php/List_of_useful_HTTP_headers
-->
<!--
# Access-Control-Allow-Origin
The 'Access Control Allow Origin' HTTP header is used to control which
sites are allowed to bypass same-origin policies and send cross-origin requests.
Secure configuration: Either do not set this header or return the 'Access-Control-Allow-Origin'
header restricting it to only a trusted set of sites.
http://enable-cors.org/
<add name="Access-Control-Allow-Origin" value="*" />
-->
<!--
# Cache-Control
The 'Cache-Control' response header controls how pages can be cached
either by proxies or the user's browser.
This response header can provide enhanced privacy by not caching
sensitive pages in the user's browser cache.
<add name="Cache-Control" value="no-store, no-cache"/>
-->
<!--
# Strict-Transport-Security
The HTTP Strict Transport Security header is used to control
if the browser is allowed to only access a site over a secure connection
and how long to remember the server response for, forcing continued usage.
Note* Currently a draft standard which only Firefox and Chrome support. But is supported by sites like PayPal.
<add name="Strict-Transport-Security" value="max-age=15768000"/>
-->
<!--
# X-Frame-Options
The X-Frame-Options header indicates whether a browser should be allowed
to render a page within a frame or iframe.
The valid options are DENY (deny allowing the page to exist in a frame)
or SAMEORIGIN (allow framing but only from the originating host)
Without this option set, the site is at a higher risk of click-jacking.
<add name="X-Frame-Options" value="SAMEORIGIN" />
-->
<!--
# X-XSS-Protection
The X-XSS-Protection header is used by Internet Explorer version 8+
The header instructs IE to enable its inbuilt anti-cross-site scripting filter.
If enabled, without 'mode=block', there is an increased risk that
otherwise, non-exploitable cross-site scripting vulnerabilities may potentially become exploitable
<add name="X-XSS-Protection" value="1; mode=block"/>
-->
<!--
# MIME type sniffing security protection
Enabled by default as there are very few edge cases where you wouldn't want this enabled.
Theres additional reading below; but the tldr, it reduces the ability of the browser (mostly IE)
being tricked into facilitating driveby attacks.
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ie/gg622941(v=vs.85).aspx
http://blogs.msdn.com/b/ie/archive/2008/07/02/ie8-security-part-v-comprehensive-protection.aspx
-->
<add name="X-Content-Type-Options" value="nosniff" />
<!-- A little extra security (by obscurity), removings fun but adding your own is better -->
<remove name="X-Powered-By" />
<add name="X-Powered-By" value="My Little Pony" />
<!--
With Content Security Policy (CSP) enabled (and a browser that supports it (http://caniuse.com/#feat=contentsecuritypolicy),
you can tell the browser that it can only download content from the domains you explicitly allow
CSP can be quite difficult to configure, and cause real issues if you get it wrong
There is website that helps you generate a policy here http://cspisawesome.com/
<add name="Content-Security-Policy" "default-src 'self'; style-src 'self' 'unsafe-inline'; script-src 'self' https://www.google-analytics.com;" />
-->
<!--//#### SECURITY Related Headers ###-->
<!--
Force the latest IE version, in various cases when it may fall back to IE7 mode
github.com/rails/rails/commit/123eb25#commitcomment-118920
Use ChromeFrame if it's installed for a better experience for the poor IE folk
-->
<add name="X-UA-Compatible" value="IE=Edge,chrome=1" />
<!--
Allow cookies to be set from iframes (for IE only)
If needed, uncomment and specify a path or regex in the Location directive
<add name="P3P" value="policyref="/w3c/p3p.xml", CP="IDC DSP COR ADM DEVi TAIi PSA PSD IVAi IVDi CONi HIS OUR IND CNT"" />
-->
</customHeaders>
</httpProtocol>
<!--
<rewrite>
<rules>
Remove/force the WWW from the URL.
Requires IIS Rewrite module http://learn.iis.net/page.aspx/460/using-the-url-rewrite-module/
Configuration lifted from http://nayyeri.net/remove-www-prefix-from-urls-with-url-rewrite-module-for-iis-7-0
NOTE* You need to install the IIS URL Rewriting extension (Install via the Web Platform Installer)
http://www.microsoft.com/web/downloads/platform.aspx
** Important Note
using a non-www version of a webpage will set cookies for the whole domain making cookieless domains
(eg. fast CD-like access to static resources like CSS, js, and images) impossible.
# IMPORTANT: THERE ARE TWO RULES LISTED. NEVER USE BOTH RULES AT THE SAME TIME!
<rule name="Remove WWW" stopProcessing="true">
<match url="^(.*)$" />
<conditions>
<add input="{HTTP_HOST}" pattern="^(www\.)(.*)$" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="http://example.com{PATH_INFO}" redirectType="Permanent" />
</rule>
<rule name="Force WWW" stopProcessing="true">
<match url=".*" />
<conditions>
<add input="{HTTP_HOST}" pattern="^example.com$" />
</conditions>
<action type="Redirect" url="http://www.example.com/{R:0}" redirectType="Permanent" />
</rule>
# E-TAGS
E-Tags are actually quite useful in cache management especially if you have a front-end caching server such as Varnish. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/HTTP_ETag / http://developer.yahoo.com/performance/rules.html#etags
But in load balancing and simply most cases ETags are mishandled in IIS, and it can be advantageous to remove them.
# removed as in https://dev59.com/3Wsz5IYBdhLWcg3wYGgz
<rewrite>
<outboundRules>
<rule name="Remove ETag">
<match serverVariable="RESPONSE_ETag" pattern=".+" />
<action type="Rewrite" value="" />
</rule>
</outboundRules>
</rewrite>
-->
<!--
### Built-in filename-based cache busting
In a managed language such as .net, you should really be using the internal bundler for CSS + js
or get cassette or similar.
If you're not using the build script to manage your filename version revving,
you might want to consider enabling this, which will route requests for
/css/style.20110203.css to /css/style.css
To understand why this is important and a better idea than all.css?v1231,
read: github.com/h5bp/html5-boilerplate/wiki/Version-Control-with-Cachebusting
<rule name="Cachebusting">
<match url="^(.+)\.\d+(\.(js|css|png|jpg|gif)$)" />
<action type="Rewrite" url="{R:1}{R:2}" />
</rule>
</rules>
</rewrite>-->
</system.webServer>
<runtime>
<assemblyBinding xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Helpers" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-3.0.0.0" newVersion="3.0.0.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Mvc" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-5.0.0.0" newVersion="5.0.0.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.Optimization" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-1.1.0.0" newVersion="1.1.0.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="System.Web.WebPages" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-3.0.0.0" newVersion="3.0.0.0" />
</dependentAssembly>
<dependentAssembly>
<assemblyIdentity name="WebGrease" publicKeyToken="31bf3856ad364e35" />
<bindingRedirect oldVersion="1.0.0.0-1.5.2.14234" newVersion="1.5.2.14234" />
</dependentAssembly>
</assemblyBinding>
</runtime>
</configuration>
编辑:如果您需要在WebAPI响应中使用Gzip压缩,请进行以下更新。 我最近才意识到我们的WebAPI没有返回Gzipped响应,我一直在想了很长时间,因为我们在web.config中打开了动态和静态压缩。我们考虑编写自己的压缩服务和响应处理程序(仍然在WebAPI 2上,而不是在.NET Core上,因为现在更容易),但这对于我们来说太麻烦了,因为这似乎是我们只需打开即可的东西。
如果您对我们自己的压缩服务感兴趣,这是我们正在研究的内容https://krzysztofjakielaszek.com/2017/03/26/webapi2-response-compression-gzip-brotli-deflate/
编辑:链接现在已经下线,但您可以在此处查看代码/内容:https://web.archive.org/web/20190608161201/https://krzysztofjakielaszek.com/2017/03/26/webapi2-response-compression-gzip-brotli-deflate/)
相反,我们发现了这篇由Ben Foster撰写的优秀文章(http://benfoster.io/blog/aspnet-web-api-compression)。如果您可以修改applicationHost.config(运行自己的服务器),您可以打开该配置文件并添加您想要压缩的mimeTypes(我从我们的Web.Config中根据API返回给客户端的内容提取了相关的内容)。保存该文件,IIS将获取您的更改,回收应用程序池,然后您的WebAPI将开始返回经过gzip压缩的响应,以满足请求它的客户端。
如果您没有看到gzipped响应,请使用Fiddler或Chrome / Firefox Dev工具检查响应内容类型,并确保其与您添加的内容匹配。我不得不在Chrome Dev Tools中更改视图模式(使用大请求行)以确保它显示总大小与传输大小。如果一切验证都正确,请尝试重新启动服务器以确保已正确应用。我曾经遇到一个语法错误,在我打开站点时,IIS弹出了一个有关配置文件中需要修复的解析错误的消息。
<httpCompression directory="%TEMP%\iisexpress\IIS Temporary Compressed Files">
<scheme name="gzip" dll="%IIS_BIN%\gzip.dll" />
<dynamicTypes>
...
<!-- compress JSON responses from Web API -->
<add mimeType="application/json" enabled="true" />
...
</dynamicTypes>
<staticTypes>
...
</staticTypes>
</httpCompression>
如果您无法访问共享主机 - 最终的IIS实例。您可以创建一个HttpModule,将以下代码添加到每个HttpApplication.Begin_Request事件中:
HttpContext context = HttpContext.Current;
context.Response.Filter = new GZipStream(context.Response.Filter, CompressionMode.Compress);
HttpContext.Current.Response.AppendHeader("Content-encoding", "gzip");
HttpContext.Current.Response.Cache.VaryByHeaders["Accept-encoding"] = true;
我的一些动态SOAP请求最近开始失控。未经压缩的SOAP约为14MB,压缩后约为3MB。
我注意到,在Fiddler中,当我在Transformer下压缩我的请求时,它变成了约470KB,而不是3MB——所以我想肯定有某种方法可以获得更好的压缩效果。
最终找到了这篇非常信息丰富的博客文章:
http://weblogs.asp.net/owscott/iis-7-compression-good-bad-how-much
然后我执行了以下命令(接着运行iisreset):
C:\Windows\System32\Inetsrv\Appcmd.exe set config -section:httpCompression -[name='gzip'].staticCompressionLevel:9 -[name='gzip'].dynamicCompressionLevel:9
将动态级别改为9,现在我的压缩SOAP与Fiddler给我的匹配了,大约只有现有压缩文件大小的1/7。
结果因情况而异,但对于SOAP来说,这是一个巨大的进步。