我在我的应用程序中遇到了一些内存泄漏问题。第一次怀疑内存泄漏是当我通过点击一个按钮来启动新的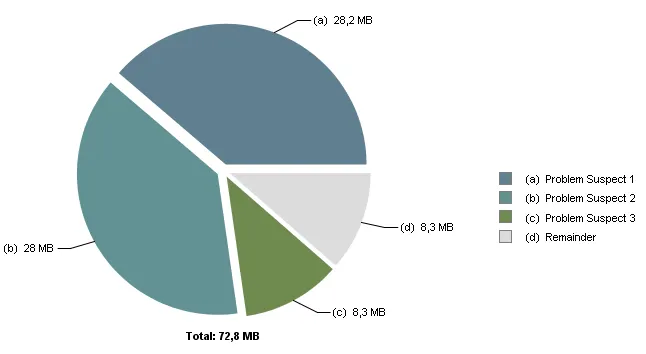 以及内存泄漏的描述:
可疑点1:
由""加载的122个实例的“android.widget.LinearLayout”占据29,585,384(38.74%)字节。
以及内存泄漏的描述:
可疑点1:
由""加载的122个实例的“android.widget.LinearLayout”占据29,585,384(38.74%)字节。
最大的实例:
嫌疑人3
我的第一个想法是查看
然后我查看了支配树,这是结果: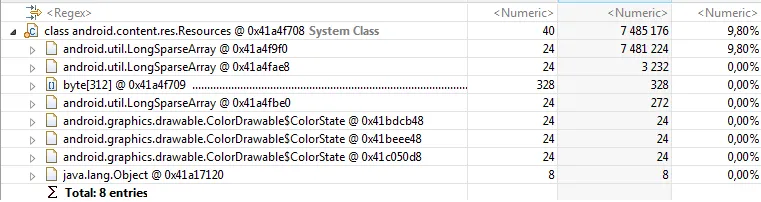 这只是列表中的第一个条目,但这是最大的一个。
这只是列表中的第一个条目,但这是最大的一个。
有了这些信息,有人能给我指点如何追踪内存泄漏吗?如果需要添加其他信息,请在评论中添加。
提前感谢。
编辑
问题可能出现在我的基类中。所有活动都从这个类继承。这个类的工作是在左上角设置一个SlidingMenu。这是这个类的代码:
Activity,对我的应用程序进行压力测试时。使用DDMS并倾卸出.hprof文件后,我打开了这个文件,并使用Eclipse Memory Analyzer得到了三个可能的内存泄漏,如图饼状图所示:
 以及内存泄漏的描述:
可疑点1:
由""加载的122个实例的“android.widget.LinearLayout”占据29,585,384(38.74%)字节。
以及内存泄漏的描述:
可疑点1:
由""加载的122个实例的“android.widget.LinearLayout”占据29,585,384(38.74%)字节。最大的实例:
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x4258c008 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x425c8688 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x425e3988 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x4296e198 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x429d3aa8 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x42a10c78 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x448a1f10 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x44a65d58 - 2 268 848 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x42a14098 - 2 268 824 (2,97%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x4258bd30 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x425c83b0 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x425ddff8 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x4296df80 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x42a109a0 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x42a13dc0 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x448a1c38 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x448cc338 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
•android.widget.LinearLayout @ 0x44a65a80 - 999 528 (1,31%) bytes.
嫌疑人2
有15个实例是由“”加载的"android.widget.FrameLayout",占用了29,405,016(38.51%)字节。
最大的实例:
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x4245b490 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x4247a330 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x425aa1d8 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x425df8b0 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x425efe68 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x42627590 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x42987a70 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x4299df20 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
•android.widget.FrameLayout @ 0x448b6f28 - 3 266 728 (4,28%) bytes.
嫌疑人3
2 682 instances of "java.lang.Class", loaded by "<system class loader>" occupy 8 662 744 (11,34%) bytes.
Biggest instances:
•class android.content.res.Resources @ 0x41a4f708 - 7 485 176 (9,80%) bytes.
我的第一个想法是查看
R.java文件,因为我可以看到一些可能的内存泄漏的十六进制引用。我试图在Eclipse Memory Analyzer中搜索这个十六进制字符串,但我无法在R.java文件中找到这些地址。然后我查看了支配树,这是结果:
 这只是列表中的第一个条目,但这是最大的一个。
这只是列表中的第一个条目,但这是最大的一个。有了这些信息,有人能给我指点如何追踪内存泄漏吗?如果需要添加其他信息,请在评论中添加。
提前感谢。
编辑
问题可能出现在我的基类中。所有活动都从这个类继承。这个类的工作是在左上角设置一个SlidingMenu。这是这个类的代码:
public class Base extends Activity implements OnSlideMenuItemClickListener {
public SlideMenu slidemenu;
ImageButton b;
Time t;
BluetoothCommunicator btCom;
BroadcastReceiver btBroadCaster;
MonitorBluetoothState bluetoothState;
public void setTab(int id) {
setContentView(id);
overridePendingTransition(R.anim.activityfade, R.anim.activityfadeout);
slidemenu = (SlideMenu) findViewById(R.id.slideMenu);
slidemenu.init(this, R.menu.slide, this, 450);
slidemenu.setHeaderImage(getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.ic_launcher));
b = (ImageButton) findViewById(R.id.BtnSlide);
b.setOnClickListener(new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v) {
slidemenu.show();
}
});
b.setOnTouchListener(new OnTouchListener() {
@Override
public boolean onTouch(View v, MotionEvent event) {
switch (event.getAction()) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
b.setImageResource(R.drawable.lincolor);
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
b.setImageResource(R.drawable.lin);
break;
}
return false;
}
});
}
@Override
public void onSlideMenuItemClick(int itemId) {
Class<?> cls = null;
switch(itemId) {
case R.id.item_one:
cls = Home.class;
break;
case R.id.item_two:
cls = History.class;
break;
case R.id.item_three:
cls = ClearHistoryDialog.class;
break;
case R.id.item_four:
cls = SendLogDialog.class;
break;
case R.id.item_five:
cls = PasswordDialog.class;
break;
case R.id.item_six:
cls = About.class;
break;
}
Intent intent = new Intent(this, cls);
startActivity(intent);
}
}
在我的其他活动中,这个setTab方法会像这样被调用:
public class Main extends Base {
public void onCreate(Bundle b) {
super.onCreate(b);
super.setTab(R.layout.Home);
}
}
家庭布局如下:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/parent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:background="#e4e8ed"
android:gravity="top" >
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/first"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:padding="0px" >
<include
android:id="@+id/tabBar"
layout="@layout/tab" />
<com.workspace.tobias
android:id="@+id/slideMenu"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent" />
<Button
android:id="@+id/nist"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="67dp"
android:layout_gravity="center_horizontal"
android:layout_marginBottom="3dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="3dp"
android:layout_marginRight="3dp"
android:layout_marginTop="3dp"
android:background="@drawable/ready"
android:textColor="#FFFFFF" />
<ListView
android:id="@+id/lastCases"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent" />
</LinearLayout>
<LinearLayout
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:id="@+id/loading"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_centerHorizontal="true"
android:layout_marginTop="300dp"
android:orientation="horizontal" >
<ProgressBar
android:id="@+id/progress"
android:layout_width="wrap_content"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:indeterminate="true" />
<TextView
android:id="@+id/loadingCases"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_gravity="center_vertical"
android:text="@string/Loading"
android:textColor="#707070"
android:textSize="18dp"
android:layout_marginLeft="10dp" />
</LinearLayout>
</RelativeLayout>
null。 - Tobias Moe Thorstensen