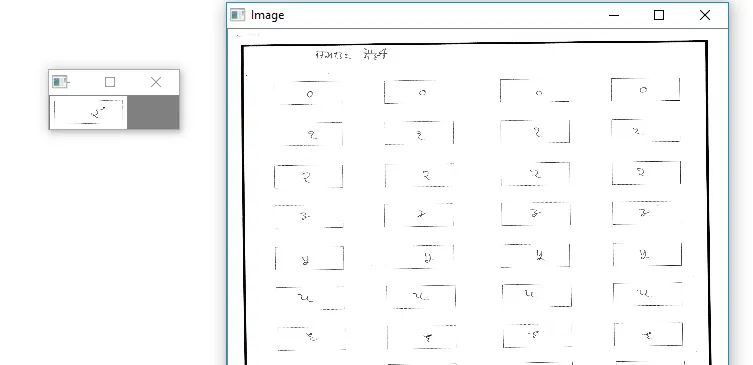
我有很多手写数字的扫描图像,位于一个小矩形内。
请帮我裁剪包含数字的每张图片,并通过为每行赋予相同的名称来保存它们。import cv2
img = cv2.imread('Data\Scan_20170612_4.jpg')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
gray = cv2.bilateralFilter(gray, 11, 17, 17)
edged = cv2.Canny(gray, 30, 200)
_, contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(edged, cv2.RETR_LIST, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
i = 0
for c in contours:
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.09 * peri, True)
if len(approx) == 4:
screenCnt = approx
cv2.drawContours(img, [screenCnt], -1, (0, 255, 0), 3)
cv2.imwrite('cropped\\' + str(i) + '_img.jpg', img)
i += 1