我想在一个矩形对象中画一个渐变,给定一个角度(Theta),让渐变的两端触及矩形的周长。
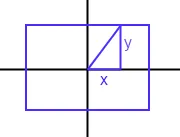
我认为使用正切函数会起作用,但是我无法消除其中的错误。有没有易于实现的算法?
最终结果
因此,这将是(angle, RectX1, RectX2, RectY1, RectY2)的一个函数。我希望以[x1, x2, y1, y2]的形式返回,以便渐变跨越整个正方形。 在我的问题中,如果原点为0,则x2=-x1且y2=-y1。但不总是在原点上。
我想在一个矩形对象中画一个渐变,给定一个角度(Theta),让渐变的两端触及矩形的周长。

我认为使用正切函数会起作用,但是我无法消除其中的错误。有没有易于实现的算法?
最终结果
因此,这将是(angle, RectX1, RectX2, RectY1, RectY2)的一个函数。我希望以[x1, x2, y1, y2]的形式返回,以便渐变跨越整个正方形。 在我的问题中,如果原点为0,则x2=-x1且y2=-y1。但不总是在原点上。
让我们称矩形的边为a和b,(x0,y0)是矩形中心的坐标。
您需要考虑四个区域:
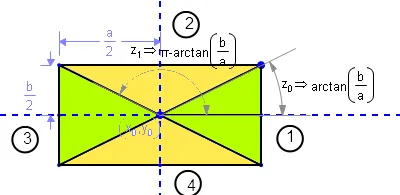
区域 起点 终点 位置
====================================================================
1 -arctan(b/a) +arctan(b/a) 右侧绿色三角形
2 +arctan(b/a) π-arctan(b/a) 上方黄色三角形
3 π-arctan(b/a) π+arctan(b/a) 左侧绿色三角形
4 π+arctan(b/a) -arctan(b/a) 下方黄色三角形
通过一些三角运算技巧,我们可以在每个区域中得出所需交点的坐标:
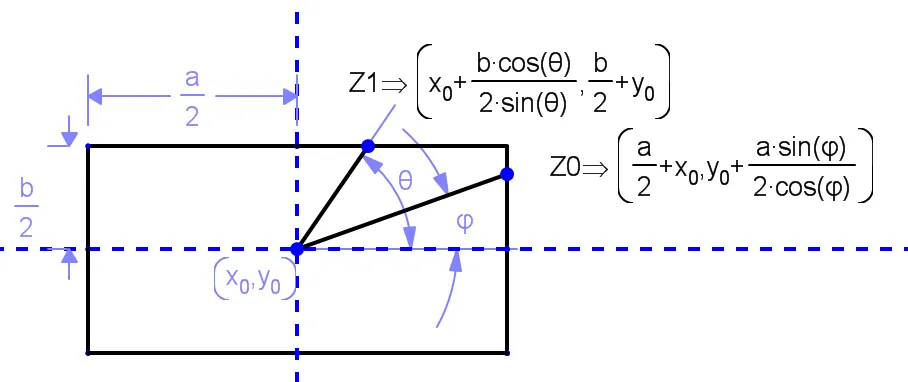
因此,当处于第1和第3区域时,Z0是交点的表达式。
当处于第2和第4区域时,Z1是交点的表达式。
所需的线从(X0,Y0)到Z0或Z1,具体取决于所处的区域。 因此,请记住Tan(φ)=Sin(φ)/Cos(φ):
区域中的线段 起点 终点
======================================================================
1 和 3 (X0,Y0) (X0 + a/2 , (a/2 * Tan(φ))+ Y0
2 和 4 (X0,Y0) (X0 + b/(2* Tan(φ)) , b/2 + Y0)
请注意每个象限中Tan(φ)的符号以及角度始终是从正X轴逆时针测量的。
希望对您有所帮助!
x(end)=X0 - a/2(请注意减号而非加号)。同样地,在区域4中,Y值的计算方式为Y(end)=Y0 - b/2。 - Felix Alcala好的,呼!,我终于搞定了。
注意:我是基于belisarius棒极了的答案进行的。如果你喜欢这个,也请点赞他的回答。我所做的只是把他说的话转化成代码。
下面是Objective-C的样子。将它转换为你最喜欢的语言应该很简单。
+ (CGPoint) edgeOfView: (UIView*) view atAngle: (float) theta
{
// Move theta to range -M_PI .. M_PI
const double twoPI = M_PI * 2.;
while (theta < -M_PI)
{
theta += twoPI;
}
while (theta > M_PI)
{
theta -= twoPI;
}
// find edge ofview
// Ref: https://dev59.com/Tm855IYBdhLWcg3w-JMr
float aa = view.bounds.size.width; // "a" in the diagram
float bb = view.bounds.size.height; // "b"
// Find our region (diagram)
float rectAtan = atan2f(bb, aa);
float tanTheta = tan(theta);
int region;
if ((theta > -rectAtan)
&& (theta <= rectAtan) )
{
region = 1;
}
else if ((theta > rectAtan)
&& (theta <= (M_PI - rectAtan)) )
{
region = 2;
}
else if ((theta > (M_PI - rectAtan))
|| (theta <= -(M_PI - rectAtan)) )
{
region = 3;
}
else
{
region = 4;
}
CGPoint edgePoint = view.center;
float xFactor = 1;
float yFactor = 1;
switch (region)
{
case 1: yFactor = -1; break;
case 2: yFactor = -1; break;
case 3: xFactor = -1; break;
case 4: xFactor = -1; break;
}
if ((region == 1)
|| (region == 3) )
{
edgePoint.x += xFactor * (aa / 2.); // "Z0"
edgePoint.y += yFactor * (aa / 2.) * tanTheta;
}
else // region 2 or 4
{
edgePoint.x += xFactor * (bb / (2. * tanTheta)); // "Z1"
edgePoint.y += yFactor * (bb / 2.);
}
return edgePoint;
}
此外,我创建了一个小的测试视图来验证其工作情况。创建此视图并将其放在某个地方,它将使另一个小视图在边缘周围移动。
@interface DebugEdgeView()
{
int degrees;
UIView *dotView;
NSTimer *timer;
}
@end
@implementation DebugEdgeView
- (void) dealloc
{
[timer invalidate];
}
- (id) initWithFrame: (CGRect) frame
{
self = [super initWithFrame: frame];
if (self)
{
self.backgroundColor = [[UIColor magentaColor] colorWithAlphaComponent: 0.25];
degrees = 0;
self.clipsToBounds = NO;
// create subview dot
CGRect dotRect = CGRectMake(frame.size.width / 2., frame.size.height / 2., 20, 20);
dotView = [[DotView alloc] initWithFrame: dotRect];
dotView.backgroundColor = [UIColor magentaColor];
[self addSubview: dotView];
// move it around our edges
timer = [NSTimer scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval: (5. / 360.)
target: self
selector: @selector(timerFired:)
userInfo: nil
repeats: YES];
}
return self;
}
- (void) timerFired: (NSTimer*) timer
{
float radians = ++degrees * M_PI / 180.;
if (degrees > 360)
{
degrees -= 360;
}
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
CGPoint edgePoint = [MFUtils edgeOfView: self atAngle: radians];
edgePoint.x += (self.bounds.size.width / 2.) - self.center.x;
edgePoint.y += (self.bounds.size.height / 2.) - self.center.y;
dotView.center = edgePoint;
});
}
@end
Javascript 版本:
function edgeOfView(rect, deg) {
var twoPI = Math.PI*2;
var theta = deg * Math.PI / 180;
while (theta < -Math.PI) {
theta += twoPI;
}
while (theta > Math.PI) {
theta -= twoPI;
}
var rectAtan = Math.atan2(rect.height, rect.width);
var tanTheta = Math.tan(theta);
var region;
if ((theta > -rectAtan) && (theta <= rectAtan)) {
region = 1;
} else if ((theta > rectAtan) && (theta <= (Math.PI - rectAtan))) {
region = 2;
} else if ((theta > (Math.PI - rectAtan)) || (theta <= -(Math.PI - rectAtan))) {
region = 3;
} else {
region = 4;
}
var edgePoint = {x: rect.width/2, y: rect.height/2};
var xFactor = 1;
var yFactor = 1;
switch (region) {
case 1: yFactor = -1; break;
case 2: yFactor = -1; break;
case 3: xFactor = -1; break;
case 4: xFactor = -1; break;
}
if ((region === 1) || (region === 3)) {
edgePoint.x += xFactor * (rect.width / 2.); // "Z0"
edgePoint.y += yFactor * (rect.width / 2.) * tanTheta;
} else {
edgePoint.x += xFactor * (rect.height / (2. * tanTheta)); // "Z1"
edgePoint.y += yFactor * (rect.height / 2.);
}
return edgePoint;
};这个问题有一个很好的(更加编程化的iOS/Objective-C)答案,可以在Find the CGPoint on a UIView rectangle intersected by a straight line at a given angle from the center point找到,其中包括以下步骤:
虚幻引擎4(UE4)C++版本。
注意:这是基于Olie的代码。基于Belisarius的答案。如果这对你有帮助,请给这些人点赞。
更改:使用UE4语法和函数,并且角度被取反。
头文件
UFUNCTION(BlueprintCallable, meta = (DisplayName = "Project To Rectangle Edge (Radians)"), Category = "Math|Geometry")
static void ProjectToRectangleEdgeRadians(FVector2D Extents, float Angle, FVector2D & EdgeLocation);
代码
void UFunctionLibrary::ProjectToRectangleEdgeRadians(FVector2D Extents, float Angle, FVector2D & EdgeLocation)
{
// Move theta to range -M_PI .. M_PI. Also negate the angle to work as expected.
float theta = FMath::UnwindRadians(-Angle);
// Ref: https://dev59.com/Tm855IYBdhLWcg3w-JMr
float a = Extents.X; // "a" in the diagram | Width
float b = Extents.Y; // "b" | Height
// Find our region (diagram)
float rectAtan = FMath::Atan2(b, a);
float tanTheta = FMath::Tan(theta);
int region;
if ((theta > -rectAtan) && (theta <= rectAtan))
{
region = 1;
}
else if ((theta > rectAtan) && (theta <= (PI - rectAtan)))
{
region = 2;
}
else if ((theta > (PI - rectAtan)) || (theta <= -(PI - rectAtan)))
{
region = 3;
}
else
{
region = 4;
}
float xFactor = 1.f;
float yFactor = 1.f;
switch (region)
{
case 1: yFactor = -1; break;
case 2: yFactor = -1; break;
case 3: xFactor = -1; break;
case 4: xFactor = -1; break;
}
EdgeLocation = FVector2D(0.f, 0.f); // This rese is nessesary, UE might re-use otherwise.
if (region == 1 || region == 3)
{
EdgeLocation.X += xFactor * (a / 2.f); // "Z0"
EdgeLocation.Y += yFactor * (a / 2.f) * tanTheta;
}
else // region 2 or 4
{
EdgeLocation.X += xFactor * (b / (2.f * tanTheta)); // "Z1"
EdgeLocation.Y += yFactor * (b / 2.f);
}
}
对于Java,LibGDX。我已经将角度设置为double类型以增加精度。
public static Vector2 projectToRectEdge(double angle, float width, float height, Vector2 out)
{
return projectToRectEdgeRad(Math.toRadians(angle), width, height, out);
}
public static Vector2 projectToRectEdgeRad(double angle, float width, float height, Vector2 out)
{
float theta = negMod((float)angle + MathUtils.PI, MathUtils.PI2) - MathUtils.PI;
float diag = MathUtils.atan2(height, width);
float tangent = (float)Math.tan(angle);
if (theta > -diag && theta <= diag)
{
out.x = width / 2f;
out.y = width / 2f * tangent;
}
else if(theta > diag && theta <= MathUtils.PI - diag)
{
out.x = height / 2f / tangent;
out.y = height / 2f;
}
else if(theta > MathUtils.PI - diag && theta <= MathUtils.PI + diag)
{
out.x = -width / 2f;
out.y = -width / 2f * tangent;
}
else
{
out.x = -height / 2f / tangent;
out.y = -height / 2f;
}
return out;
}
PYTHON
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
twoPI = math.pi * 2.0
PI = math.pi
def get_points(width, height, theta):
theta %= twoPI
aa = width
bb = height
rectAtan = math.atan2(bb,aa)
tanTheta = math.tan(theta)
xFactor = 1
yFactor = 1
# determine regions
if theta > twoPI-rectAtan or theta <= rectAtan:
region = 1
elif theta > rectAtan and theta <= PI-rectAtan:
region = 2
elif theta > PI - rectAtan and theta <= PI + rectAtan:
region = 3
xFactor = -1
yFactor = -1
elif theta > PI + rectAtan and theta < twoPI - rectAtan:
region = 4
xFactor = -1
yFactor = -1
else:
print(f"region assign failed : {theta}")
raise
# print(region, xFactor, yFactor)
edgePoint = [0,0]
## calculate points
if (region == 1) or (region == 3):
edgePoint[0] += xFactor * (aa / 2.)
edgePoint[1] += yFactor * (aa / 2.) * tanTheta
else:
edgePoint[0] += xFactor * (bb / (2. * tanTheta))
edgePoint[1] += yFactor * (bb / 2.)
return region, edgePoint
l_x = []
l_y = []
theta = 0
for _ in range(10000):
r, (x, y) = get_points(600,300, theta)
l_x.append(x)
l_y.append(y)
theta += (0.01 / PI)
if _ % 100 == 0:
print(r, x,y)
plt.plot(l_x, l_y)
plt.show()
Unity C#(从Winter的Java代码转换而来)
public Vector2 DetermineRectangleEdge(float aDegrees, float aWidth, float aHeight) {
if (aDegrees < -90)
aDegrees += 360f;
float ANGLE = Mathf.Deg2Rad * aDegrees;
float diag = Mathf.Atan2(aHeight, aWidth);
float tangent = Mathf.Tan(ANGLE);
Vector2 OUT = Vector2.zero;
if (ANGLE > -diag && ANGLE <= diag)
{
OUT.x = aWidth / 2f;
OUT.y = aWidth / 2f * tangent;
_ObjectRectTransform.sizeDelta = _VerticalSize;
}
else if(ANGLE > diag && ANGLE <= Mathf.PI - diag)
{
OUT.x = aHeight / 2f / tangent;
OUT.y = aHeight / 2f;
_ObjectRectTransform.sizeDelta = _HorizontalSize;
}
else if(ANGLE > Mathf.PI - diag && ANGLE <= Mathf.PI + diag)
{
OUT.x = -aWidth / 2f;
OUT.y = -aWidth / 2f * tangent;
_ObjectRectTransform.sizeDelta = _VerticalSize;
}
else
{
OUT.x = -aHeight / 2f / tangent;
OUT.y = -aHeight / 2f;
_ObjectRectTransform.sizeDelta = _HorizontalSize;
}
return OUT;
}