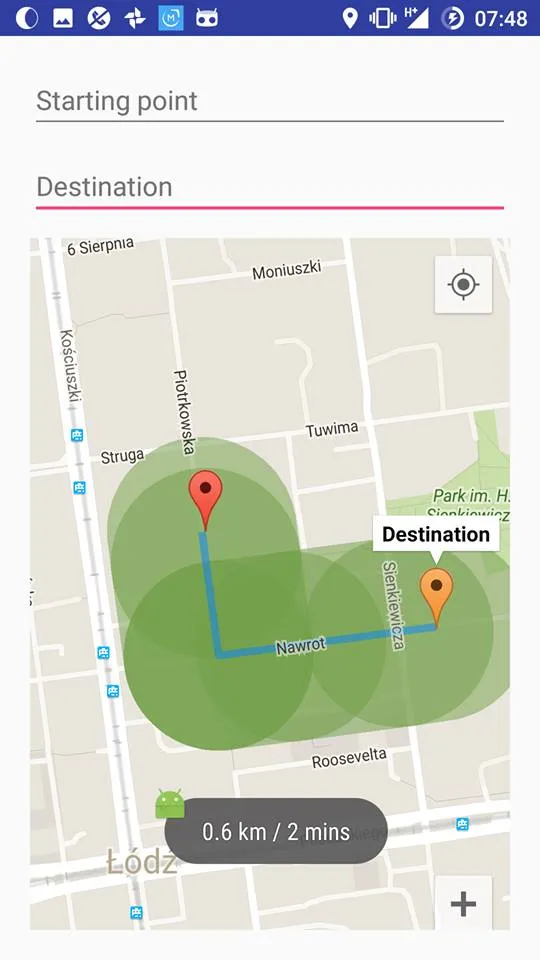
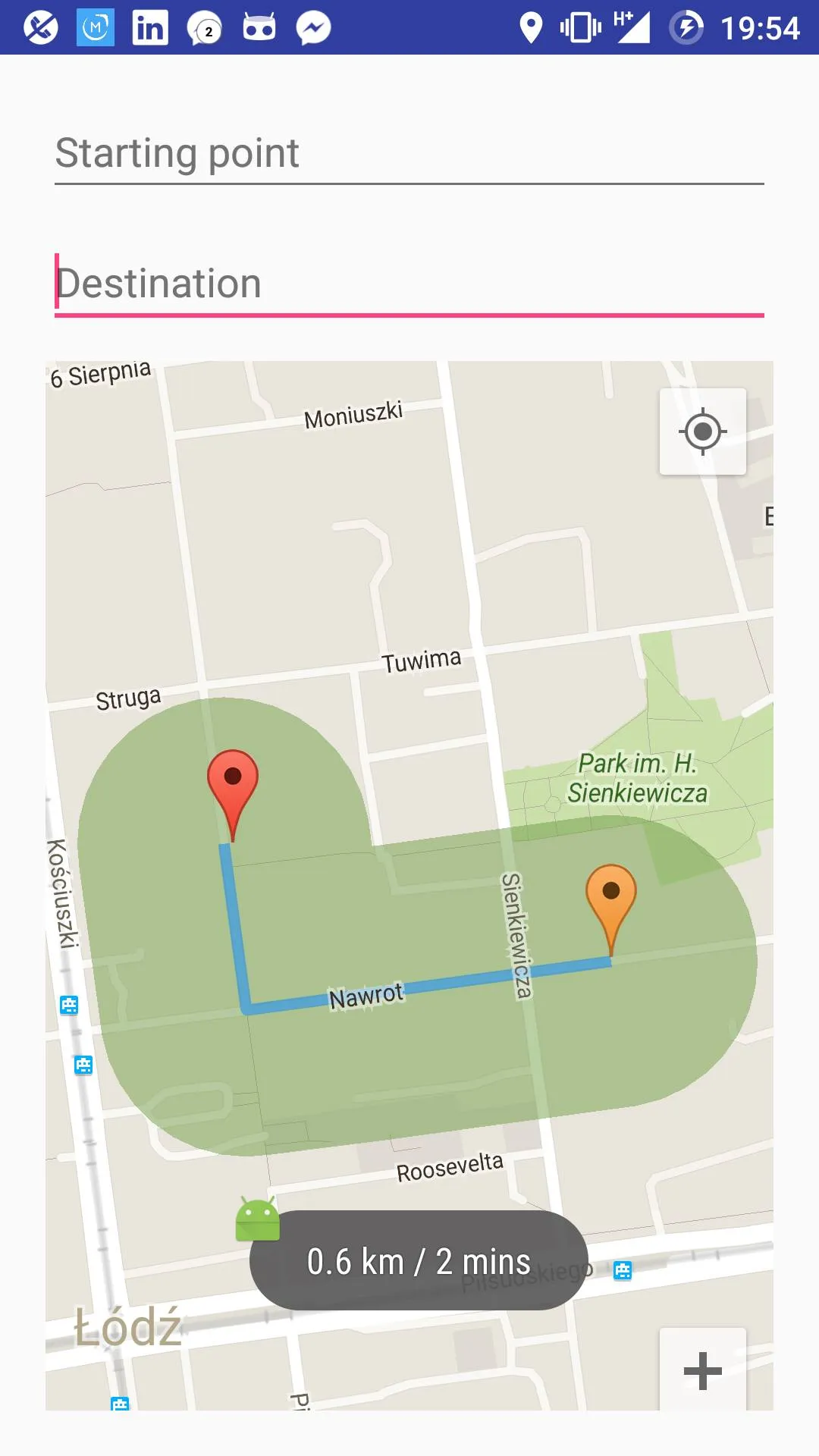
我正在尝试绘制一个复杂的多边形,围绕着一条路线,按照给定的半径跟随其步骤。为此,我在路线的每个步骤(坐标)周围绘制了50边形的均匀多边形(实际上是圆形)。现在,我获得了所有绘制在路线周围的圆圈的坐标集,我可以在地图上看到它们,但它们重叠在一起,这不太好看,而且在地图上添加如此大量的覆盖物也不是一个好的做法。
现在我需要做的是将我现有的所有多边形合并成一个多边形,并在地图上绘制它。
我尝试删除每两个多边形的交点(测试多边形1的点是否位于多边形2内,反之亦然),并将其余的坐标合并到一个数组中,然后构建我的新多边形,但它没有成功。以下是我如何执行此操作的代码片段:
我尝试删除每两个多边形的交点(测试多边形1的点是否位于多边形2内,反之亦然),并将其余的坐标合并到一个数组中,然后构建我的新多边形,但它没有成功。以下是我如何执行此操作的代码片段:
public ArrayList<PolygonOptions> polygons = new ArrayList<>();
// lineOptions is the set of route coordinates
for (int i = 0; i < lineOptions.getPoints().size() - 1; i++) {
// Draw a circle around each point of the route
PolygonOptions circle1 = drawCircle(lineOptions.getPoints().get(i), 0.1);
PolygonOptions circle2 = drawCircle(lineOptions.getPoints().get(i + 1), 0.1);
// Draw a convex hull between every two successive circles
PolygonOptions convexHull = convexHull(circle1, circle2);
convexHull.strokeWidth(0);
convexHull.fillColor(0x7F729E47);
activity.range.add(activity.mMap.addPolygon(convexHull));
polygons.add(convexHull);
}
if (polygons.size() == 1) {
pts.addAll(polygons.get(0).getPoints());
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < polygons.size() - 1; i++) {
ArrayList<LatLng> pts1 = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<LatLng> pts2 = new ArrayList<>();
pts1.addAll(polygons.get(i).getPoints());
pts2.addAll(polygons.get(i + 1).getPoints());
for (int j = 0; j < pts1.size(); j++) {
if (pointInPolygon(pts1.get(j), pts2)) {
pts1.remove(j);
}
}
for (int j = 0; j < pts2.size(); j++) {
if (pointInPolygon(pts2.get(j), pts1)) {
pts2.remove(j);
}
}
pts.addAll(pts1);
pts.addAll(pts2);
}
}
// This part didn't work
// PolygonOptions range = new PolygonOptions();
// range.addAll(pts);
// range.strokeWidth(0);
// range.fillColor(0x7F729E47);
// activity.range.add(activity.mMap.addPolygon(range));