使用VisualVM并检查Tomcat 8.5的catalina.out日志,我发现几乎每次(大约11次中有7次)进行full GC时,日志都会显示OutOfMemory(在完全相同的时间点)。
使用与内存管理相关的Tomcat参数:-Xms3G -Xmx=6G -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+UseStringDeduplication -XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=100
起初,我认为这是由于默认的-XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio值(为70),因为我看到最大堆大小(和已使用的堆当然)在full GC期间会显著下降 - 至10-20%左右。但是添加XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=100并没有解决它。
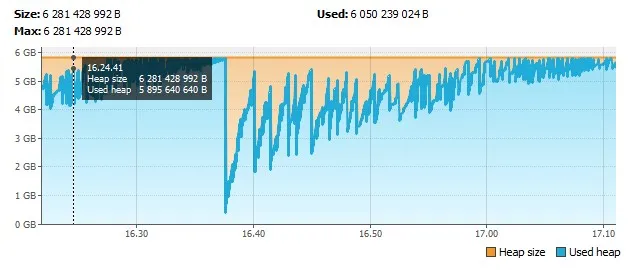
尽管这是一张使用不同的JVM参数(目前无法获得旧JVM参数的图表)的内存使用情况图表,但在进行完全GC后,内存使用情况迅速增长,最大堆大小相同且该最大堆大小不会下降。 任何想法为什么会发生这种情况?
更新:我忘了提到之前当堆大小没有达到满时,就会发生完整的GC和OutOfMemory-大约5GB。在那时,我从未见过堆达到6GB。
使用与内存管理相关的Tomcat参数:-Xms3G -Xmx=6G -XX:+UseG1GC -XX:+UseStringDeduplication -XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=100
起初,我认为这是由于默认的-XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio值(为70),因为我看到最大堆大小(和已使用的堆当然)在full GC期间会显著下降 - 至10-20%左右。但是添加XX:MaxHeapFreeRatio=100并没有解决它。
尽管这是一张使用不同的JVM参数(目前无法获得旧JVM参数的图表)的内存使用情况图表,但在进行完全GC后,内存使用情况迅速增长,最大堆大小相同且该最大堆大小不会下降。 任何想法为什么会发生这种情况?
更新:我忘了提到之前当堆大小没有达到满时,就会发生完整的GC和OutOfMemory-大约5GB。在那时,我从未见过堆达到6GB。