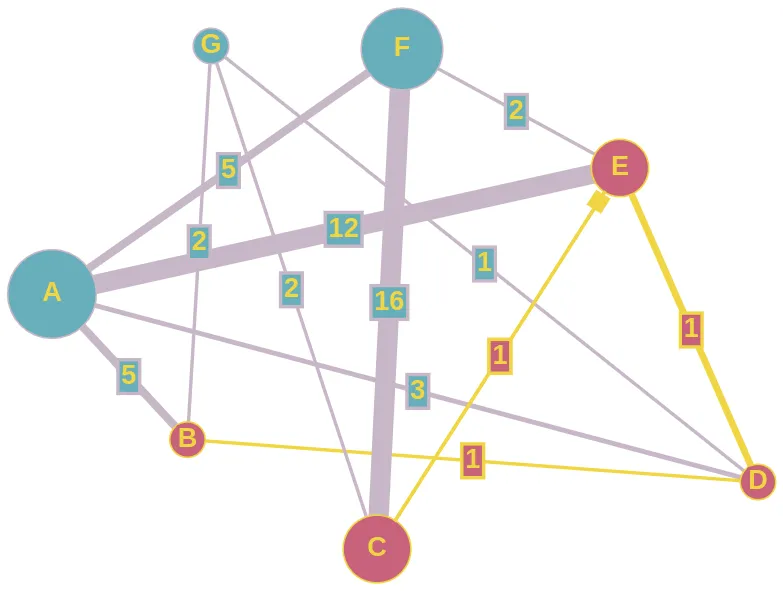
我正在尝试使用数组在Python中实现Dijkstra算法。这是我的实现。
def extract(Q, w):
m=0
minimum=w[0]
for i in range(len(w)):
if w[i]<minimum:
minimum=w[i]
m=i
return m, Q[m]
def dijkstra(G, s, t='B'):
Q=[s]
p={s:None}
w=[0]
d={}
for i in G:
d[i]=float('inf')
Q.append(i)
w.append(d[i])
d[s]=0
S=[]
n=len(Q)
while Q:
u=extract(Q,w)[1]
S.append(u)
#w.remove(extract(Q, d, w)[0])
Q.remove(u)
for v in G[u]:
if d[v]>=d[u]+G[u][v]:
d[v]=d[u]+G[u][v]
p[v]=u
return d, p
B='B'
A='A'
D='D'
G='G'
E='E'
C='C'
F='F'
G={B:{A:5, D:1, G:2}, A:{B:5, D:3, E:12, F:5}, D:{B:1, G:1, E:1, A:3}, G:{B:2, D:1, C:2}, C:{G:2, E:1, F:16}, E:{A:12, D:1, C:1, F:2}, F:{A:5, E:2, C:16}}
print "Assuming the start vertex to be B:"
print "Shortest distances", dijkstra(G, B)[0]
print "Parents", dijkstra(G, B)[1]
我期望你的答案是:
Assuming the start vertex to be B:
Shortest distances {'A': 4, 'C': 4, 'B': 0, 'E': 2, 'D': 1, 'G': 2, 'F': 4}
Parents {'A': 'D', 'C': 'G', 'B': None, 'E': 'D', 'D': 'B', 'G': 'D', 'F': 'E'}
然而,我得到的答案是:
Assuming the start vertex to be B:
Shortest distances {'A': 4, 'C': 4, 'B': 0, 'E': 2, 'D': 1, 'G': 2, 'F': 10}
Parents {'A': 'D', 'C': 'G', 'B': None, 'E': 'D', 'D': 'B', 'G': 'D', 'F': 'A'}.
对于节点 F,程序给出了错误的答案。请问有人能告诉我原因吗?