a) 不是最高效的方法,但很容易写成一行代码。
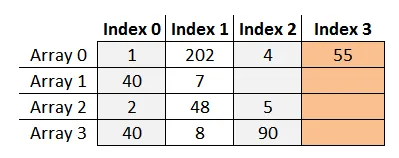
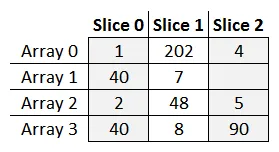
var arr1 = new int[] { 1, 202, 4, 55 };
var arr2 = new int[] { 40, 7 };
var arr3 = new int[] { 2, 48, 5 };
var arr4 = new int[] { 40, 8, 90 };
var max = new int[][] { arr1, arr2, arr3, arr4 }
.Select(arr => new {
IArray = arr,
SArray = String.Join("",arr.Select(i => i.ToString("X8")))
})
.OrderByDescending(x => x.SArray)
.First()
.IArray;
b) 通过实现`IComparer`实现更好的效果
public class ArrayComparer : IComparer<int[]>
{
public int Compare(int[] x, int[] y)
{
for(int i=0;i < Math.Min(x.Length,y.Length);i++)
{
if (x[i] > y[i]) return 1;
if (x[i] < y[i]) return -1;
}
return x.Length - y.Length;
}
}
var max2 = new int[][] { arr1, arr2, arr3, arr4 }
.OrderByDescending(x => x, new ArrayComparer())
.First();
c) 最好的选择
var arrays = new int[][] { arr1, arr2, arr3, arr4 };
var max3 = arrays[0];
ArrayComparer comparer = new ArrayComparer();
for (int i = 1; i < arrays.Length; i++)
{
if(comparer.Compare(arrays[i],max3)>0) max3 = arrays[i];
}
d) 通过扩展“Max”来创建通用版本
var max4 = new int[][] { arr1, arr2, arr3, arr4 }
.Max(new SOExtensions.Comparer<int>())
.ToArray();
public static class SOExtensions
{
public static IEnumerable<T> Max<T>(this IEnumerable<IEnumerable<T>> lists, IComparer<IEnumerable<T>> comparer)
{
var max = lists.First();
foreach (var list in lists.Skip(1))
{
if (comparer.Compare(list, max) > 0) max = list;
}
return max;
}
public class Comparer<T> : IComparer<IEnumerable<T>> where T: IComparable<T>
{
public int Compare(IEnumerable<T> x, IEnumerable<T> y)
{
foreach(var ab in x.Zip(y,(a,b)=>new{a,b}))
{
var res=ab.a.CompareTo(ab.b);
if (res != 0) return res;
}
return x.Count() - y.Count();
}
}
}
结论
在我的测试案例中,它们的相对表现为:4000T、270T、T、6T
因此,如果您想要速度,请不要使用利用Sort/OrderBy的算法,因为其成本为O(N*Log(N))(而Max为O(N))。