我找到的大多数Android网络套接字示例只支持单向数据流,而我需要双向数据流的解决方案。最终我了解了AsyncTask。这个示例展示了如何从套接字获取数据并将数据发送回去。由于接收数据的套接字是阻塞的,所以该阻塞需要在UI线程之外的线程中运行。
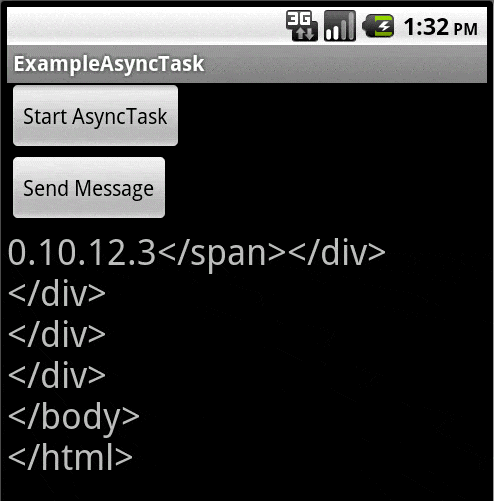
为了举例说明,此代码连接到一个Web服务器。按下“启动AsyncTask”按钮将打开套接字。一旦套接字打开,Web服务器就会等待请求。按下“发送消息”按钮将向服务器发送请求。服务器的任何响应都将显示在TextView中。对于HTTP,请注意,Web服务器会在所有数据发送完毕后与客户端断开连接。对于其他TCP数据流,则会保持连接直到其中一方断开。
屏幕截图:
AndroidManifest.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<manifest xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
package="com.exampleasynctask"
android:versionCode="1"
android:versionName="1.0">
<uses-sdk android:minSdkVersion="8" />
<uses-permission android:name="android.permission.INTERNET" />
<application android:icon="@drawable/icon" android:label="@string/app_name">
<activity android:name=".MainActivity"
android:label="@string/app_name">
<intent-filter>
<action android:name="android.intent.action.MAIN" />
<category android:name="android.intent.category.LAUNCHER" />
</intent-filter>
</activity>
</application>
</manifest>
res\layout\main.xml:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:orientation="vertical"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
>
<Button android:id="@+id/btnStart" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Start AsyncTask"></Button>
<Button android:id="@+id/btnSend" android:layout_width="wrap_content" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Send Message"></Button>
<TextView android:id="@+id/textStatus" android:textSize="24sp" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="Status Goes Here" />
</LinearLayout>
src\com.exampleasynctask\MainActivity.java:
package com.exampleasynctask;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.net.InetSocketAddress;
import java.net.Socket;
import java.net.SocketAddress;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.AsyncTask;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.util.Log;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.View.OnClickListener;
import android.widget.Button;
import android.widget.TextView;
public class MainActivity extends Activity {
Button btnStart, btnSend;
TextView textStatus;
NetworkTask networktask;
@Override
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) {
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
btnStart = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnStart);
btnSend = (Button)findViewById(R.id.btnSend);
textStatus = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.textStatus);
btnStart.setOnClickListener(btnStartListener);
btnSend.setOnClickListener(btnSendListener);
networktask = new NetworkTask(); //Create initial instance so SendDataToNetwork doesn't throw an error.
}
private OnClickListener btnStartListener = new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v){
btnStart.setVisibility(View.INVISIBLE);
networktask = new NetworkTask(); //New instance of NetworkTask
networktask.execute();
}
};
private OnClickListener btnSendListener = new OnClickListener() {
public void onClick(View v){
textStatus.setText("Sending Message to AsyncTask.");
networktask.SendDataToNetwork("GET / HTTP/1.1\r\n\r\n");
}
};
public class NetworkTask extends AsyncTask<Void, byte[], Boolean> {
Socket nsocket; //Network Socket
InputStream nis; //Network Input Stream
OutputStream nos; //Network Output Stream
@Override
protected void onPreExecute() {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "onPreExecute");
}
@Override
protected Boolean doInBackground(Void... params) { //This runs on a different thread
boolean result = false;
try {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "doInBackground: Creating socket");
SocketAddress sockaddr = new InetSocketAddress("192.168.1.1", 80);
nsocket = new Socket();
nsocket.connect(sockaddr, 5000); //10 second connection timeout
if (nsocket.isConnected()) {
nis = nsocket.getInputStream();
nos = nsocket.getOutputStream();
Log.i("AsyncTask", "doInBackground: Socket created, streams assigned");
Log.i("AsyncTask", "doInBackground: Waiting for inital data...");
byte[] buffer = new byte[4096];
int read = nis.read(buffer, 0, 4096); //This is blocking
while(read != -1){
byte[] tempdata = new byte[read];
System.arraycopy(buffer, 0, tempdata, 0, read);
publishProgress(tempdata);
Log.i("AsyncTask", "doInBackground: Got some data");
read = nis.read(buffer, 0, 4096); //This is blocking
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.i("AsyncTask", "doInBackground: IOException");
result = true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
Log.i("AsyncTask", "doInBackground: Exception");
result = true;
} finally {
try {
nis.close();
nos.close();
nsocket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
Log.i("AsyncTask", "doInBackground: Finished");
}
return result;
}
public void SendDataToNetwork(String cmd) { //You run this from the main thread.
try {
if (nsocket.isConnected()) {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "SendDataToNetwork: Writing received message to socket");
nos.write(cmd.getBytes());
} else {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "SendDataToNetwork: Cannot send message. Socket is closed");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "SendDataToNetwork: Message send failed. Caught an exception");
}
}
@Override
protected void onProgressUpdate(byte[]... values) {
if (values.length > 0) {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "onProgressUpdate: " + values[0].length + " bytes received.");
textStatus.setText(new String(values[0]));
}
}
@Override
protected void onCancelled() {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "Cancelled.");
btnStart.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
@Override
protected void onPostExecute(Boolean result) {
if (result) {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "onPostExecute: Completed with an Error.");
textStatus.setText("There was a connection error.");
} else {
Log.i("AsyncTask", "onPostExecute: Completed.");
}
btnStart.setVisibility(View.VISIBLE);
}
}
@Override
protected void onDestroy() {
super.onDestroy();
networktask.cancel(true); //In case the task is currently running
}
}