是的,有一个O(n)算法。
将树视为未根据的图形-每个节点具有双向边,不形成循环。
对于具有相邻节点a_i的给定节点p,我们将计算高度Hpa_i。 Hpa_i的高度是子树的高度
以根p为根(即在此部分算法中,我们暂时考虑将节点a_i视为p的父节点而获得的)。
如果您对每个节点到叶子节点的最长路径感兴趣(您的问题及其标题让人怀疑您实际上要计算什么),则只需max{ Hpa_i for all i }。 相应的i值给出了最长的路径本身。
另一方面,如果您对通过p的最长路径感兴趣,那么它将是从{ len(p--a_i) + Ha_ip for all i }选择的最大对的总和,并且两个相应的i值给出了最长的路径本身。
因此,如果我们拥有每个节点的高度,则获取最终结果就是简单的O(n)工作。
现在需要计算所有节点的高度。为此,从一个特殊的深度优先搜索开始。它接受两个节点作为参数。第一个节点p是正在搜索的节点,第二个节点q ∈ {a_i} 是当前被认为是p的父节点的相邻节点。让U成为将节点对映射到高度的映射:(p, q) -> Hpq
function search_and_label(p, q)
if ((p, q) maps to height Hpq in U ) { return Hpq }
if (p == null) { add (p, q) -> 0 to U and return 0 }
let h = max(all x adjacent to p, not equal to q) {
len(p--x) + search_and_label(x, p)
}
add (p, q) -> h to U
return h
现在我们可以找到所有的高度。
Add mappings (p, x)->null to U for all nodes p and adjacent nodes x
Also add a mapping (p, z)->null to U for all nodes p having < 3 adjacent
while (U contains a mapping of the form (p, x)->null)
search_and_label(p, x)
这将是一个O(n)的计算,因为它在每条边上都花费了恒定的工作量,而树中边的数量为n-1。
代码
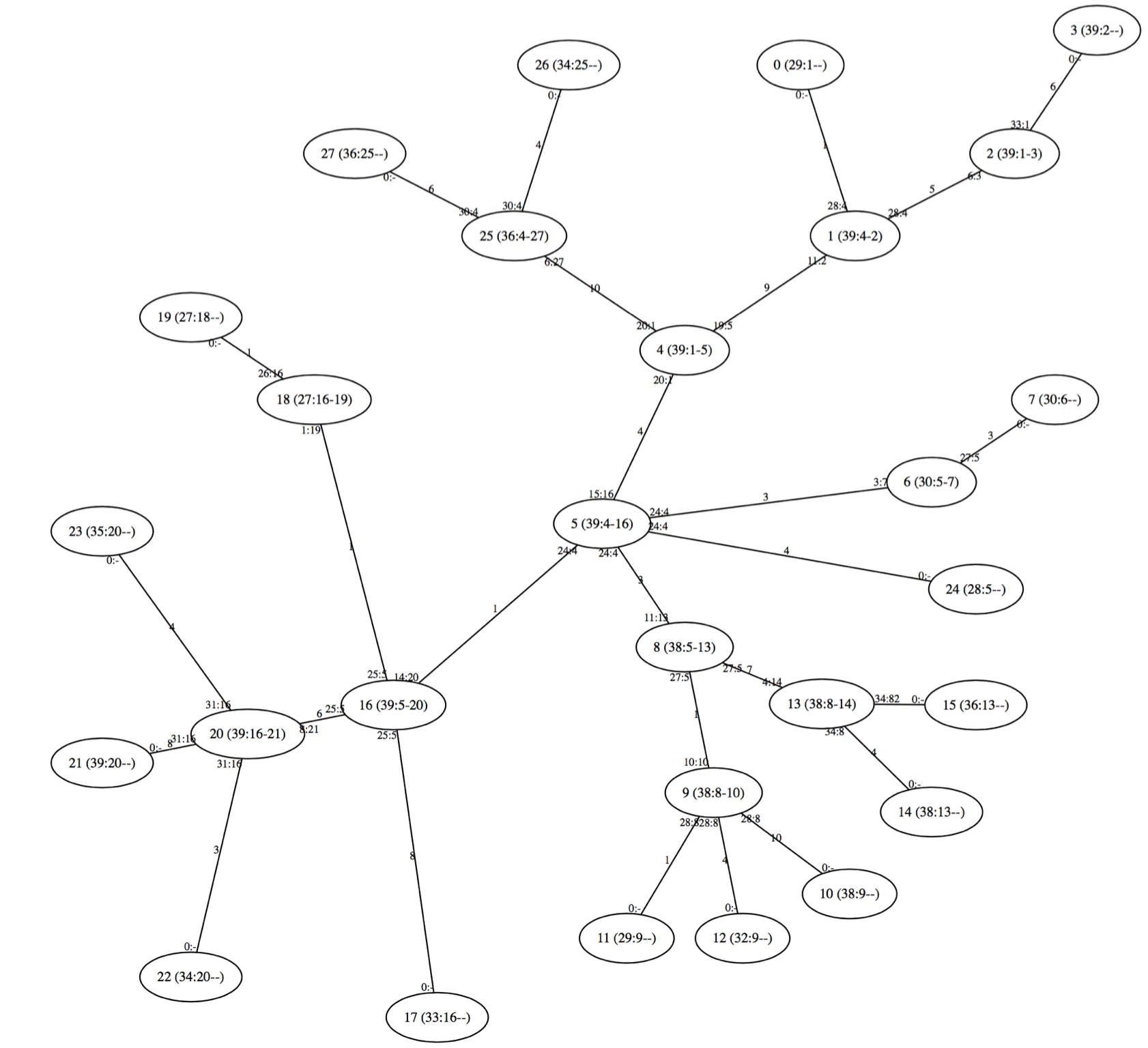
今天下雨了,所以这里有一些代码,可以在O(n)的时间内生成一个随机树并用最长路径信息标记它。首先是典型的输出。每个节点都带有自己的编号,然后是包含它的最长路径的长度,接着是该路径上相邻节点的编号。小的边缘标签是高度信息。首先是相反子树的高度,然后是该子树中最长叶节点路径所在的节点:
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Random;
class Graph {
final Map<Node, Map<Node, EdgeData>> edges = new HashMap<>();
static class Node {
final int id;
Node a, b;
double len;
Node(int i) {
this.id = i;
}
}
static class EdgeData {
final double len;
Double h;
Node next;
EdgeData(double len) {
this.len = len;
}
}
Node addNode() {
Node node = new Node(currentNodeIndex++);
edges.put(node, new HashMap<>());
return node;
}
private int currentNodeIndex = 0;
void addEdge(Node x, Node y, double len) {
edges.get(x).put(y, new EdgeData(len));
edges.get(y).put(x, new EdgeData(len));
}
EdgeData decorateSubtree(Node p, Node q) {
Map<Node, EdgeData> adjacent = edges.get(p);
EdgeData data = adjacent.get(q);
if (data.h == null) {
data.h = 0.0;
for (Map.Entry<Node, EdgeData> x : adjacent.entrySet()) {
if (x.getKey() != q) {
double hNew = x.getValue().len + decorateSubtree(x.getKey(), p).h;
if (hNew > data.h) {
data.h = hNew;
data.next = x.getKey();
}
}
}
}
return data;
}
Node decorateNode(Node p) {
if (p.a == null) {
double ha = 0.0, hb = 0.0;
for (Map.Entry<Node, EdgeData> x : edges.get(p).entrySet()) {
double hNew = x.getValue().len + decorateSubtree(x.getKey(), p).h;
if (hNew > ha) {
p.b = p.a;
hb = ha;
p.a = x.getKey();
ha = hNew;
} else if (hNew > hb) {
p.b = x.getKey();
hb = hNew;
}
}
p.len = ha + hb;
}
return p;
}
void decorateAll() {
for (Node p : edges.keySet()) {
decorateNode(p);
}
}
class RandomTreeBuilder {
final Random gen = new Random();
final long seed;
final float[] partitions;
final int maxLen;
final int radius;
RandomTreeBuilder(long seed, float[] partitions, int maxLen, int radius) {
this.seed = seed;
this.partitions = partitions;
this.maxLen = maxLen;
this.radius = radius;
}
private void growTree(Node p, int radius) {
if (radius > 0) {
float random = gen.nextFloat();
float pSum = 0f;
for (float partition : partitions) {
pSum += partition;
if (random < pSum) {
return;
}
Node q = addNode();
addEdge(p, q, 1 + gen.nextInt(maxLen));
growTree(q, radius - 1);
}
}
}
void build() {
if (seed != 0) {
gen.setSeed(seed);
}
edges.clear();
Node p = addNode();
Node q = addNode();
addEdge(p, q, 1 + gen.nextInt(maxLen));
growTree(p, radius);
growTree(q, radius);
}
}
class TreePrinter {
PrintStream stream;
TreePrinter(PrintStream stream) {
this.stream = stream;
}
void print() {
stream.println("graph tree {");
stream.println(" graph [layout = twopi overlap=false ranksep=1.7]");
Node p = edges.keySet().iterator().next();
Node q = edges.get(p).keySet().iterator().next();
printEdge(p, q);
print(p, q);
print(q, p);
for (Node x : edges.keySet()) {
printNode(decorateNode(x));
}
stream.println("}");
}
private void printEdge(Node p, Node q) {
EdgeData dq = decorateSubtree(p, q);
EdgeData dp = decorateSubtree(q, p);
stream.format(" n%d--n%d [label=\"%.0f\" fontsize=8 "
+ "headlabel=\"%.0f:%s\" taillabel=\"%.0f:%s\"]\n",
p.id, q.id, dq.len,
dp.h, dp.next == null ? "-" : dp.next.id,
dq.h, dq.next == null ? "-" : dq.next.id);
}
private void printNode(Node p) {
stream.format(" n%d [ label=\"%d (%.0f:%s-%s)\" fontsize=10 ]\n",
p.id, p.id, p.len,
p.a == null ? "-" : p.a.id, p.b == null ? "-" : p.b.id);
}
private void print(Node p, Node q) {
for (Node x : edges.get(p).keySet()) {
if (x != q) {
printEdge(p, x);
print(x, p);
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws FileNotFoundException {
PrintStream stream = args.length > 0
? new PrintStream(new File(args[0]))
: System.out;
Graph graph = new Graph();
graph.new RandomTreeBuilder(42L, new float[]{0.3f, 0.1f, 0.3f, 0.2f}, 10, 5)
.build();
graph.new TreePrinter(stream).print();
}
}
