C#,17毫秒,如果你真的想要一个检查。
class Program
{
static bool IsPandigital(int n)
{
int digits = 0; int count = 0; int tmp;
for (; n > 0; n /= 10, ++count)
{
if ((tmp = digits) == (digits |= 1 << (n - ((n / 10) * 10) - 1)))
return false;
}
return digits == (1 << count) - 1;
}
static void Main()
{
int pans = 0;
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
for (int i = 123456789; i <= 123987654; i++)
{
if (IsPandigital(i))
{
pans++;
}
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("{0}pcs, {1}ms", pans, sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
对于在十进制下与维基百科定义一致的检查:
const int min = 1023456789;
const int expected = 1023;
static bool IsPandigital(int n)
{
if (n >= min)
{
int digits = 0;
for (; n > 0; n /= 10)
{
digits |= 1 << (n - ((n / 10) * 10));
}
return digits == expected;
}
return false;
}
为了列举您给定范围内的数字,生成排列即可。以下并不是严格意义上对您问题的回答,因为它没有实现检查。它使用通用的排列实现,未优化这种特殊情况 - 它仍然在13毫秒内生成所需的720个排列(换行可能会混乱):
static partial class Permutation
{
public static IEnumerable<IEnumerable<T>> Permute<T>(T[] items, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
int length = items.Length;
IntPair[] transform = new IntPair[length];
if (comparer == null)
{
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
transform[i] = new IntPair(i, i);
};
}
else
{
int[] initialorder = new int[length];
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
initialorder[i] = i;
}
Array.Sort(initialorder, delegate(int x, int y)
{
return comparer.Compare(items[x], items[y]);
});
for (int i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
transform[i] = new IntPair(initialorder[i], i);
}
for (int i = 1; i < length; i++)
{
if (comparer.Compare(
items[transform[i - 1].Second],
items[transform[i].Second]) == 0)
{
transform[i].First = transform[i - 1].First;
}
}
}
yield return ApplyTransform(items, transform);
while (true)
{
int decreasingpart = length - 2;
for (;decreasingpart >= 0 &&
transform[decreasingpart].First >= transform[decreasingpart + 1].First;
--decreasingpart) ;
if (decreasingpart < 0) yield break;
int greater = length - 1;
for (;greater > decreasingpart &&
transform[decreasingpart].First >= transform[greater].First;
greater--) ;
Swap(ref transform[decreasingpart], ref transform[greater]);
Array.Reverse(transform, decreasingpart + 1, length - decreasingpart - 1);
yield return ApplyTransform(items, transform);
}
}
#region Overloads
public static IEnumerable<IEnumerable<T>> Permute<T>(T[] items)
{
return Permute(items, null);
}
public static IEnumerable<IEnumerable<T>> Permute<T>(IEnumerable<T> items, IComparer<T> comparer)
{
List<T> list = new List<T>(items);
return Permute(list.ToArray(), comparer);
}
public static IEnumerable<IEnumerable<T>> Permute<T>(IEnumerable<T> items)
{
return Permute(items, null);
}
#endregion Overloads
#region Utility
public static IEnumerable<T> ApplyTransform<T>(
T[] items,
IntPair[] transform)
{
for (int i = 0; i < transform.Length; i++)
{
yield return items[transform[i].Second];
}
}
public static void Swap<T>(ref T x, ref T y)
{
T tmp = x;
x = y;
y = tmp;
}
public struct IntPair
{
public IntPair(int first, int second)
{
this.First = first;
this.Second = second;
}
public int First;
public int Second;
}
#endregion
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
int pans = 0;
int[] digits = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 };
Stopwatch sw = new Stopwatch();
sw.Start();
foreach (var p in Permutation.Permute(digits))
{
pans++;
if (pans == 720) break;
}
sw.Stop();
Console.WriteLine("{0}pcs, {1}ms", pans, sw.ElapsedMilliseconds);
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
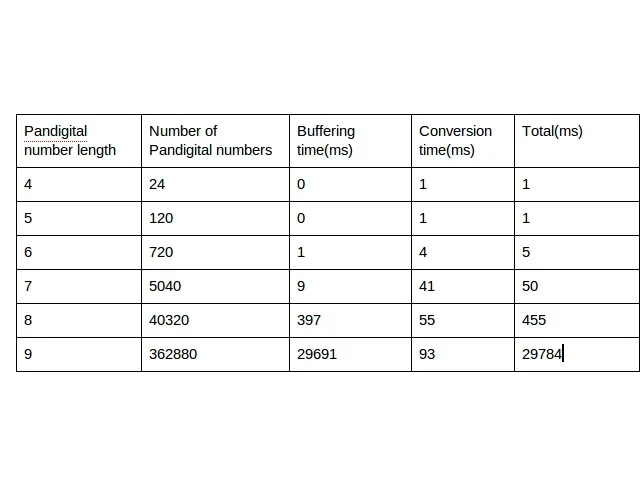 @andras:您能否尝试运行代码以生成九位数全数字数?需要多长时间?
@andras:您能否尝试运行代码以生成九位数全数字数?需要多长时间?
std::next_permutation? - kennytm