这是我写的一些东西,因为我找不到其他能做到这一点的东西。
输入
在项目A中编写一个常量字符串类。
[GenerateResource]
public static class ResourceFileName
{
public static class ThisSupports
{
public static class NestedClasses
{
[Comment("Comment value")]
public const string ResourceKey = "Resource Value";
}
}
}
输出
然后在项目中将生成一个包含常量类的资源。
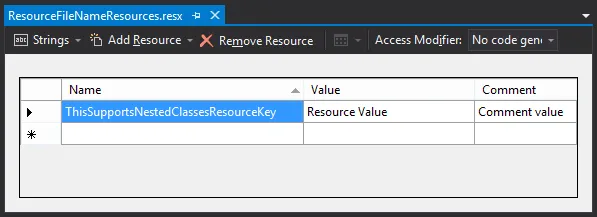
你所需要做的就是在某个地方拥有这段代码:
源代码
public class CommentAttribute : Attribute
{
public CommentAttribute(string comment)
{
this.Comment = comment;
}
public string Comment { get; set; }
}
public class GenerateResourceAttribute : Attribute
{
public string FileName { get; set; }
}
public class ResourceGenerator
{
public ResourceGenerator(IEnumerable<Assembly> assemblies)
{
foreach (var assembly in assemblies)
{
foreach (var type in assembly.GetTypes())
{
var attribute = type.GetCustomAttribute<GenerateResourceAttribute>(false);
if (attribute != null)
{
var outputDirectory = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory();
var index = outputDirectory.LastIndexOf(typeof(ResourceGenerator).Assembly.GetName().Name);
if (index >= 0)
{
outputDirectory = outputDirectory.Substring(0, index);
outputDirectory = Path.Combine(outputDirectory, type.Assembly.GetName().Name);
if (!Directory.Exists(outputDirectory))
{
outputDirectory = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory();
}
}
var fileName = attribute.FileName;
if (fileName == null)
{
fileName = type.Name + "Resources";
}
fileName = Path.Combine(outputDirectory, fileName);
if (!fileName.EndsWith(".resx", StringComparison.InvariantCultureIgnoreCase))
{
fileName += ".resx";
}
using (var resx = new ResXResourceWriter(fileName))
{
var tuples = this.GetTuplesRecursive("", type).OrderBy(t => t.Item1);
foreach (var tuple in tuples)
{
var key = tuple.Item1 + tuple.Item2.Name;
var value = tuple.Item2.GetValue(null);
string comment = null;
var commentAttribute = tuple.Item2.GetCustomAttribute<CommentAttribute>();
if (commentAttribute != null)
{
comment = commentAttribute.Comment;
}
resx.AddResource(new ResXDataNode(key, value) { Comment = comment });
}
}
}
}
}
}
private IEnumerable<Tuple<string, FieldInfo>> GetTuplesRecursive(string prefix, Type type)
{
foreach (var field in type.GetFields(BindingFlags.Public | BindingFlags.Static))
{
yield return new Tuple<string, FieldInfo>(prefix, field);
}
foreach (var nestedType in type.GetNestedTypes())
{
foreach (var tuple in this.GetTuplesRecursive(prefix + nestedType.Name, nestedType))
{
yield return tuple;
}
}
}
}
然后创建一个小项目,其中包含对所有程序集的引用,并使用[GenerateResource]进行资源生成。
public class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
var assemblies = AppDomain.CurrentDomain.GetAssemblies().ToList();
string path = Directory.GetCurrentDirectory();
foreach (string dll in Directory.GetFiles(path, "*.dll"))
{
assemblies.Add(Assembly.LoadFile(dll));
}
assemblies = assemblies.Distinct().ToList();
new ResourceGenerator(assemblies);
}
}
然后你的属性可以使用静态类
ResourceFileName.ThisSupports.NestedClasses.ResourceKey,而其他代码可以使用资源文件。
你可能需要根据自己的需要进行调整。
