我能做的就是模拟触摸(使用dispatchGesture()和AccessibilityNodeInfo.ACTION_CLICK)。
我找到了这些相关链接,但不知道它们是否有用:
下面是我的工作代码,用于将鼠标坐标(在PictureBox控件内部)发送到远程手机并模拟触摸。
Windows Forms应用程序:
private void pictureBox1_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
foreach (ListViewItem item in lvConnections.SelectedItems)
{
// Remote screen resolution
string[] tokens = item.SubItems[5].Text.Split('x'); // Ex: 1080x1920
int xClick = (e.X * int.Parse(tokens[0].ToString())) / (pictureBox1.Size.Width);
int yClick = (e.Y * int.Parse(tokens[1].ToString())) / (pictureBox1.Size.Height);
Client client = (Client)item.Tag;
if (e.Button == MouseButtons.Left)
client.sock.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("TOUCH" + xClick + "<|>" + yClick + Environment.NewLine));
}
}
编辑:
我的上一次尝试是使用鼠标坐标(C# Windows表单应用程序)和自定义的安卓例程进行“滑动屏幕”(参考上述链接的“滑动屏幕”代码):
private Point mdownPoint = new Point();
private void pictureBox1_MouseDown(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
foreach (ListViewItem item in lvConnections.SelectedItems)
{
// Remote screen resolution
string[] tokens = item.SubItems[5].Text.Split('x'); // Ex: 1080x1920
Client client = (Client)item.Tag;
if (e.Button == MouseButtons.Left)
{
xClick = (e.X * int.Parse(tokens[0].ToString())) / (pictureBox1.Size.Width);
yClick = (e.Y * int.Parse(tokens[1].ToString())) / (pictureBox1.Size.Height);
// Saving start position:
mdownPoint.X = xClick;
mdownPoint.Y = yClick;
client.sock.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("TOUCH" + xClick + "<|>" + yClick + Environment.NewLine));
}
}
}
private void PictureBox1_MouseMove(object sender, MouseEventArgs e)
{
foreach (ListViewItem item in lvConnections.SelectedItems)
{
// Remote screen resolution
string[] tokens = item.SubItems[5].Text.Split('x'); // Ex: 1080x1920
Client client = (Client)item.Tag;
if (e.Button == MouseButtons.Left)
{
xClick = (e.X * int.Parse(tokens[0].ToString())) / (pictureBox1.Size.Width);
yClick = (e.Y * int.Parse(tokens[1].ToString())) / (pictureBox1.Size.Height);
client.sock.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("MOUSESWIPESCREEN" + mdownPoint.X + "<|>" + mdownPoint.Y + "<|>" + xClick + "<|>" + yClick + Environment.NewLine));
}
}
}
Android的AccessibilityService:
public void Swipe(int x1, int y1, int x2, int y2, int time) {
if (android.os.Build.VERSION.SDK_INT >= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {
System.out.println(" ======= Swipe =======");
GestureDescription.Builder gestureBuilder = new GestureDescription.Builder();
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(x1, y1);
path.lineTo(x2, y2);
gestureBuilder.addStroke(new GestureDescription.StrokeDescription(path, 100, time));
dispatchGesture(gestureBuilder.build(), new GestureResultCallback() {
@Override
public void onCompleted(GestureDescription gestureDescription) {
System.out.println("SWIPE Gesture Completed :D");
super.onCompleted(gestureDescription);
}
}, null);
}
}
这会生成以下结果(但仍无法像TeamViewer一样绘制“图案密码”)。但正如下面的评论所说,我认为使用类似的方法可以使用连续手势来实现。对于此方向上的任何建议都将受到欢迎。
编辑2:
毫无疑问,解决方案是像之前的编辑中所说的继续手势。
以下是我在这里找到的假定修复代码 =>
Android AccessibilityService:
// Simulates an L-shaped drag path: 200 pixels right, then 200 pixels down.
Path path = new Path();
path.moveTo(200,200);
path.lineTo(400,200);
final GestureDescription.StrokeDescription sd = new GestureDescription.StrokeDescription(path, 0, 500, true);
// The starting point of the second path must match
// the ending point of the first path.
Path path2 = new Path();
path2.moveTo(400,200);
path2.lineTo(400,400);
final GestureDescription.StrokeDescription sd2 = sd.continueStroke(path2, 0, 500, false); // 0.5 second
HongBaoService.mService.dispatchGesture(new GestureDescription.Builder().addStroke(sd).build(), new AccessibilityService.GestureResultCallback(){
@Override
public void onCompleted(GestureDescription gestureDescription){
super.onCompleted(gestureDescription);
HongBaoService.mService.dispatchGesture(new GestureDescription.Builder().addStroke(sd2).build(),null,null);
}
@Override
public void onCancelled(GestureDescription gestureDescription){
super.onCancelled(gestureDescription);
}
},null);
那么,我的疑问是:如何正确发送鼠标坐标以执行任意方向的拖动?有什么想法吗?
编辑3:
我找到了两个用于执行拖动的例程,但它们使用UiAutomation + injectInputEvent()。据我所知,事件注入仅在系统应用程序中工作,如here和here所述,我不想要它。
这些是找到的例程:
- public boolean swipe(int downX, int downY, int upX, int upY, int steps, boolean drag)
- public boolean swipe(Point[] segments, int segmentSteps)
pictureBox1_MouseDown和pictureBox1_MouseMove(C# Windows Forms应用程序)的所有点分别发送到动态填充的Point[]中,在pictureBox1_MouseUp上发送cmd以执行例程并使用这个填充的数组。如果您有第一个例程的想法,请告诉我:D。如果在阅读此编辑后您有可能的解决方案,请在回答中向我展示,而我将尝试并测试这个想法。

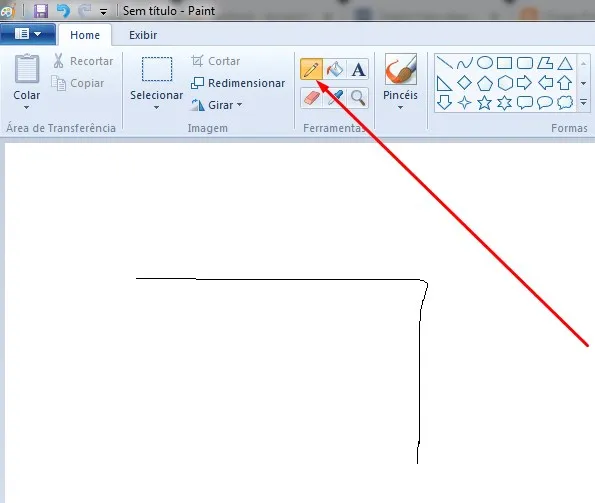

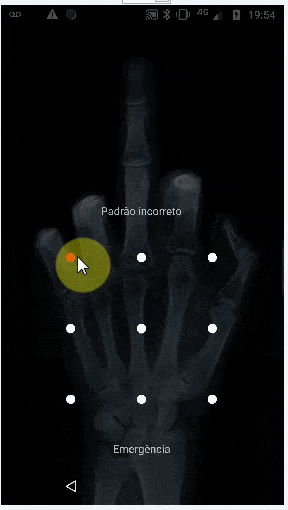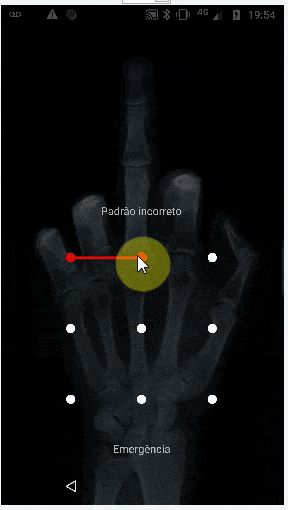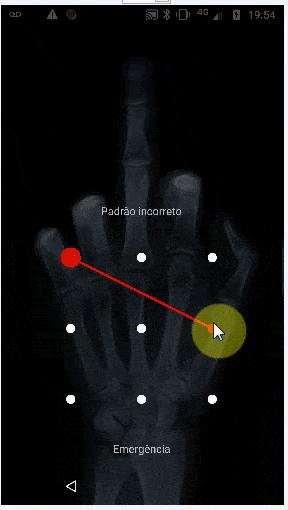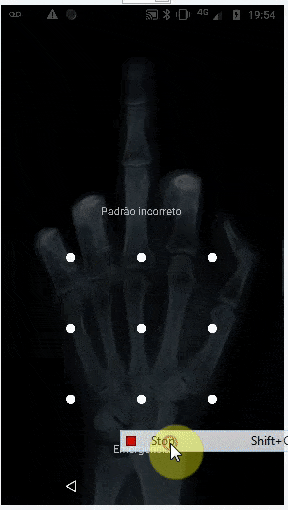
StrokeDescription.continueStroke()可能是一个解决方案。请查看此处的 连续手势 部分 链接。 - FLASHCODERpictureBox1_MouseDown不应该发送坐标。它只应该存储初始坐标,然后在pictureBox1_MouseUp上发送它们,因为那标志着鼠标移动的结束。 - Greggz