我有一组点,它们代表多边形的顶点(x,y)。
points= [(421640.3639270504, 4596366.353552659), (421635.79361391126, 4596369.054192241), (421632.6774913164, 4596371.131607305), (421629.14588570886, 4596374.870954419), (421625.6142801013, 4596377.779335507), (421624.99105558236, 4596382.14190714), (421630.1845932406, 4596388.062540068), (421633.3007158355, 4596388.270281575), (421637.87102897465, 4596391.8018871825), (421642.4413421138, 4596394.918009778), (421646.5961722403, 4596399.903805929), (421649.71229483513, 4596403.850894549), (421653.8940752105, 4596409.600842565), (421654.69809098693, 4596410.706364258), (421657.60647207545, 4596411.329588776), (421660.514853164, 4596409.875398233), (421661.3458191893, 4596406.136051118), (421661.5535606956, 4596403.22767003), (421658.85292111343, 4596400.94251346), (421656.5677645438, 4596399.696064423), (421655.52905701223, 4596396.164458815), (421652.82841743, 4596394.502526765), (421648.46584579715, 4596391.8018871825), (421646.38843073393, 4596388.270281575), (421645.55746470863, 4596386.400608018), (421647.21939675923, 4596384.115451449), (421649.5045533288, 4596382.661260904), (421650.7510023668, 4596378.714172284), (421647.8426212782, 4596375.8057911955), (421644.9342401897, 4596372.897410107), (421643.6877911517, 4596370.404512031), (421640.3639270504, 4596366.353552659)]
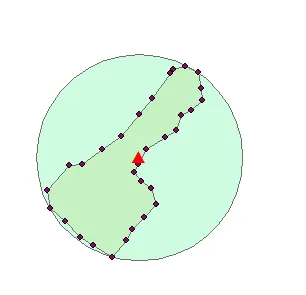
我需要找到最小的包围圆(面积、中心点的x和y坐标以及半径)
我正在使用从此页面派生的Python代码:Nayuki的最小包围圆
当我运行代码时,结果每次都会改变,例如:
>>> make_circle(points)
(421643.0645666326, 4596393.82736687, 23.70763190712525)
>>> make_circle(points)
(421647.8426212782, 4596375.8057911955, 0.0)
>>> make_circle(points)
(421648.9851995629, 4596388.841570718, 24.083963460031157)
当返回值为圆心的x、y坐标和半径时,
在使用商业软件(如ArcGIS)处理一组点时,正确的结果为:
421646.74552, 4596389.82475, 24.323246
所使用的代码:
#
# Smallest enclosing circle
#
# Copyright (c) 2014 Project Nayuki
# https://www.nayuki.io/page/smallest-enclosing-circle
#
# This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify
# it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by
# the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or
# (at your option) any later version.
#
# This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
# but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
# MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
# GNU General Public License for more details.
#
# You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License
# along with this program (see COPYING.txt).
# If not, see <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
#
import math, random
# Data conventions: A point is a pair of floats (x, y). A circle is a triple of floats (center x, center y, radius).
#
# Returns the smallest circle that encloses all the given points. Runs in expected O(n) time, randomized.
# Input: A sequence of pairs of floats or ints, e.g. [(0,5), (3.1,-2.7)].
# Output: A triple of floats representing a circle.
# Note: If 0 points are given, None is returned. If 1 point is given, a circle of radius 0 is returned.
#
def make_circle(points):
# Convert to float and randomize order
shuffled = [(float(p[0]), float(p[1])) for p in points]
random.shuffle(shuffled)
# Progressively add points to circle or recompute circle
c = None
for (i, p) in enumerate(shuffled):
if c is None or not _is_in_circle(c, p):
c = _make_circle_one_point(shuffled[0 : i + 1], p)
return c
# One boundary point known
def _make_circle_one_point(points, p):
c = (p[0], p[1], 0.0)
for (i, q) in enumerate(points):
if not _is_in_circle(c, q):
if c[2] == 0.0:
c = _make_diameter(p, q)
else:
c = _make_circle_two_points(points[0 : i + 1], p, q)
return c
# Two boundary points known
def _make_circle_two_points(points, p, q):
diameter = _make_diameter(p, q)
if all(_is_in_circle(diameter, r) for r in points):
return diameter
left = None
right = None
for r in points:
cross = _cross_product(p[0], p[1], q[0], q[1], r[0], r[1])
c = _make_circumcircle(p, q, r)
if c is None:
continue
elif cross > 0.0 and (left is None or _cross_product(p[0], p[1], q[0], q[1], c[0], c[1]) > _cross_product(p[0], p[1], q[0], q[1], left[0], left[1])):
left = c
elif cross < 0.0 and (right is None or _cross_product(p[0], p[1], q[0], q[1], c[0], c[1]) < _cross_product(p[0], p[1], q[0], q[1], right[0], right[1])):
right = c
return left if (right is None or (left is not None and left[2] <= right[2])) else right
def _make_circumcircle(p0, p1, p2):
# Mathematical algorithm from Wikipedia: Circumscribed circle
ax = p0[0]; ay = p0[1]
bx = p1[0]; by = p1[1]
cx = p2[0]; cy = p2[1]
d = (ax * (by - cy) + bx * (cy - ay) + cx * (ay - by)) * 2.0
if d == 0.0:
return None
x = ((ax * ax + ay * ay) * (by - cy) + (bx * bx + by * by) * (cy - ay) + (cx * cx + cy * cy) * (ay - by)) / d
y = ((ax * ax + ay * ay) * (cx - bx) + (bx * bx + by * by) * (ax - cx) + (cx * cx + cy * cy) * (bx - ax)) / d
return (x, y, math.hypot(x - ax, y - ay))
def _make_diameter(p0, p1):
return ((p0[0] + p1[0]) / 2.0, (p0[1] + p1[1]) / 2.0, math.hypot(p0[0] - p1[0], p0[1] - p1[1]) / 2.0)
_EPSILON = 1e-12
def _is_in_circle(c, p):
return c is not None and math.hypot(p[0] - c[0], p[1] - c[1]) < c[2] + _EPSILON
# Returns twice the signed area of the triangle defined by (x0, y0), (x1, y1), (x2, y2)
def _cross_product(x0, y0, x1, y1, x2, y2):
return (x1 - x0) * (y2 - y0) - (y1 - y0) * (x2 - x0)