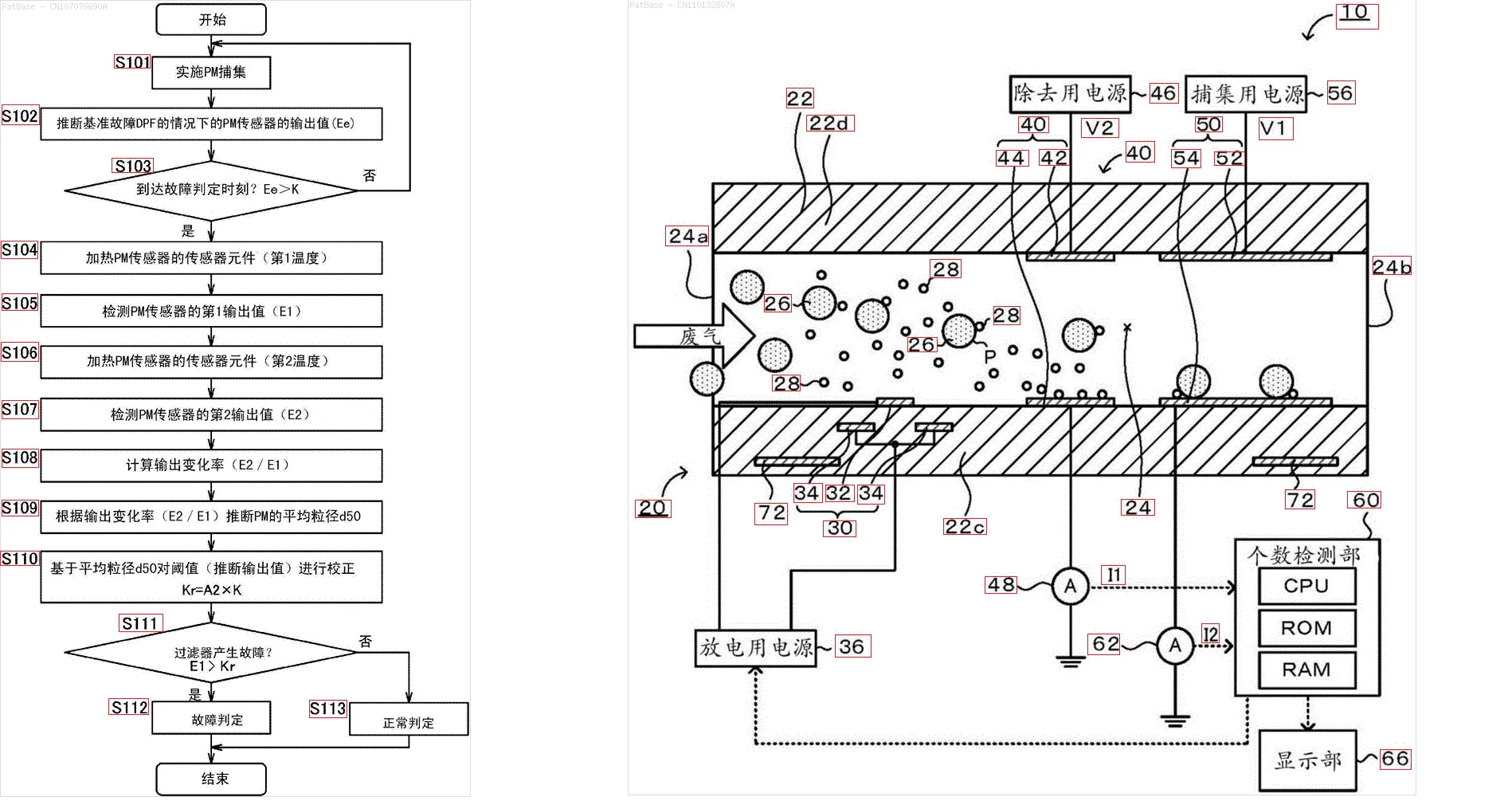
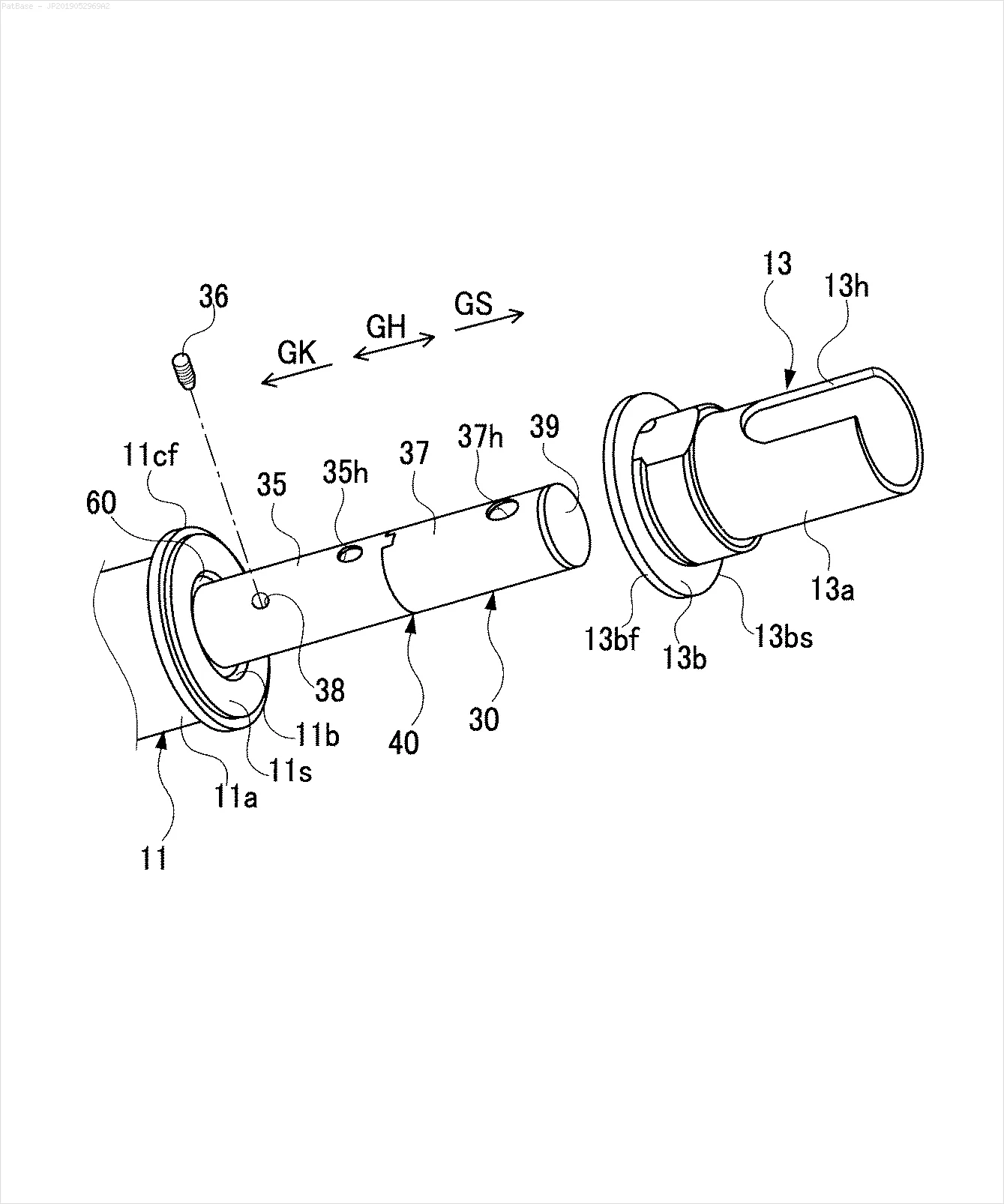
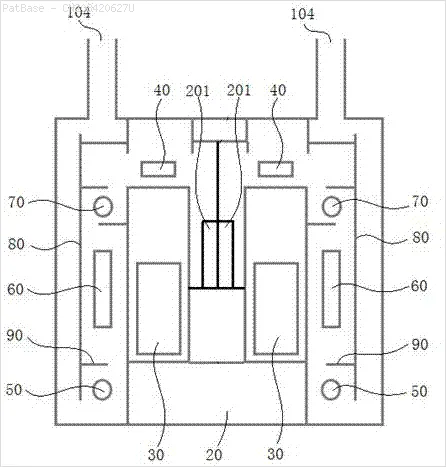
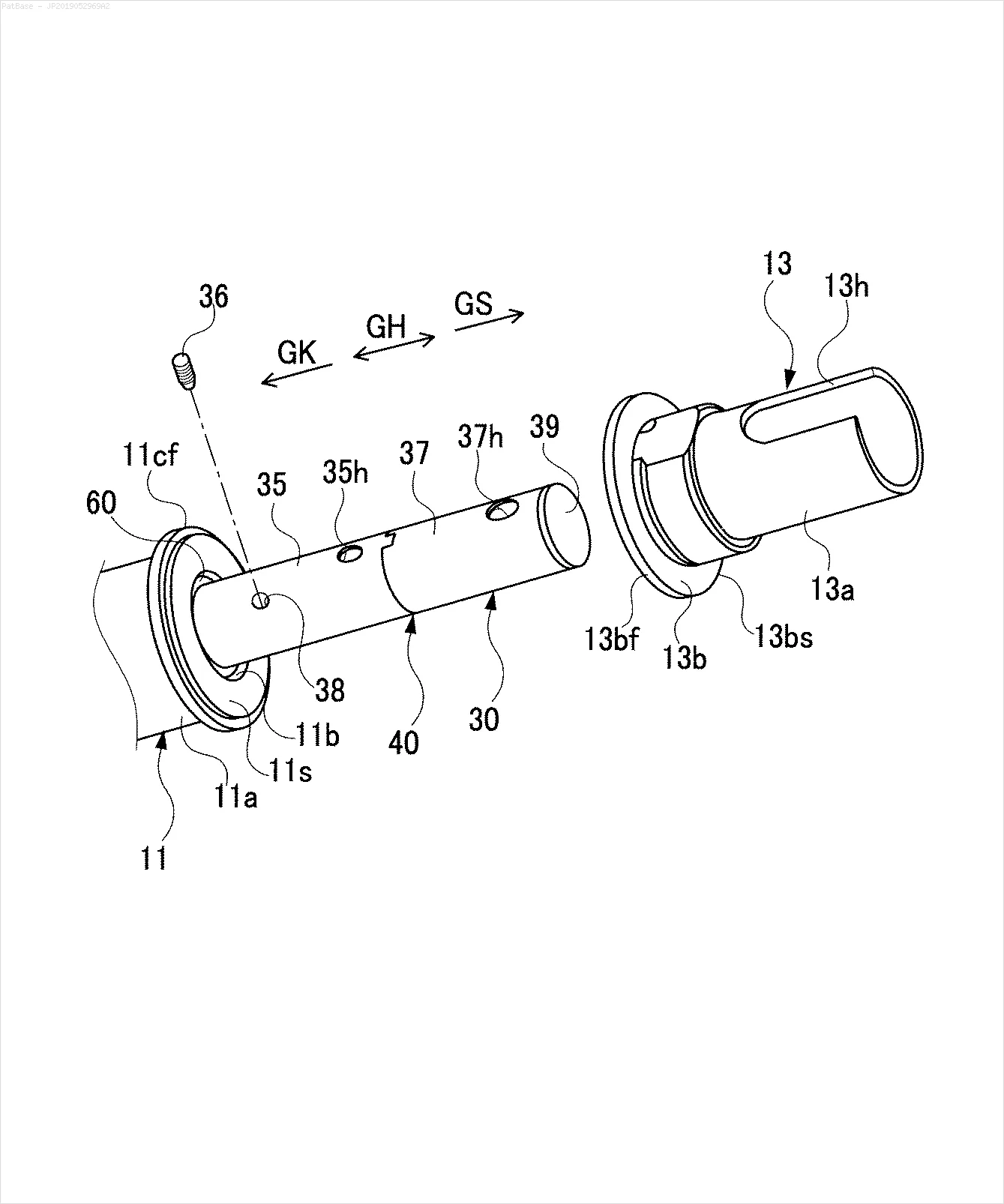
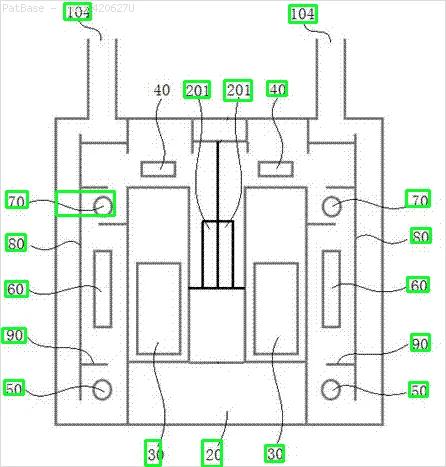
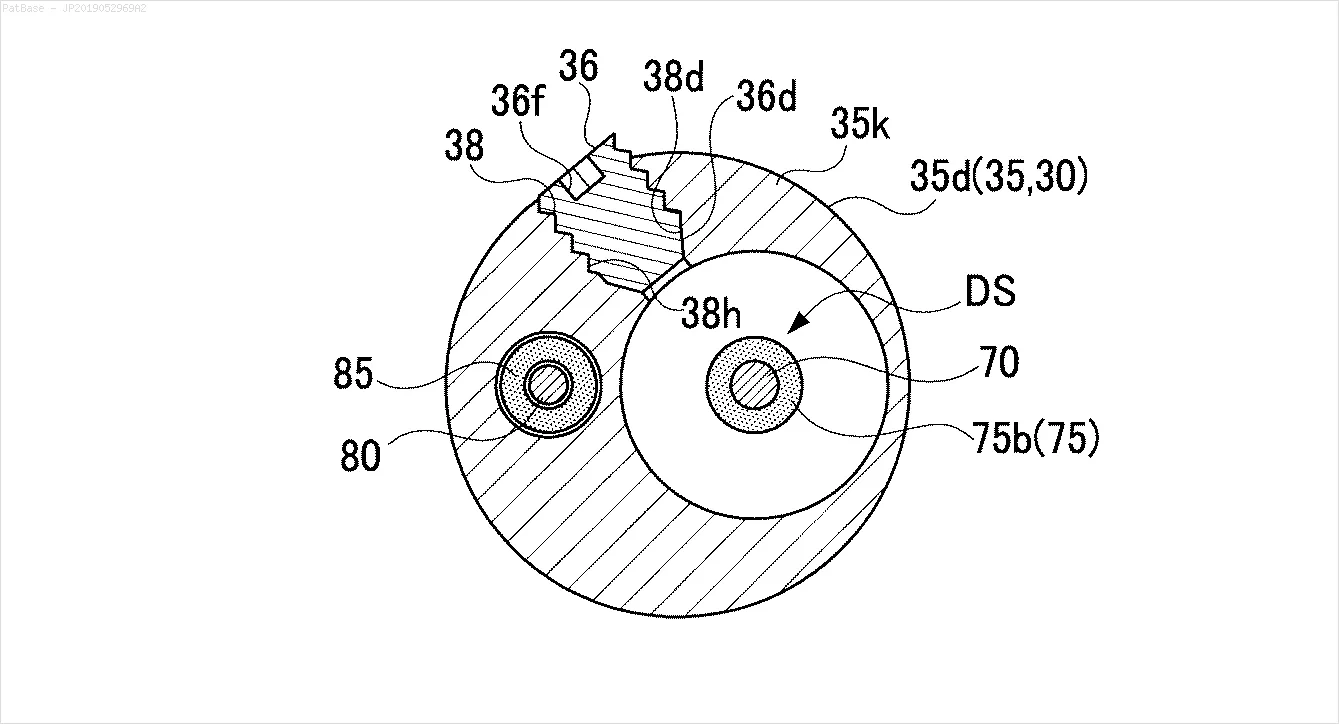
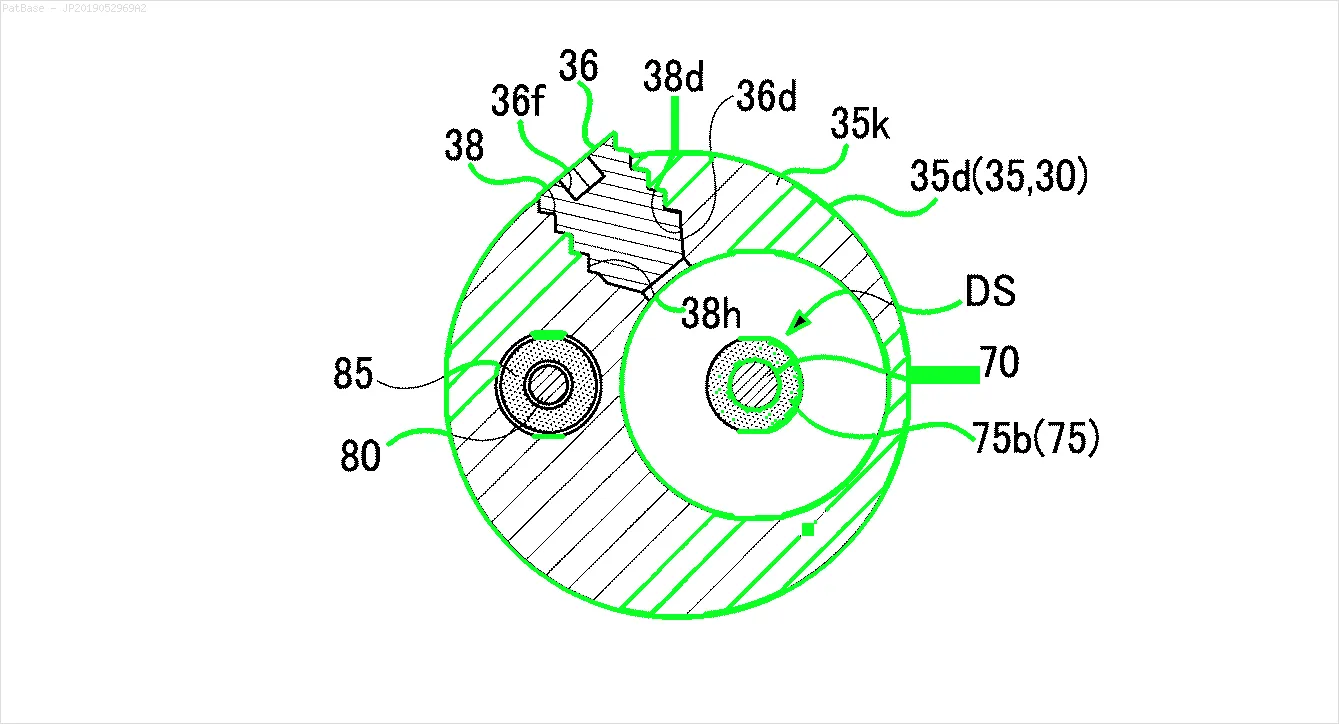
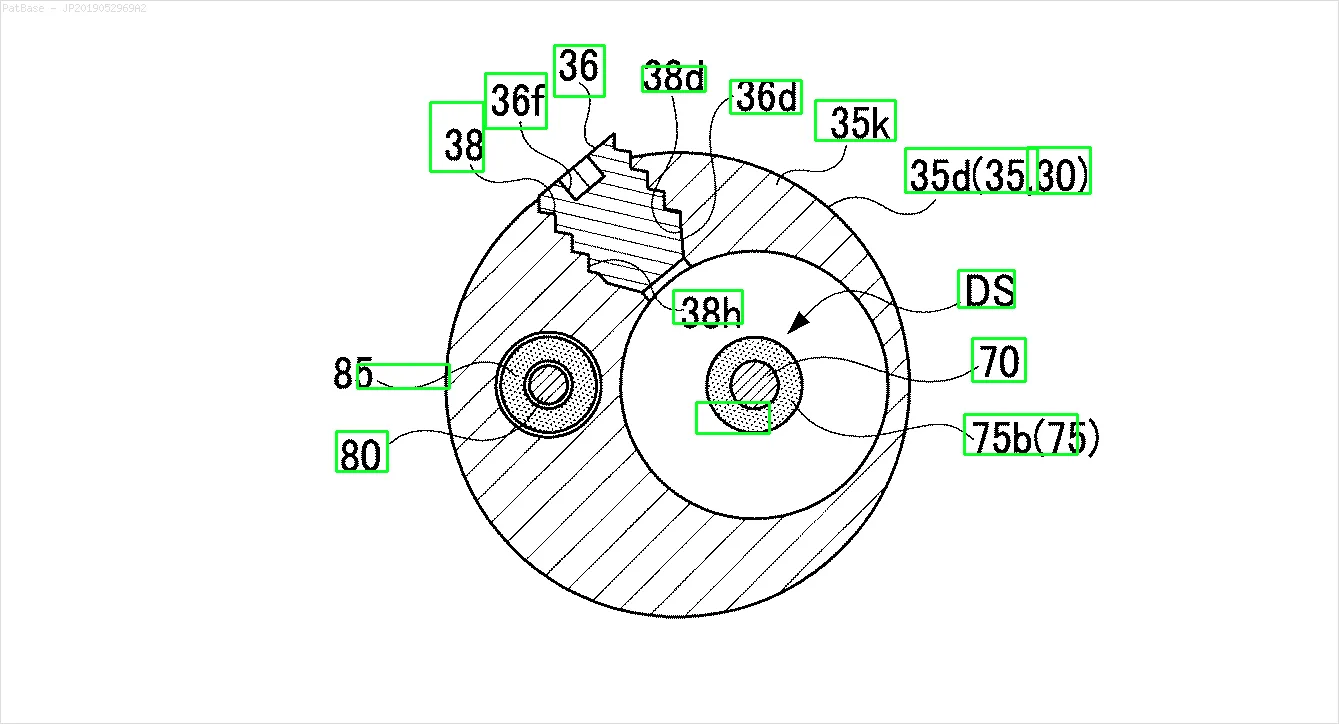
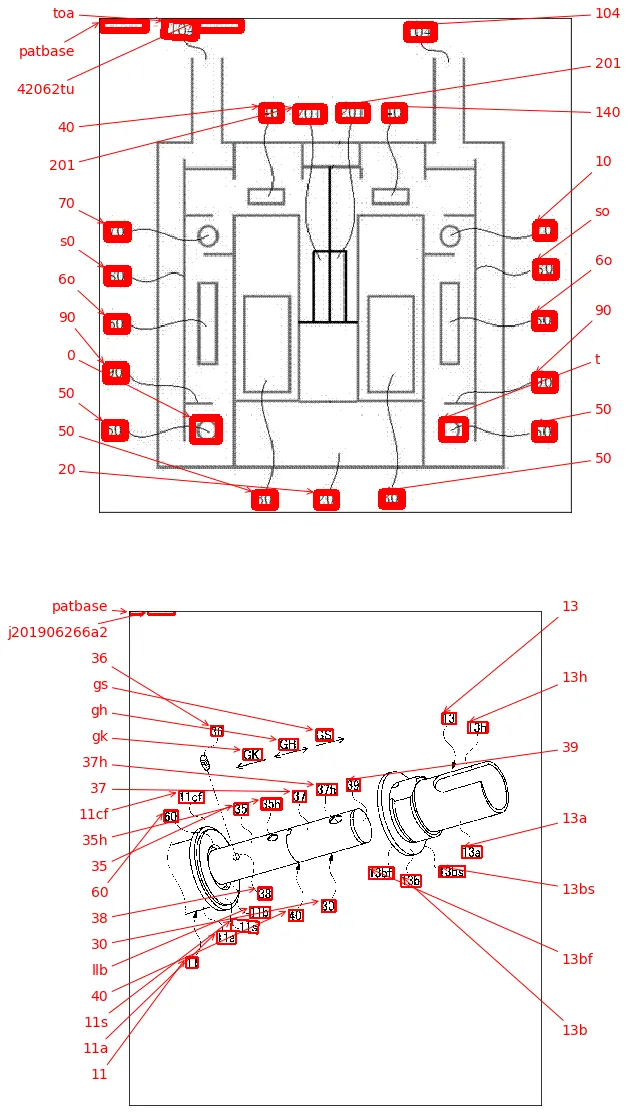
我有多个图像示意图,其中所有标签都包含字母数字字符,而不仅仅是文本标签本身。 我希望我的YOLO模型能够识别其中的所有数字和字母数字字符。
如何训练我的YOLO模型来完成这项任务。 可以在此处找到数据集。 https://drive.google.com/open?id=1iEkGcreFaBIJqUdAADDXJbUrSj99bvoi
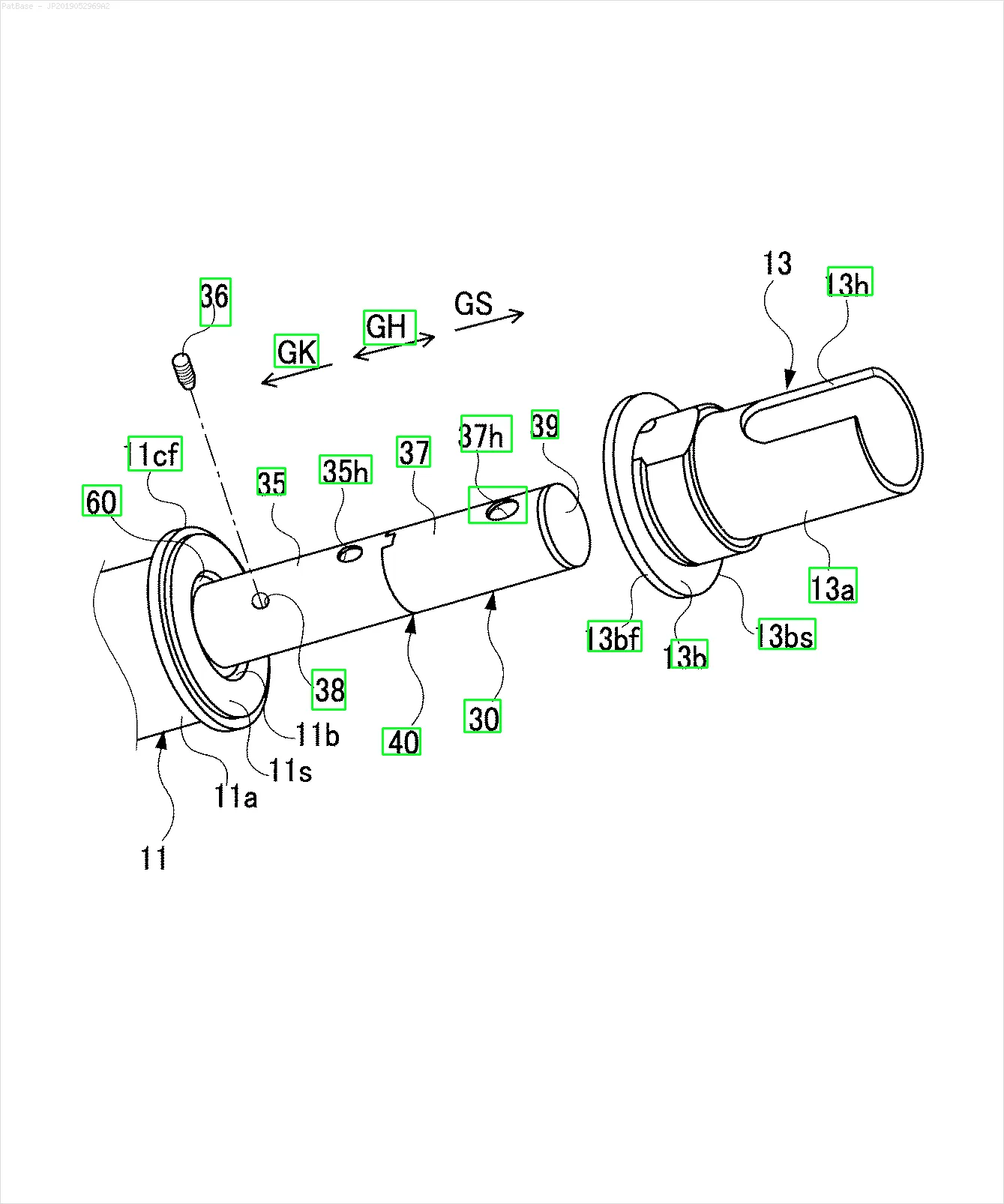
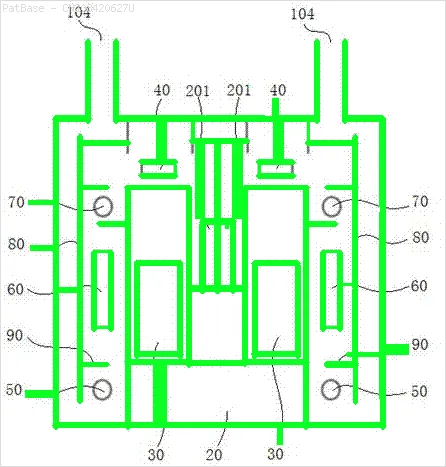
例如:请参见边界框。 我希望YOLO能检测出文本所在的位置。 但目前不必识别其中的文本。
可以在此处下载这些图像here
这是我使用opencv尝试过的方法,但它不能处理数据集中的所有图像。
import cv2
import numpy as np
import pytesseract
pytesseract.pytesseract.tesseract_cmd = r"C:\Users\HPO2KOR\AppData\Local\Tesseract-OCR\tesseract.exe"
image = cv2.imread(r'C:\Users\HPO2KOR\Desktop\Work\venv\Patent\PARTICULATE DETECTOR\PD4.png')
gray = cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
thresh = cv2.threshold(gray, 0, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY_INV + cv2.THRESH_OTSU)[1]
clean = thresh.copy()
horizontal_kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (15,1))
detect_horizontal = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, horizontal_kernel, iterations=2)
cnts = cv2.findContours(detect_horizontal, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if len(cnts) == 2 else cnts[1]
for c in cnts:
cv2.drawContours(clean, [c], -1, 0, 3)
vertical_kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (1,30))
detect_vertical = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, vertical_kernel, iterations=2)
cnts = cv2.findContours(detect_vertical, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if len(cnts) == 2 else cnts[1]
for c in cnts:
cv2.drawContours(clean, [c], -1, 0, 3)
cnts = cv2.findContours(clean, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if len(cnts) == 2 else cnts[1]
for c in cnts:
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area < 100:
cv2.drawContours(clean, [c], -1, 0, 3)
elif area > 1000:
cv2.drawContours(clean, [c], -1, 0, -1)
peri = cv2.arcLength(c, True)
approx = cv2.approxPolyDP(c, 0.02 * peri, True)
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
if len(approx) == 4:
cv2.rectangle(clean, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), 0, -1)
open_kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (2,2))
opening = cv2.morphologyEx(clean, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, open_kernel, iterations=2)
close_kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_RECT, (3,2))
close = cv2.morphologyEx(opening, cv2.MORPH_CLOSE, close_kernel, iterations=4)
cnts = cv2.findContours(close, cv2.RETR_EXTERNAL, cv2.CHAIN_APPROX_SIMPLE)
cnts = cnts[0] if len(cnts) == 2 else cnts[1]
for c in cnts:
x,y,w,h = cv2.boundingRect(c)
area = cv2.contourArea(c)
if area > 500:
ROI = image[y:y+h, x:x+w]
ROI = cv2.GaussianBlur(ROI, (3,3), 0)
data = pytesseract.image_to_string(ROI, lang='eng',config='--psm 6')
if data.isalnum():
cv2.rectangle(image, (x, y), (x + w, y + h), (36,255,12), 2)
print(data)
cv2.imwrite('image.png', image)
cv2.imwrite('clean.png', clean)
cv2.imwrite('close.png', close)
cv2.imwrite('opening.png', opening)
cv2.waitKey()
有没有任何模型或者opencv技术或一些预训练的模型可以替我完成这个任务?我只需要在图像中找到所有字母数字字符周围的边界框,然后识别出其中的内容。不过目前第二部分并不重要。