如何在iOS中获取缓冲多边形的坐标(纬度和经度)?
5
- Nitesh
2
2请更新您的问题,说明您已经做了什么以及尝试了什么。解释您需要什么样的帮助。 - rmaddy
@rmaddy:大多数不同的地图API中都编写了绘制多边形的方法,我们只需传递一组纬度和经度坐标数组,剩下的都由这些函数处理,但是在这里,我需要一个通用算法,它将考虑缓冲坐标的给定坐标来执行。这是我在Mapbox API中未找到的。 - Nitesh
5个回答
2
虽然@Ravikant Paudel的解决方案很全面,但对我没用,所以我自己实现了这个方法。此外,我使用kotlin实现了这个方法,并在这里添加,以便其他遇到类似问题的人会发现它有用。
方法:
- 找到多边形每个顶点的角平分线角度theta。
- 画一个半径为bufferedDistance / sin(angleBisctorTheta)的圆。
- 找到圆与角平分线的交点。
- 两个交点中内部的那个将给出缩小多边形的缓冲顶点,而外部的交点将给出缓冲多边形的顶点。
- 此方法不考虑两个交点都在多边形内或外的特殊情况->在这种情况下,形成的缓冲多边形将是畸形的。
代码:
private fun computeAngleBisectorTheta(
prevLatLng: LatLng,
currLatLng: LatLng,
nextLatLng: LatLng
): Double {
var phiBisector = 0.0
try {
val aPrime = getDeltaPrimeVector(prevLatLng, currLatLng)
val cPrime = getDeltaPrimeVector(nextLatLng, currLatLng)
val thetaA = atan2(aPrime[1], aPrime[0])
val thetaC = atan2(cPrime[1], cPrime[0])
phiBisector = (thetaA + thetaC) / 2.0
} catch (e: Exception) {
logger.error("[Error] in computeAngleBisectorSlope: $e")
}
return phiBisector
}
private fun getDeltaPrimeVector(
aLatLng: LatLng,
bLatLng: LatLng
): ArrayList<Double> {
val arrayList: ArrayList<Double> = ArrayList<Double>(2)
try {
val aX = convertToXY(aLatLng.latitude)
val aY = convertToXY(aLatLng.longitude)
val bX = convertToXY(bLatLng.latitude)
val bY = convertToXY(bLatLng.longitude)
arrayList.add((aX - bX))
arrayList.add((aY - bY))
} catch (e: Exception) {
logger.error("[Error] in getDeltaPrimeVector: $e")
}
return arrayList
}
private fun convertToXY(coordinate: Double) =
EARTH_RADIUS * toRad(coordinate)
private fun convertToLatLngfromXY(coordinate: Double) =
toDegrees(coordinate / EARTH_RADIUS)
private fun computeBufferedVertices(
angle: Double, bufDis: Int,
centerLatLng: LatLng
): ArrayList<LatLng> {
var results = ArrayList<LatLng>()
try {
val distance = bufDis / sin(angle)
var slope = tan(angle)
var inverseSlopeSquare = sqrt(1 + slope * slope * 1.0)
var distanceByInverseSlopeSquare = distance / inverseSlopeSquare
var slopeIntoDistanceByInverseSlopeSquare = slope * distanceByInverseSlopeSquare
var p1X: Double = convertToXY(centerLatLng.latitude) + distanceByInverseSlopeSquare
var p1Y: Double =
convertToXY(centerLatLng.longitude) + slopeIntoDistanceByInverseSlopeSquare
var p2X: Double = convertToXY(centerLatLng.latitude) - distanceByInverseSlopeSquare
var p2Y: Double =
convertToXY(centerLatLng.longitude) - slopeIntoDistanceByInverseSlopeSquare
val tempLatLng1 = LatLng(convertToLatLngfromXY(p1X), convertToLatLngfromXY(p1Y))
results.add(tempLatLng1)
val tempLatLng2 = LatLng(convertToLatLngfromXY(p2X), convertToLatLngfromXY(p2Y))
results.add(tempLatLng2)
} catch (e: Exception) {
logger.error("[Error] in computeBufferedVertices: $e")
}
return results
}
private fun getVerticesOutsidePolygon(
verticesArray: ArrayList<LatLng>,
polygon: ArrayList<LatLng>
): LatLng {
if (isPointInPolygon(
verticesArray[0].latitude,
verticesArray[0].longitude,
polygon
)
) {
if (sPointInPolygon(
verticesArray[1].latitude,
verticesArray[1].longitude,
polygon
)
) {
logger.error("[ERROR] Malformed polygon! Both Vertices are inside the polygon! $verticesArray")
} else {
return verticesArray[1]
}
} else {
if (PolygonGeofenceHelper.isPointInPolygon(
verticesArray[1].latitude,
verticesArray[1].longitude,
polygon
)
) {
return verticesArray[0]
} else {
logger.error("[ERROR] Malformed polygon! Both Vertices are outside the polygon!: $verticesArray")
}
}
//returning a vertice anyway because there is no fall back policy designed if both vertices are inside or outside the polygon
return verticesArray[0]
}
private fun toRad(angle: Double): Double {
return angle * Math.PI / 180
}
private fun toDegrees(radians: Double): Double {
return radians * 180 / Math.PI
}
private fun getVerticesInsidePolygon(
verticesArray: ArrayList<LatLng>,
polygon: ArrayList<LatLng>
): LatLng {
if (isPointInPolygon(
verticesArray[0].latitude,
verticesArray[0].longitude,
polygon
)
) {
if (isPointInPolygon(
verticesArray[1].latitude,
verticesArray[1].longitude,
polygon
)
) {
logger.error("[ERROR] Malformed polygon! Both Vertices are inside the polygon! $verticesArray")
} else {
return verticesArray[0]
}
} else {
if (PolygonGeofenceHelper.isPointInPolygon(
verticesArray[1].latitude,
verticesArray[1].longitude,
polygon
)
) {
return verticesArray[1]
} else {
logger.error("[ERROR] Malformed polygon! Both Vertices are outside the polygon!: $verticesArray")
}
}
//returning a vertice anyway because there is no fall back policy designed if both vertices are inside or outside the polygon
return LatLng(0.0, 0.0)
}
fun getBufferedPolygon(
polygon: ArrayList<LatLng>,
bufferDistance: Int,
isOutside: Boolean
): ArrayList<LatLng> {
var bufferedPolygon = ArrayList<LatLng>()
var isBufferedPolygonMalformed = false
try {
for (i in 0 until polygon.size) {
val prevLatLng: LatLng = polygon[if (i - 1 < 0) polygon.size - 1 else i - 1]
val centerLatLng: LatLng = polygon[i]
val nextLatLng: LatLng = polygon[if (i + 1 == polygon.size) 0 else i + 1]
val computedVertices =
computeBufferedVertices(
computeAngleBisectorTheta(
prevLatLng, centerLatLng, nextLatLng
), bufferDistance, centerLatLng
)
val latLng = if (isOutside) {
getVerticesOutsidePolygon(
computedVertices,
polygon
)
} else {
getVerticesInsidePolygon(
computedVertices,
polygon
)
}
if (latLng.latitude == 0.0 && latLng.longitude == 0.0) {
isBufferedPolygonMalformed = true
break
}
bufferedPolygon.add(latLng)
}
if (isBufferedPolygonMalformed) {
bufferedPolygon = polygon
logger.error("[Error] Polygon generated is malformed returning the same polygon: $polygon , $bufferDistance, $isOutside")
}
} catch (e: Exception) {
logger.error("[Error] in getBufferedPolygon: $e")
}
return bufferedPolygon
}
您需要传递一个包含多边形中点的数组和缓冲距离作为第三个参数,以获得外部缓冲区或内部缓冲区。(注意:我假设此列表中的顶点相邻)。
我尽可能全面地回答了这个问题。如有改进或更好的方法,请随时提出建议。
您可以在我的个人主页上找到上述代码背后的详细数学知识。
- 查找角平分线
- 将纬度和经度近似为二维笛卡尔坐标系。
- 要检查点是否在多边形内,我使用了这篇GeeksforGeeks文章中提到的方法。
- Vineet Tambe
1
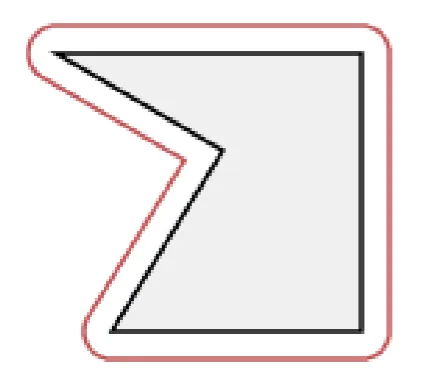
我在应用程序中遇到了同样的问题,最终在this site的帮助下找到了解决方案。
我是一位安卓开发者,我的代码可能对你没有用,但核心概念是相同的。
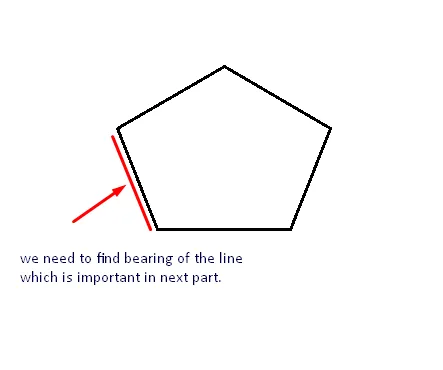
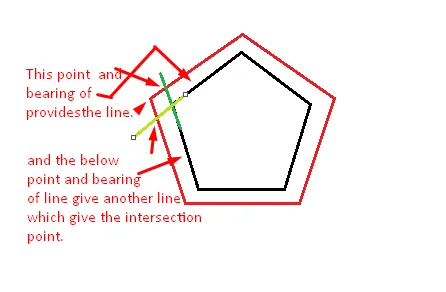
- 首先,我们需要使用两个经纬度点的帮助来找到线的方位角。(我使用了computeDistanceAndBearing(double lat1, double lon1,double lat2, double lon2)函数来完成这个过程)
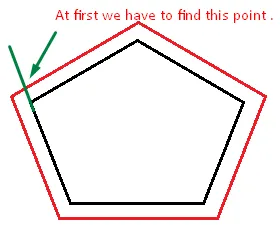
- 对所有多边形点进行此操作,然后您将获得新的点,可以连接以进行缓冲。
这是我在我的Android位置应用程序中所做的方式,其中包含 。
。
这是我的代码 //computeDistanceAndBearing(double lat1, double lon1, double lat2, double lon2)
public static double[] computeDistanceAndBearing(double lat1, double lon1,
double lat2, double lon2) {
// Based on http://www.ngs.noaa.gov/PUBS_LIB/inverse.pdf
// using the "Inverse Formula" (section 4)
double results[] = new double[3];
int MAXITERS = 20;
// Convert lat/long to radians
lat1 *= Math.PI / 180.0;
lat2 *= Math.PI / 180.0;
lon1 *= Math.PI / 180.0;
lon2 *= Math.PI / 180.0;
double a = 6378137.0; // WGS84 major axis
double b = 6356752.3142; // WGS84 semi-major axis
double f = (a - b) / a;
double aSqMinusBSqOverBSq = (a * a - b * b) / (b * b);
double L = lon2 - lon1;
double A = 0.0;
double U1 = Math.atan((1.0 - f) * Math.tan(lat1));
double U2 = Math.atan((1.0 - f) * Math.tan(lat2));
double cosU1 = Math.cos(U1);
double cosU2 = Math.cos(U2);
double sinU1 = Math.sin(U1);
double sinU2 = Math.sin(U2);
double cosU1cosU2 = cosU1 * cosU2;
double sinU1sinU2 = sinU1 * sinU2;
double sigma = 0.0;
double deltaSigma = 0.0;
double cosSqAlpha = 0.0;
double cos2SM = 0.0;
double cosSigma = 0.0;
double sinSigma = 0.0;
double cosLambda = 0.0;
double sinLambda = 0.0;
double lambda = L; // initial guess
for (int iter = 0; iter < MAXITERS; iter++) {
double lambdaOrig = lambda;
cosLambda = Math.cos(lambda);
sinLambda = Math.sin(lambda);
double t1 = cosU2 * sinLambda;
double t2 = cosU1 * sinU2 - sinU1 * cosU2 * cosLambda;
double sinSqSigma = t1 * t1 + t2 * t2; // (14)
sinSigma = Math.sqrt(sinSqSigma);
cosSigma = sinU1sinU2 + cosU1cosU2 * cosLambda; // (15)
sigma = Math.atan2(sinSigma, cosSigma); // (16)
double sinAlpha = (sinSigma == 0) ? 0.0 : cosU1cosU2 * sinLambda
/ sinSigma; // (17)
cosSqAlpha = 1.0 - sinAlpha * sinAlpha;
cos2SM = (cosSqAlpha == 0) ? 0.0 : cosSigma - 2.0 * sinU1sinU2
/ cosSqAlpha; // (18)
double uSquared = cosSqAlpha * aSqMinusBSqOverBSq; // defn
A = 1 + (uSquared / 16384.0) * // (3)
(4096.0 + uSquared * (-768 + uSquared * (320.0 - 175.0 * uSquared)));
double B = (uSquared / 1024.0) * // (4)
(256.0 + uSquared * (-128.0 + uSquared * (74.0 - 47.0 * uSquared)));
double C = (f / 16.0) * cosSqAlpha * (4.0 + f * (4.0 - 3.0 * cosSqAlpha)); // (10)
double cos2SMSq = cos2SM * cos2SM;
deltaSigma = B
* sinSigma
* // (6)
(cos2SM + (B / 4.0)
* (cosSigma * (-1.0 + 2.0 * cos2SMSq) - (B / 6.0) * cos2SM
* (-3.0 + 4.0 * sinSigma * sinSigma)
* (-3.0 + 4.0 * cos2SMSq)));
lambda = L
+ (1.0 - C)
* f
* sinAlpha
* (sigma + C * sinSigma
* (cos2SM + C * cosSigma * (-1.0 + 2.0 * cos2SM * cos2SM))); // (11)
double delta = (lambda - lambdaOrig) / lambda;
if (Math.abs(delta) < 1.0e-12) {
break;
}
}
double distance = (b * A * (sigma - deltaSigma));
results[0] = distance;
if (results.length > 1) {
double initialBearing = Math.atan2(cosU2 * sinLambda, cosU1 * sinU2
- sinU1 * cosU2 * cosLambda);
initialBearing *= 180.0 / Math.PI;
results[1] = initialBearing;
if (results.length > 2) {
double finalBearing = Math.atan2(cosU1 * sinLambda, -sinU1 * cosU2
+ cosU1 * sinU2 * cosLambda);
finalBearing *= 180.0 / Math.PI;
results[2] = finalBearing;
}
}
return results;
}
//computeDestinationAndBearing(double lat1, double lon1,double brng, double dist)
计算目的地和航向,输入参数为起点纬度、起点经度、方位角和距离。
public static double[] computeDestinationAndBearing(double lat1, double lon1,
double brng, double dist) {
double results[] = new double[3];
double a = 6378137, b = 6356752.3142, f = 1 / 298.257223563; // WGS-84
// ellipsiod
double s = dist;
double alpha1 = toRad(brng);
double sinAlpha1 = Math.sin(alpha1);
double cosAlpha1 = Math.cos(alpha1);
double tanU1 = (1 - f) * Math.tan(toRad(lat1));
double cosU1 = 1 / Math.sqrt((1 + tanU1 * tanU1)), sinU1 = tanU1 * cosU1;
double sigma1 = Math.atan2(tanU1, cosAlpha1);
double sinAlpha = cosU1 * sinAlpha1;
double cosSqAlpha = 1 - sinAlpha * sinAlpha;
double uSq = cosSqAlpha * (a * a - b * b) / (b * b);
double A = 1 + uSq / 16384
* (4096 + uSq * (-768 + uSq * (320 - 175 * uSq)));
double B = uSq / 1024 * (256 + uSq * (-128 + uSq * (74 - 47 * uSq)));
double sinSigma = 0, cosSigma = 0, deltaSigma = 0, cos2SigmaM = 0;
double sigma = s / (b * A), sigmaP = 2 * Math.PI;
while (Math.abs(sigma - sigmaP) > 1e-12) {
cos2SigmaM = Math.cos(2 * sigma1 + sigma);
sinSigma = Math.sin(sigma);
cosSigma = Math.cos(sigma);
deltaSigma = B
* sinSigma
* (cos2SigmaM + B
/ 4
* (cosSigma * (-1 + 2 * cos2SigmaM * cos2SigmaM) - B / 6
* cos2SigmaM * (-3 + 4 * sinSigma * sinSigma)
* (-3 + 4 * cos2SigmaM * cos2SigmaM)));
sigmaP = sigma;
sigma = s / (b * A) + deltaSigma;
}
double tmp = sinU1 * sinSigma - cosU1 * cosSigma * cosAlpha1;
double lat2 = Math.atan2(sinU1 * cosSigma + cosU1 * sinSigma * cosAlpha1,
(1 - f) * Math.sqrt(sinAlpha * sinAlpha + tmp * tmp));
double lambda = Math.atan2(sinSigma * sinAlpha1, cosU1 * cosSigma - sinU1
* sinSigma * cosAlpha1);
double C = f / 16 * cosSqAlpha * (4 + f * (4 - 3 * cosSqAlpha));
double L = lambda
- (1 - C)
* f
* sinAlpha
* (sigma + C * sinSigma
* (cos2SigmaM + C * cosSigma * (-1 + 2 * cos2SigmaM * cos2SigmaM)));
double lon2 = (toRad(lon1) + L + 3 * Math.PI) % (2 * Math.PI) - Math.PI; // normalise
// to
// -180...+180
double revAz = Math.atan2(sinAlpha, -tmp); // final bearing, if required
results[0] = toDegrees(lat2);
results[1] = toDegrees(lon2);
results[2] = toDegrees(revAz);
return results;
}
private static double toRad(double angle) {
return angle * Math.PI / 180;
}
private static double toDegrees(double radians) {
return radians * 180 / Math.PI;
}
//计算交点(LatLng p1, double brng1, LatLng p2, double brng2)
public static LatLng computeIntersectionPoint(LatLng p1, double brng1, LatLng p2, double brng2) {
double lat1 = toRad(p1.latitude), lng1 = toRad(p1.longitude);
double lat2 = toRad(p2.latitude), lng2 = toRad(p2.longitude);
double brng13 = toRad(brng1), brng23 = toRad(brng2);
double dlat = lat2 - lat1, dlng = lng2 - lng1;
double delta12 = 2 * Math.asin(Math.sqrt(Math.sin(dlat / 2) * Math.sin(dlat / 2)
+ Math.cos(lat1) * Math.cos(lat2) * Math.sin(dlng / 2) * Math.sin(dlng / 2)));
if (delta12 == 0) return null;
double initBrng1 = Math.acos((Math.sin(lat2) - Math.sin(lat1) * Math.cos(delta12)) / (Math.sin(delta12) * Math.cos(lat1)));
double initBrng2 = Math.acos((Math.sin(lat1) - Math.sin(lat2) * Math.cos(delta12)) / (Math.sin(delta12) * Math.cos(lat2)));
double brng12 = Math.sin(lng2 - lng1) > 0 ? initBrng1 : 2 * Math.PI - initBrng1;
double brng21 = Math.sin(lng2 - lng1) > 0 ? 2 * Math.PI - initBrng2 : initBrng2;
double alpha1 = (brng13 - brng12 + Math.PI) % (2 * Math.PI) - Math.PI;
double alpha2 = (brng21 - brng23 + Math.PI) % (2 * Math.PI) - Math.PI;
double alpha3 = Math.acos(-Math.cos(alpha1) * Math.cos(alpha2) + Math.sin(alpha1) * Math.sin(alpha2) * Math.cos(delta12));
double delta13 = Math.atan2(Math.sin(delta12) * Math.sin(alpha1) * Math.sin(alpha2), Math.cos(alpha2) + Math.cos(alpha1) * Math.cos(alpha3));
double lat3 = Math.asin(Math.sin(lat1) * Math.cos(delta13) + Math.cos(lat1) * Math.sin(delta13) * Math.cos(brng13));
double dlng13 = Math.atan2(Math.sin(brng13) * Math.sin(delta13) * Math.cos(lat1), Math.cos(delta13) - Math.sin(lat1) * Math.sin(lat3));
double lng3 = lng1 + dlng13;
return new LatLng(toDegrees(lat3), (toDegrees(lng3) + 540) % 360 - 180);
}
我建议您浏览上述网站并获取知识,就像我也做了一样。
希望这可以帮助您,我知道它不是在iOS上,但概念与我通过更改JavaScript代码完成的项目相同。
干杯!
- Ravikant Paudel
3
嘿,Ravikant,我正在尝试使用这个解决方案,但在第三步卡住了。你能否提供更多关于如何传递函数computeIntersectionPoint的详细信息? - Rana Ranvijay Singh
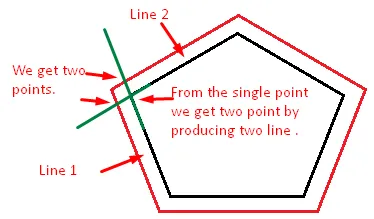
在这种情况下,您通过两条生成的线来找到交点。
- 获取绿线和红线的交点的latlng,这将给出2个latlng 1和2。
- 使用点1和点2的方向,并使用该函数。
谢谢您的回复,我对这个轴承概念还有点陌生。我仍然不明白我需要在computeIntersectionPoint函数中传递什么参数。我可以向您展示我正在尝试实现它的方式。您能否请分享您的电子邮件地址或通过rana.ranvijay@weboniselab.com给我发邮件? - Rana Ranvijay Singh
0
我的要求与此类似。最终我自己编写了算法。https://github.com/RanaRanvijaySingh/PolygonBuffer
您只需要使用这行代码
double distance = 0.0001;
List bufferedPolygonList = AreaBuffer.buffer(pointList, distance);
- Rana Ranvijay Singh
-1
我建议使用Turf.js库进行缓冲以及许多基本的GIS操作。你可以从返回的路径中检索出每条边。对于几何缓冲,它易于使用、非常轻便,并且在我的应用程序中使用MapBox.js或leaflet时没有任何问题。
更多细节:Turf.js Buffer
但是,如果你正在寻找一种大地距离缓冲,那可能会有问题。我会使用Arcgis Javascript API。
- Teng Ma
1
我可以在iOS上熟练使用JS,并且无论如何,问题明确地问及iOS。 - ingconti
-2
- Iman Nia
3
1问题标记为Swift,而不是Objective-C。 - Ccr
@Ccr 没关系,在大型项目中使用C++库在Swift和Objective-C中非常普遍,这是不可避免的。顺便说一下,它不是Objective-C,而是一个C++库。 - Iman Nia
正如Ccr所指出的那样,@zich,你不能(很容易地)在iOS上使用C++绘图方法。正确的方法是使用CoreGraphics或类似的方法。 - ingconti
网页内容由stack overflow 提供, 点击上面的可以查看英文原文,
原文链接
原文链接